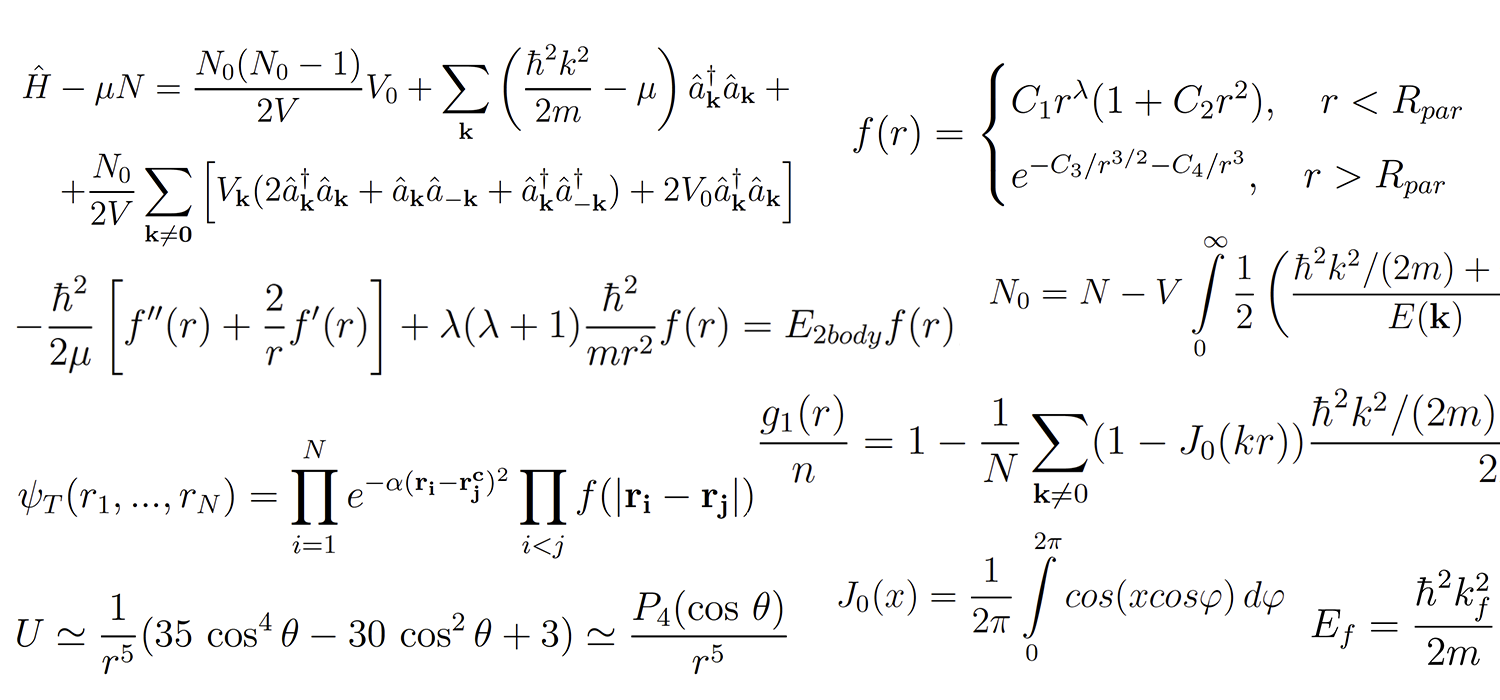
تخصصي هو فيزياء المادة المكثفة. بالطبع ، في عملية الغمر فيها ، يلزم دراسة العديد من المقالات العلمية ، ولكن يمكن أن يستغرق الكثير من الوقت لتحليل مقال واحد على الأقل. يتم نشر أكثر من ألف مقال شهريًا على
arxiv في قسم
cond-mat . هناك حالة لا يملك فيها العديد من الباحثين ، وخاصة المبتدئين ، رؤية شاملة لمجال علمهم. الأداة الموصوفة في هذه المقالة تلخص محتويات قاعدة بيانات المقالات العلمية ومصممة لتسريع العمل مع الأدب.
من الجدير بالذكر أننا نقوم باختراع دراجة ، فقط ستركبنا مجانًا (أسعار
نظائرها المدفوعة غير لائقة لدرجة أنه لا يتم قبولها للإشارة).
سيتم تجميع الدراجة في Python ،
ويستخدم Gensim في النمذجة المواضيعية ،
ويتم استخدام
Plot.ly للتصور. في نهاية المقال توجد روابط إلى أجهزة الكمبيوتر المحمولة Jupyter و GitHub.
المادة المصدر للعمل هي شروح ونصوص المقالات العلمية. إذا كان الأول متاحًا لنا في نموذج XML "جاهز" ، فيجب تحويل ملفات PDF للمقالات إلى txt ، ونتيجة لهذه العملية يبقى الكثير من "القمامة" في النصوص ، لذلك يجب تنظيفها بجدية.
شرح توضيحي للعينة<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <feed xmlns="http://www.w3.org/2005/Atom"> <link href="http://arxiv.org/api/query?search_query%3D%26id_list%3D1706.09062%26start%3D0%26max_results%3D10" rel="self" type="application/atom+xml"/> <title type="html">ArXiv Query: search_query=&id_list=1706.09062&start=0&max_results=10</title> <id>http://arxiv.org/api/ECEwpFhuO79sa+LzMzx6/iStFak</id> <updated>2018-05-01T00:00:00-04:00</updated> <opensearch:totalResults xmlns:opensearch="http://a9.com/-/spec/opensearch/1.1/">1</opensearch:totalResults> <opensearch:startIndex xmlns:opensearch="http://a9.com/-/spec/opensearch/1.1/">0</opensearch:startIndex> <opensearch:itemsPerPage xmlns:opensearch="http://a9.com/-/spec/opensearch/1.1/">10</opensearch:itemsPerPage> <entry> <id>http://arxiv.org/abs/1706.09062v1</id> <updated>2017-06-27T22:03:24Z</updated> <published>2017-06-27T22:03:24Z</published> <title>On Bose-Einstein condensation and superfluidity of trapped photons with coordinate-dependent mass and interactions</title> <summary> The condensate density profile of trapped two-dimensional gas of photons in an optical microcavity, filled by a dye solution, is analyzed taking into account a coordinate-dependent effective mass of cavity photons and photon-photon coupling parameter. The profiles for the densities of the superfluid and normal phases of trapped photons in the different regions of the system at the fixed temperature are analyzed. The radial dependencies of local mean-field phase transition temperature $T_c^0 (r)$ and local Kosterlitz-Thouless transition temperature $T_c (r)$ for trapped microcavity photons are obtained. The coordinate dependence of cavity photon effective mass and photon-photon coupling parameter is important for the mirrors of smaller radius with the high trapping frequency, which provides BEC and superfluidity for smaller critical number of photons at the same temperature. We discuss a possibility of an experimental study of the density profiles for the normal and superfluid components in the system under consideration. </summary> <author> <name>Oleg L. Berman</name> </author> <author> <name>Roman Ya. Kezerashvili</name> </author> <author> <name>Yurii E. Lozovik</name> </author> <arxiv:doi xmlns:arxiv="http://arxiv.org/schemas/atom">10.1364/JOSAB.34.001649</arxiv:doi> <link title="doi" href="http://dx.doi.org/10.1364/JOSAB.34.001649" rel="related"/> <arxiv:comment xmlns:arxiv="http://arxiv.org/schemas/atom">14 page 5, figures</arxiv:comment> <link href="http://arxiv.org/abs/1706.09062v1" rel="alternate" type="text/html"/> <link title="pdf" href="http://arxiv.org/pdf/1706.09062v1" rel="related" type="application/pdf"/> <arxiv:primary_category xmlns:arxiv="http://arxiv.org/schemas/atom" term="cond-mat.mes-hall" scheme="http://arxiv.org/schemas/atom"/> <category term="cond-mat.mes-hall" scheme="http://arxiv.org/schemas/atom"/> </entry> </feed>
نص عينةOn Bose-Einstein condensation and super¬‚uidity of trapped photons with
coordinate-dependent mass and interactions
Oleg L. Berman1,2, Roman Ya. Kezerashvili1,2, and Yurii E. Lozovik3,4
1Physics Department, New York City College of Technology, The City University of New York,
2The Graduate School and University Center, The City University of New York,
Brooklyn, NY 11201, USA
3Institute of Spectroscopy, Russian Academy of Sciences, 142190 Troitsk, Moscow, Russia
4National Research University Higher School of Economics, Moscow, Russia
New York, NY 10016, USA
(Dated: June 29, 2017)
The condensate density pro¬Ѓle of trapped two-dimensional gas of photons in an optical micro-
cavity, ¬Ѓlled by a dye solution, is analyzed taking into account a coordinate-dependent e¬Ђective
mass of cavity photons and photon-photon coupling parameter. The pro¬Ѓles for the densities of the
super¬‚uid and normal phases of trapped photons in the di¬Ђerent regions of the system at the ¬Ѓxed
temperature are analyzed. The radial dependencies of local mean-¬Ѓeld phase transition temperature
T 0
c (r) and local Kosterlitz-Thouless transition temperature Tc(r) for trapped microcavity photons
are obtained. The coordinate dependence of cavity photon e¬Ђective mass and photon-photon cou-
pling parameter is important for the mirrors of smaller radius with the high trapping frequency,
which provides BEC and super¬‚uidity for smaller critical number of photons at the same temper-
ature. We discuss a possibility of an experimental study of the density pro¬Ѓles for the normal and
super¬‚uid components in the system under consideration.
Key words: Photons in a microcavity; Bose-Einstein condensation of photons; super¬‚uidity of
photons.
PACS numbers: 03.75.Hh, 42.55.Mv, 67.85.Bc, 67.85.Hj
I.
INTRODUCTION
When a system of bosons is cooled to low temperatures, a substantial fraction of the particles spontaneously occupy
the single lowest energy quantum state. This phenomenon is known as Bose-Einstein condensation (BEC) and its
occurs in many-particle systems of bosons with masses m and temperature T when the de Broglie wavelength of the
Bose particle exceeds the mean interparticle distance [1]. The most remarkable consequence of BEC is that there
should be a temperature below which a ¬Ѓnite fraction of all the bosons ЂњcondenseЂќ into the same one-particle state
with macroscopic properties described by a single condensate wavefunction, promoting quantum physics to classical
time- and length scales.
Most recently, the observations at room temperature of the BEC of two-dimensional photon gas con¬Ѓned in an optical
microcavity, formed by spherical mirrors and ¬Ѓlled by a dye solution, were reported [2Ђ“5]. The interaction between
microcavity photons is achieved through the interaction of the photons with the non-linear media of a microcavity,
¬Ѓlled by a dye solution. While the main contribution to the interaction in the experiment, reported in Ref. 2, is
thermooptic, it is not a contact interaction.
It is known that BEC for bosons can exist without particle-particle
interactions [6] (see Ref. 1 for the details), but at least the interactions with the surrounding media are necessary to
achieve thermodynamical equilibrium. For photon BEC it can be achieved by interaction with incoherent phonons [7].
The in¬‚uence of interactions on condensate-number ¬‚uctuations in a BEC of microcavity photons was studied in Ref. 8.
The kinetics of photon thermalization and condensation was analyzed in Refs. 9Ђ“11. The kinetics of trapped photon
gas in a microcavity, ¬Ѓlled by a dye solution, was studied, and, a crossover between driven-dissipative system laser
dynamics and a thermalized Bose-Einstein condensation of photons was observed [12].
In previous theoretical studies the equation of motion for a BEC of photons con¬Ѓned by the axially symmetrical
trap in a microcavity was obtained.
It was assumed that the changes of the cavity width are much smaller than
the width of the trap [13]. This assumption results in the coordinate-independent e¬Ђective photon mass mph and
photon-photon coupling parameter g. In this Paper, we study the local super¬‚uid and normal density pro¬Ѓles for
trapped two-dimensional gas of photons with the coordinate-dependent e¬Ђective mass and photon-photon coupling
parameter in a an optical microcavity, ¬Ѓlled by a dye solution. We propose the approach to study the local BEC
and local super¬‚uidity of cavity photon gas in the framework of local density approximation (LDA) in the traps of
larger size without the assumption, that total changes of the cavity width are much smaller than the size of the trap.
In this case, we study the e¬Ђects of coordinate-dependent e¬Ђective mass and photon-photon coupling parameter on
the super¬‚uid and normal density pro¬Ѓles as well as the pro¬Ѓles of the local temperature of the phase transition for
trapped cavity photons. Such approach is useful for the mirrors of smaller radius with the high trapping frequency,
2
which provide BEC and super¬‚uidity for smaller critical number of photons at the same temperature.
The paper is organized in the following way.
In Sec. II, we obtain the condensate density pro¬Ѓle for trapped
microcavity photon BEC with locally variable mass and interactions. The expression for the number of particles in a
condensate is analyzed in Sec. III. In Sec. IV, the dependence of the condensate parameters on the geometry of the
trap is discussed. In Sec. V, we study the collective excitation spectrum and super¬‚uidity of 2D weakly-interacting
Bose gas of cavity photons. The results of our calculations are discussed in Sec. VI. The proposed experiment for
measuring the distribution of the local density of a photon BEC is described in Sec. VII. The conclusions follow in
Sec. VIII.
II. THE CONDENSATE DENSITY PROFILE
While at ¬Ѓnite temperatures there is no true BEC in any in¬Ѓnite untrapped two-dimensional (2D) system, a true
2D BEC quantum phase transition can be obtained in the presence of a con¬Ѓning potential [14, 15]. In an in¬Ѓnite
translationally invariant two-dimensional system, without a trap, super¬‚uidity occurs via a Kosterlitz€'Thouless
super¬‚uid (KTS) phase transition [16]. While KTS phase transition occurs in systems, characterized by thermal
equilibrium, it survives in a dissipative highly nonequilibrium system driven into a steady state [17].
The trap for the cavity photons can be formed by the concave spherical mirrors of the microcavity, that provide
the axial symmetry for a trapped gas of photons. Thus the transverse (along xy plane of the cavity) con¬Ѓnement
of photons can be achieved by using an optical microcavity with a variable width. Let us introduce the frame of
reference, where z€'axis is directed along the axis of cavity mirrors, and (x, y) plane is perpendicular to this axis. The
energy spectrum E(k) for small wave vectors k of photons, con¬Ѓned in z direction in an ideal microcavity with the
coordinate-dependent width L(r), is given by [2]
E(k) =
ЇhЂcњn
...
[23] L. Onsager, ЂњStatistical Hydrodynamics,Ђќ Nuovo Cimento Suppl. 6, 279 (1949).
[24] RP Feynman, ЂњApplication of Quantum Mechanics to Liquid Helium,Ђќ Prog. Low Temp. Phys. 1, 17 (1955).
[25] PC Hohenberg and PC Martin, ЂњMicroscopic Theory of Super¬‚uid Helium,Ђќ Ann. Phys. 34, 291 (1965).
[26] G. Blatter, MY FeigelЂman, YB Geshkenbein, AI Larkin, and VM Vinokur, ЂњVortices in high-temperature super-
conductors,Ђќ Rev. Mod. Phys. 66, 1125 (1994).
[27] NS Voronova and Yu. E. Lozovik, ЂњExcitons in cores of exciton-polariton vortices,Ђќ Phys. Rev. B 86, 195305 (2012);
NS Voronova, AA Elistratov, and Yu. E. Lozovik, ЂњDetuning-Controlled Internal Oscillations in an Exciton-Polariton
Condensate,Ђќ Phys. Rev. Lett. 115, 186402 (2015) .
[28] A. Gri¬ѓn, ЂњConserving and gapless approximations for an inhomogeneous Bose gas at ¬Ѓnite temperatures,Ђќ Phys. Rev. B
53, 9341 (1996).
[29] AA Abrikosov, LP Gorkov and IE Dzyaloshinski, Methods of Quantum Field Theory in Statistical Physics (Prentice-
Hall, Englewood Cli¬Ђs. NJ, 1963).
[30] OL Berman, Yu. E. Lozovik, and DW Snoke, ЂњTheory of Bose-Einstein condensation and super¬‚uidity of two-
dimensional polaritons in an in-plane harmonic potential,Ђќ Phys. Rev. B 77, 155317 (2008).
[31] OL Berman, R. Ya. Kezerashvili, and K. Ziegler, ЂњSuper¬‚uidity and collective properties of excitonic polaritons in gapped
graphene in a microcavityЂќ, Phys. Rev. B 86, 235404 (2012).
[32] A. Amo, J. Lefr`ere, S. Pigeon, C. Adrados, C. Ciuti, I. Carusotto, R. Houdrґe, E. Giacobino, and A. Bramati, ЂњSuper¬‚uidity
of polaritons in semiconductor microcavities,Ђќ Nature Physics 5, 805 (2009).
[33] JP Fernґandez and WJ Mullin, ЂњThe Two-Dimensional Bose€'Einstein Condensate,Ђќ J. Low. Temp. Phys. 128, 233
من التعليقات التوضيحية نحتاج إلى معلومات
فقط عن المؤلفين والأقسام الفرعية للمقالات.
أدناه ، على سبيل المثال ، نعتبر مجموعة من المقالات من قسم cond-mat للعام 2017. كل شيء موصوف يسهل إعادة إنتاجه لأي قسم آخر.
إن أبسط طريقة لبدء دراسة النصوص هي إنشاء قائمة بالكلمات الرئيسية التي تهمنا وحساب نسبة المقالات التي تظهر فيها.
دعونا نقيم التغيير في الحصة ، على سبيل المثال ، مقارنة بعام 2010.
الفرق في الأسهم للسنتين 2017 و 2010. (ملاحظة: تم منح جائزة نوبل في الفيزياء في عام 2016 لدراسة المراحل الطوبولوجية للمادة)علاوة على ذلك ، بناءً على محتوى النصوص ، نقوم ببناء نموذج
word2vec (من أجل التصور فمن الأفضل أن تأخذ نافذة أوسع ، 20 كلمة). لكل مفتاح ، نأخذ أقرب N من الجيران وبمساعدة t-SNE نحسب إحداثياتهم ثنائية الأبعاد. نحن ننظر في كيفية ارتباط الكلمات الرئيسية ببعضها البعض:
سحابة الكلمات الرئيسية والأقمار الصناعية ، N = 100. كلما كان الجار Nth أبعد ، تم إبراز الكلمة. الأزواج ذات الصلة: الجرافين + أشباه الموصلات ، Qubit + Dot ، Topolog + Hall ، Bose + التكثيفيوجد في arxiv أقسام فرعية لكل قسم. نجد في الأقسام الفرعية التي تم العثور على الكلمات الرئيسية:
فك أسماء التقسيمات الفرعيةيصف ما سبق العمل مع مجموعة من الكلمات الرئيسية التي ترغب في إنشائها يدويًا ، ولكن ربما تم تخطي بعض المواضيع. دعونا نبني نموذج
LDA ونلقي نظرة على الموضوعات:
لكل موضوع ، نحصل على قائمة بالمقالات المقابلة له:
كما تعلم ، من المفيد دائمًا عند قراءة المقالات دراسة الروابط. هل يمكننا جمع بعض المعلومات عنها؟ نستطيع! دعونا نلقي نظرة على ذيل النص.
الذيل[23] L. Onsager, ЂњStatistical Hydrodynamics,Ђќ Nuovo Cimento Suppl. 6, 279 (1949).
[24] RP Feynman, ЂњApplication of Quantum Mechanics to Liquid Helium,Ђќ Prog. Low Temp. Phys. 1, 17 (1955).
[25] PC Hohenberg and PC Martin, ЂњMicroscopic Theory of Super¬‚uid Helium,Ђќ Ann. Phys. 34, 291 (1965).
[26] G. Blatter, MY FeigelЂman, YB Geshkenbein, AI Larkin, and VM Vinokur, ЂњVortices in high-temperature super-
conductors,Ђќ Rev. Mod. Phys. 66, 1125 (1994).
[27] NS Voronova and Yu. E. Lozovik, ЂњExcitons in cores of exciton-polariton vortices,Ђќ Phys. Rev. B 86, 195305 (2012);
NS Voronova, AA Elistratov, and Yu. E. Lozovik, ЂњDetuning-Controlled Internal Oscillations in an Exciton-Polariton
Condensate,Ђќ Phys. Rev. Lett. 115, 186402 (2015) .
[28] A. Gri¬ѓn, ЂњConserving and gapless approximations for an inhomogeneous Bose gas at ¬Ѓnite temperatures,Ђќ Phys. Rev. B
53, 9341 (1996).
[29] AA Abrikosov, LP Gorkov and IE Dzyaloshinski, Methods of Quantum Field Theory in Statistical Physics (Prentice-
Hall, Englewood Cli¬Ђs. NJ, 1963).
[30] OL Berman, Yu. E. Lozovik, and DW Snoke, ЂњTheory of Bose-Einstein condensation and super¬‚uidity of two-
dimensional polaritons in an in-plane harmonic potential,Ђќ Phys. Rev. B 77, 155317 (2008).
[31] OL Berman, R. Ya. Kezerashvili, and K. Ziegler, ЂњSuper¬‚uidity and collective properties of excitonic polaritons in gapped
graphene in a microcavityЂќ, Phys. Rev. B 86, 235404 (2012).
[32] A. Amo, J. Lefr`ere, S. Pigeon, C. Adrados, C. Ciuti, I. Carusotto, R. Houdrґe, E. Giacobino, and A. Bramati, ЂњSuper¬‚uidity
of polaritons in semiconductor microcavities,Ђќ Nature Physics 5, 805 (2009).
[33] JP Fernґandez and WJ Mullin, ЂњThe Two-Dimensional Bose€'Einstein Condensate,Ђќ J. Low. Temp. Phys. 128, 233
يعالج PDF Converter قسمًا ببليوغرافيا بشكل جيد. وهذا يعني أنه يمكن استرداد الروابط ببعض التعبيرات العادية. ونتيجة لذلك ، نحصل على قائمة بالمقالات التي يتم الاستشهاد بها كثيرًا ، والتي يجب قراءتها.
تحقق من هذه الروابط على
Google Scholar :
قم بعمل قائمة بالمؤلفين الأكثر نشاطًا لكل قسم فرعي - نستخرج ونحسب محتويات علامة المؤلف من التعليقات التوضيحية. عدد المقالات المنشورة من قبل مؤلف معين هو سمة مفهومة ، ولكن غير موثوقة ، يمكن استكمالها بواسطة وسيط عدد المؤلفين المشاركين (انظر دفاتر الملاحظات).
الكتاب من mes-hall لا مثيل له: متوسط سرعة عملهم أكثر من مقال واحد في الأسبوع ...أخيرًا ، نقدر نسبة الأقسام الفرعية:
أجهزة الكمبيوتر المحمولة التجريبية:
cond-mat.17 ،
astro-ph.17 ،
cs.17 ،
math.17جيثب :
ilovescience