En este artículo, veremos cómo crear una aplicación desde cero que funcione con los servicios de Windows y muestre los errores del sistema en WinForm (C #).
El resumen de este artículo:
- Creación de servicios
- Visor de eventos
- Código de servicio
- Comprobación del servicio (Inicio manual del servicio)
- Mapeo WinForm
Creación de servicios
Abra Visual Studio. Archivo siguiente → Nuevo → Proyecto → (Escritorio de Windows) → Servicio de Windows (.Net Framework) → Ok.
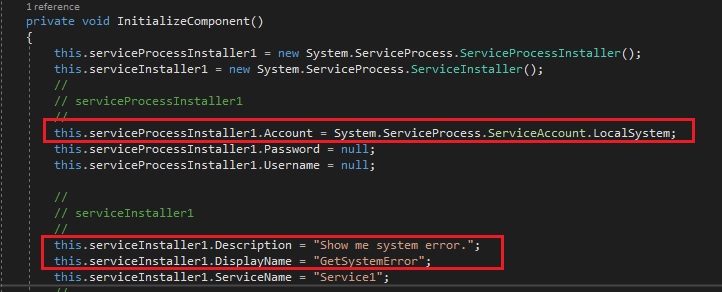
A continuación, debe crear un instalador. En la ventana que se abre, haga clic en RMB y seleccione "Agregar instalador". Tendrá "ProjectInstaller.cs [Diseño]" creado, después de lo cual deberá ir al código "F7" o "Ver código" de RMB. Debe encontrar la línea "InitializeComponent ();", colocar el cursor sobre ella y presionar "F12", luego debe agregar las siguientes líneas:
this.serviceProcessInstaller1.Account = System.ServiceProcess.ServiceAccount.LocalSystem;
Pero debe agregar estas líneas solo en la siguiente secuencia y lugar. De lo contrario, habrá un error al instalar el servicio.
Visor de eventos
Esto es necesario para verificar el correcto funcionamiento de nuestro programa.
Visor de eventos: un programa para ver el registro de eventos que se encuentra en cada computadora con Windows. Cada programa que se ejecuta en una computadora publica una notificación en el registro de eventos antes de detenerse. Cualquier acceso al sistema, cambios de seguridad, ajuste del sistema operativo, fallas de hardware y fallas del controlador, todo esto entra en el registro de eventos. El Visor de eventos escanea archivos de registro de texto, los combina y los coloca en la interfaz.
¿Cómo abrirlo? - Inicio → Visor de eventos (en búsqueda) → “Ver registros de eventos”.
A continuación, "Vistas personalizadas" → "Eventos administrativos". Aquí podemos ver todos los errores, advertencias e información sobre ellos.
Hay 3 tipos de registros: Aplicación (Aplicación), Sistema (Sistema) y Seguridad (Seguridad). Solo necesitamos un sistema (Sistema).
Código de servicio
Encontramos el archivo .cs con el nombre del servicio, lo tengo "Service1.cs", ábralo. El archivo debe tener 2 métodos anulados:
- OnStart (string [] args): ejecutado cuando se inicia el servicio,
- OnStop (): se ejecuta cuando se detiene el servicio.
También hay algunos métodos más, pero no los necesitamos ahora. Puedes encontrarlos tú mismo.
Los datos que obtenemos se almacenarán en un archivo de texto actualizado, por lo que agregamos
using System.IO;
Agregue el código al método OnStart (cadena [] args):
EventLog myLog;
A continuación, debe recopilar la solución "Solución" -> "Reconstruir solución". Después de un ensamblaje exitoso, puede verificar la operación.
Comprobación del servicio (Inicio manual del servicio)
El servicio de Windows no se puede iniciar como una aplicación normal. Solo puede ejecutar la línea de comandos como administrador.
