One of the answers to the question “why do we need astronautics” is that the technologies developed for the space industry are used on earth. CMOS sensors, longer-lasting car tires or blankets for the Ministry of Emergency Situations use technologies originally created for space. But if you try to google this list, all or almost all of the technologies mentioned will be created by NASA. For many years, the agency has been specifically tracking and publishing developments created for space and transmitted for everyday use within the framework of the Spinoff program. Roscosmos would have come in handy a similar program.
 Spinoff Annual Cover
Spinoff Annual CoverThe essence of the program
By decision of Congress, the technology transfer program was launched by NASA in 1964. A company interested in the know-how developed by the agency can apply, determine the licensing conditions and start using it. Licenses can cost from zero dollars (for startups) and to multi-valued amounts for exclusive use rights, each contract is unique. If the result is a success story, she will find a place in Spinoff magazine. It traces its history to reports on the use of technology published in 1973 and 1974. The publications aroused such great public interest that the agency began to publish beautiful color magazines every year, which are sent out free of charge upon request. The first Spinoff magazine was published in 1976, each new issue describes about fifty technologies, and the total number of products and services developed using technologies created by NASA is estimated to exceed 2000.
The FAQ on the program’s official website emphasizes that the agency does not advertise goods or services mentioned in the magazine, nor does it guarantee the properties or characteristics declared by the manufacturer. But this does not prevent the magazine from remaining an excellent source of systematic information, as technologies invented for space are used in everyday life. Moreover, there are misconceptions in society: barcodes, solar panels or MRI devices are not space spinoffs. Recently, NASA
celebrated 40 years of the program with the publication of the most striking results: the list includes digital camera CMOS sensors, winglets (wingtips), baby foods enriched with omega-3 unsaturated fatty acids, memory pillows and mattresses, aerodynamic trucks and much more .
And we have?
What is good to be a popularizer - you will find pleasant surprises. In fact, it’s hard to name another proposal to write an advertisement for the United Rocket and Space Corporation in Medusa. The original idea was to talk about technologies developed for space and applied on earth. Unfortunately, there was a serious limitation - medical devices and technologies cannot be mentioned. I had to show some ingenuity, and you can
read the result
on the Medusa website . But it was rather difficult to search and select information - Roskosmos still has no analogue of the Spinoff program, the information is scattered around various sources, not systematized, and, I'm afraid, something has already been lost.
Here, by publishing an unpaid post, I can freely talk about domestic technologies, not excluding medicine.
Costumes "Penguin", "Regent" and "Adele"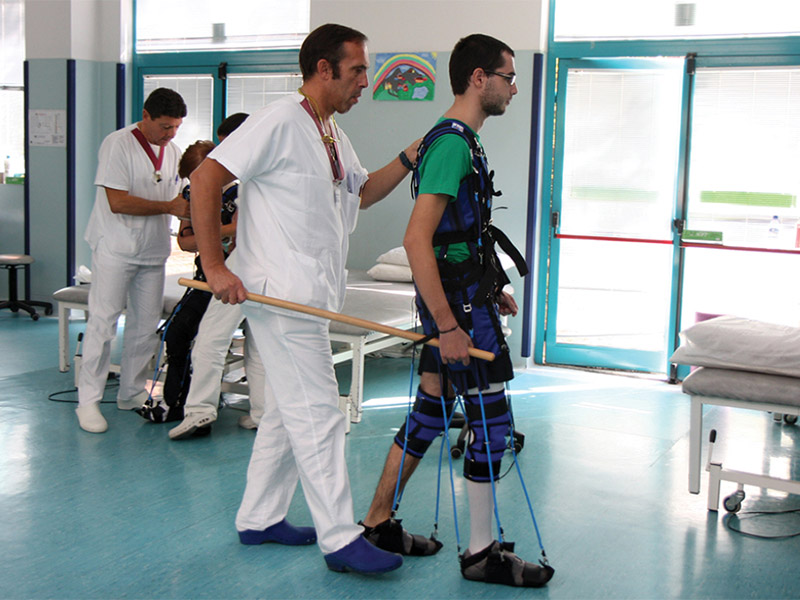 Photo IBMP RAS
Photo IBMP RASThe Penguin costume is probably the most widely known Soviet / Russian space spinoff. With an increase in the duration of space flights, it turned out that in zero gravity the muscles begin to atrophy, and so that the astronauts could live normally after returning to Earth, it was necessary to give the muscles a load. For this the Penguin costume was invented. Structurally, it is simple - elastic bands are stretched along the jumpsuit, the force of which can be regulated. And it turned out that the idea is useful in terrestrial conditions. The Regent costume developed on the basis of the Penguin is used to rehabilitate people who have suffered a stroke (or other cerebrovascular accident), a head injury, or who suffer from paresis. In the “Adele” variant, the same idea helps children with cerebral palsy.
Dry immersion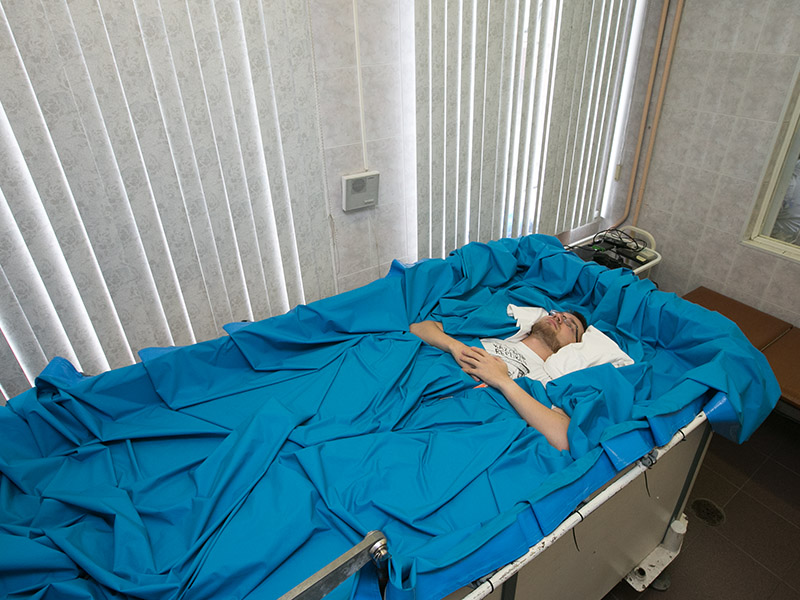 Photo IBMP RAS
Photo IBMP RASThis invention also relates to the study of the effects of weightlessness on the human body. Under water, you can effectively train your work in spacesuits, but firstly, you won’t keep a person like that for a long time, and secondly, the effect of gravity is felt perfectly inside the spacesuit. But if you immerse a person in the bath, but so that the water does not touch the skin, you can get the effects of weightlessness after a few days. So they came up with the method of dry immersion, which turned out to be useful not only in astronautics, but also in cardiology (the fight against edema), traumatology and surgery (postoperative rehabilitation), and even for the rehabilitation of premature babies.
Oxygen concentrator "Courier"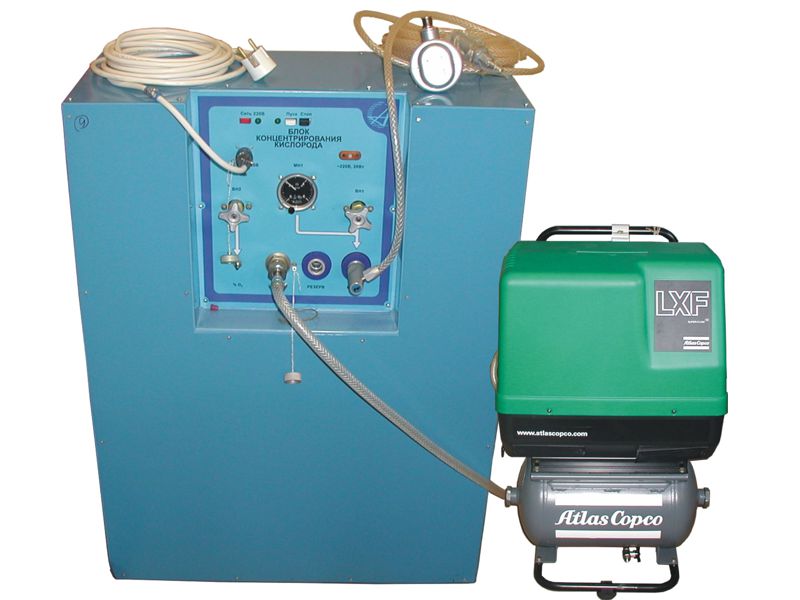 Oxygen concentrator KKA-01 CJSC "SKB EO at IMBP RAS"
Oxygen concentrator KKA-01 CJSC "SKB EO at IMBP RAS"At Apollo 13, astronauts nearly died due to the dangerous concentration of carbon dioxide, despite the perfectly normal amount of oxygen in the inhaled air. And in the event of an accident on a spaceship, the atmosphere may be breathable if harmful impurities are removed from it. The Courier apparatus is based on this principle, in which oxygen is filtered by special filters - zeolites. The idea turned out to be potentially very interesting for disaster medicine - a field hospital is much easier to provide with electricity from diesel generators than with oxygen cylinders.
And these are only the most striking examples from the
list of spinoffs on the website of the IBMP RAS . It should be used as one of the sources for the domestic analogue of the Spinoff program - here are a lot of solutions that were invented for space and in demand on the earth's market. But it is not surprising that it is limited only by the activity of the Institute of Biological Chemistry, RAS, and it should be supplemented with the achievements of other enterprises.
Sometimes commercial products are the result of scientific experiments in space. For example, from 2003 to 2008, the Bioecology experiment
was conducted at the ISS, the purpose of which was to study the effect of space flight conditions on bacteria. The result of the experiment is, among other things, the Micefit plant growth stimulator produced for sale. The result of the Antigen experiment is a technology for the production of hepatitis B vaccine based on space-enhanced yeast.
Some products are the result of space enterprises collaborating with Earth organizations. It has a long history, back in the book of B.E. Chertoka "Missiles and People" tells how the chance meeting of S.P. The queen with the surgeon Alexander Vishnevsky led to the creation of urination stimulants for paralyzed people. In the 21st century, ORKK in conjunction with Pilyugina ”and the company“ Tekhnosvet ”is working on installations combining microwave and radiofrequency ablation (evaporation) of cancerous tumors.
And sometimes hi-tech is made at the space enterprise. In
the RSC Energia Museum you can see not only spacecraft, but also conversion food processors, vacuum cleaners and scooters. The trams of the Ust-Katavsky Car-Building Plant
proudly carry the production
nameplate at the branch of the space enterprise. For trams, an automated control system is implemented that implements "smart brakes", protects against human errors and fixes telemetry, which can facilitate and improve maintenance of equipment. In 2019, at the INNOPROM exhibition, NPO Avtomatiki (which is engaged in launch vehicle control systems) presented a tractor tractor demonstrating an unmanned control system. The complex, combining an inertial navigation system, GPS / GLONASS navigation and technical vision using neural networks, is installed on agricultural machinery and controls it with an accuracy of three centimeters. Only public roads are left for man - according to the law, unmanned aerial vehicles cannot drive on them without a driver. The United Rocket and Space Corporation and the Moscow Institute of Heat Engineering Corporation JSC are working on the development of domestic equipment for hydraulic fracturing, which is now in great demand in oil and gas production. PJSC NPO Iskra, which creates solid propellant rocket engines for the space industry, also produces compressor equipment and pumping stations for the oil and gas industry.
Information about some technologies will not be easy to obtain. In 1989, V.P. Mikhailova
“Achievements of astronautics in earth technology” . The presence of the Spinoff program at NASA and its absence in the USSR is very noticeable - the story is mainly about American technology. And to find sources of very interesting information
“Scientists at the Mining Institute of the Kola Branch of the USSR Academy of Sciences widely use the methodology and tools they created to analyze samples of the lunar soil, to study rock samples delivered from different areas of the Kola Peninsula and the Urals.“ Now is not a fact of what happens.
Conclusion
The difference in the organizational structure of NASA and Roscosmos will lead to a difference in directories - in the domestic analogue of Spinoff it makes sense to talk not only about the developed technologies, but also about the high-tech products of the enterprises of the state corporation. But in any case, such a systematized catalog will be a vivid and visual means of popularizing astronautics.