Ejecute la línea de comando como administrador. Ingrese los siguientes comandos:
cd C:\Windows\Microsoft.NET\Framework\v4.0.30319 InstallUtil.exe \ .exe (InstallUtil.exe C:\Users\\source\repos\WindowsService1\WindowsService1 \bin\Debug\WindowsService1.exe) : InstallUtil.exe -u \ .exe
A continuación, presione la tecla Win + R. Ingrese "Services.msc". Encontramos nuestro servicio en la lista, hacemos clic en él y hacemos clic en "Inicio". Después de un lanzamiento exitoso, se generará un archivo en la ruta especificada en el código, que contendrá una lista de errores del sistema.
No olvides eliminar el servicio después de la verificación.
Mapeo WinForm
Para mostrar en la consola, si lo intenta, puede encontrar artículos, pero no lo encontré para mostrar en WinForm, así que aquí está. Por defecto, se crea un proyecto de servicio de tipo Aplicación. Para mostrar a través de la consola, este parámetro debe cambiarse en la configuración, para que WinForm lo deje como está. A continuación, debe agregar el formulario al proyecto. “WindowsService1” → RMB → Agregar → Formulario de Windows → Agregar. Y haz el siguiente diseño. A continuación, cambie el archivo "Program.cs".
Agregar usando:
using System.Windows.Forms; using System.Security.Principal; using System.ComponentModel; using System.Diagnostics;
Y cambie el método principal:
static void Main(string[] args) { WindowsPrincipal windowsPricipal = new WindowsPrincipal(WindowsIdentity.GetCurrent()); bool hasAdministrativeRight = windowsPricipal.IsInRole(WindowsBuiltInRole.Administrator); if (hasAdministrativeRight == false)
Agregue una nueva clase "SystemError". ("WindowsService1" -> RMB -> Agregar -> Clase -> Agregar). Aquí almacenaremos datos de error. Cambiarlo:
public string EntryType{ get; set; } public string EventLog{ get; set; } public string MachineName { get; set; } public string AppName { get; set; } public string Message { get; set; } public string TimeWritten { get; set; }
Además en "Service1.cs" agregamos el método "RunFromForm (string [] args)" que inicia el servicio.
public void RunFromForm(string[] args) { OnStart(args); OnStop(); }
Agregue una nueva clase "GetListErrors". ("WindowsService1" -> RMB -> Agregar -> Clase -> Agregar). Aquí obtendremos los datos del archivo. Agregar usando:
using System.IO;
Cambiarlo:
string filepath = AppDomain.CurrentDomain.BaseDirectory + @"\ServiceLog.txt"; SystemError systemError; public List<SystemError> listSysErrs; public void ReadFile()
A continuación, cambie el código del formulario "Form1.cs". Agregar usando:
using System.ServiceProcess; using System.Diagnostics;
Cambiarlo:
Service1 service = new Service1(); List<SystemError> listSysErrs; string[] args; public Form1(string[] args) { InitializeComponent(); this.args = args; if (Environment.UserInteractive)
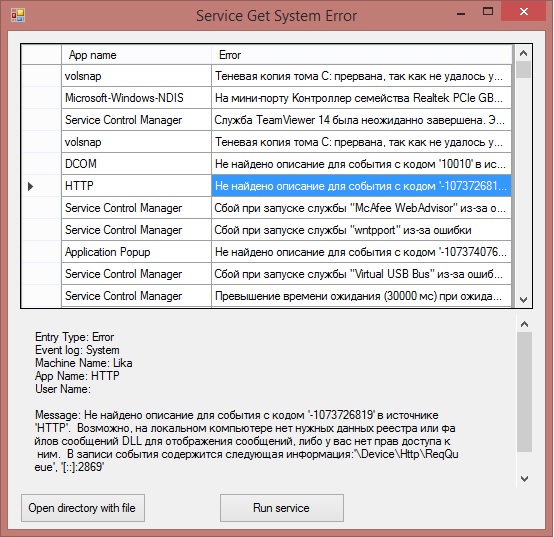
Ahora puede iniciar el servicio como una aplicación normal. El resultado es el siguiente: