Selbst in einem guten Netzwerk ist es aus gestalterischer Sicht von Zeit zu Zeit erforderlich, die Konfigurationen bestimmter Entitäten zu aktualisieren. Zu den zwingendsten und am meisten erwarteten Gründen für solche Aktivitäten gehört die Migration zur Koordinierung der physischen und logischen Ebenen, der Entwicklung des Netzwerks als Teil des technologischen Evolutionsprozesses, der Harmonisierung der Architektur der verbundenen Segmente und der Lösung von Wachstumsproblemen. Tatsächlich besteht der Lebenszyklus eines Netzwerks fast immer aus Änderungen mit dem einen oder anderen Risikograd und einer umfassenden Auswirkung auf einen Dienst, bei deren Bewertung der Faktor Mensch nicht ignoriert werden kann. Obwohl es durchaus angebracht ist, diese Beschreibung auf die meisten Bereiche menschlicher Aktivitäten zu verallgemeinern, weist die Funktionsweise von Kommunikationsnetzwerken einige Merkmale auf, die Verständnis oder zumindest Aufmerksamkeit verdienen - die Elemente von Kommunikationsnetzwerken stehen in enger Kommunikation, interagieren eng und machen nicht nur direkt, sondern auch indirekt Auswirkungen aufeinander. Eine kompetente Strategie der laufenden Arbeit wird daher nur dann produktiver, wenn sie durch Mechanismen unterstützt wird, die die Wahrscheinlichkeit menschlicher Fehler so weit wie möglich verringern. Im nächsten Artikel der Reihe
„Warum sollten Netzwerktechniker programmieren ?
“ Werde ich auf Optionen für die Verwendung der Automatisierung in einer solchen Aufgabe eingehen.
In vielen „Primern“ der Netzwerkarchitektur werden die Begriffe „große Netzwerke“ und „hierarchische Netzwerke“ in Bezug auf das Design einer IGP-Domäne fast synonym verwendet. Es wird ein einfaches und auf den ersten Blick verständliches Design angegeben - die Aufteilung einer Domäne in Domänen. Gleichzeitig ist die Sättigungsschwelle eine rein individuelle Sache. In einigen Fällen können tausend moderne Router normalerweise in einem IGP-Bereich koexistieren, andernfalls reichen dreihundert aus, um die Betriebseigenschaften erheblich zu verringern. Zum größten Teil wird diese Schwelle durch die dem IGP auferlegten Protokolle bestimmt. Unter den Bedingungen einer gewissen Variabilität und Unsicherheit der Grenzen und Skalen des zukünftigen Netzwerks findet der „Bison“ der Industrie einen flexibleren Weg, um eine flache Domäne mit der anschließenden Migration seiner Formteile in separate Gebiete aufzubauen. Mit anderen Worten, wenn Sie nicht „morgen morgen schauen“ können, bauen Sie ein flaches Netzwerk auf und teilen Sie es auf, sobald die ersten Anzeichen einer Verschlechterung der Konvergenzzeit oder einer übermäßigen Komplexität der Ausnutzung auftreten, da das Fehlen einer Hierarchie immer noch besser ist als das falsche, das unter Unsicherheit ausgewählt wurde Struktur [1, 2, 3].
Ganz allgemeine Beschreibungen und abstrakte Beispiele nehmen an, dass es sich um eine überwachsene Region der OSPFv2-Domäne handelt, deren Topologie der physikalischen Fasern / Kanäle es bereits ermöglicht, die Grenzen zukünftiger Regionen in der amorphen Struktur zu erkennen. Ich bin kein Befürworter einer Änderung nach dem Prinzip „Alles oder Nichts“. Es kann vorkommen, dass der Raum der Chancen aufgrund unvorhergesehener Umstände zu eng und die erwarteten Risiken zu groß werden. Das Ändern der OSPFv2-Region ist eine destruktive Operation. Daher ist das einfachste Schema des Migrationsprozesses, das darin besteht, Router nacheinander von der zukünftigen Grenze nach unten in eine neue Region zu übertragen, in allen Topologien praktisch. Glücklicherweise wurde vor einiger Zeit in Empfehlungen für die Entwicklung von OSPF die Möglichkeit des Aufbaus von Konnektivität in mehreren Bereichen umrissen [4]. Bei dieser Gelegenheit können wir die Migration in drei Phasen unterteilen:
- Aufbau zusätzlicher (sekundärer) Konnektivität in einem neuen Bereich
- Übertragung eines neuen Bereichs in den Hauptmodus und des alten in einen zusätzlichen Bereich
- Entfernen der Konnektivität innerhalb des alten Bereichs
In der ersten Phase wird die Topologie der neuen Region allmählich erweitert, in der zweiten Phase wird die Topologie der alten Region enger. Vorbehaltlich der Kongruenz der Topologien der alten und neuen Bereiche erhalten wir ein konsistentes Routing zwischen den übersetzten und nicht übersetzten Knoten, was wiederum die Unterteilung der Stufen in unabhängige Unterstufen ermöglicht, bei denen jeweils mit einem Teil der Knoten gearbeitet werden kann. Es ist ratsam, die Auswahl der Knoten für die Arbeit im Rahmen der Teilstufe unter dem Gesichtspunkt der tatsächlichen Nutzung der Kanäle in einem bestimmten Netzwerk zu betrachten, um ein erneutes Laden an der Grenze zwischen dem alten und dem neuen Gebiet zu verhindern. Trotz der Tatsache, dass der Artikel der Programmierung gewidmet ist, halte ich es nicht für überflüssig, ein paar Worte über das Verhalten von Protokollen zu sagen, die IGP im Zusammenhang mit sich ändernden Domänen auferlegt werden. LDP verhält sich ziemlich vorhersehbar. Eine reibungslose Übersetzung wird durch die Bereitstellung von IP-Konnektivität zwischen gezielten Transportadressen und Schnittstellensitzungen erreicht. Aufgrund der Tatsache, dass BGP ein sehr flexibles Protokoll ist, sollten Sie diesem Flugzeug besondere Aufmerksamkeit schenken. Es ist gut, wenn BGP den übersetzten Knoten keine besonderen Freiheiten in Form von Änderungen in den lokalen Einstellungen oder anderen Kriterien einführt, die die lokale Routing-Entscheidung bestimmen, die zwischen den Knoten inkonsistent ist. Mit anderen Worten, das Verhalten von BGP ist auch vorhersehbar, wenn die Routenauswahl innerhalb der Region nicht der folgenden IGP-Pfadregel widersprach. Es gibt einen subtilen Punkt, der mit der Arbeit von RSVP während des Zeitraums der Koexistenz zweier Bereiche verbunden ist. Die Tatsache, dass die TED-Tabelle aus zwei Quellen mit unterschiedlicher Sichtbarkeit gefüllt wird, gibt Anlass zum Nachdenken. Sie können beispielsweise die FRR-Mechanismen verlieren, bis die Arbeit abgeschlossen ist. Dies kann passieren, wenn Router mit höherer Sichtbarkeit, die sich in zwei Bereichen befinden, die ERO über einen Router mit geringerer Sichtbarkeit berechnen, d. H. durch ein übersetztes Netzwerksegment ohne topologische Informationen über einen anderen Bereich. Dies kann nicht als Katastrophe bezeichnet werden, da der Pfad irgendwann festgelegt wird, aber Sie sollten ihn nicht vergessen. Besondere Kunst erfordert die Kombination der Arbeit der Einführung von IGP-Hierarchien mit der gleichen Art von Arbeit in der BGP-Ebene, beispielsweise durch Migration von Vollmaschen in Routenreflektoren. Die Einführung von Hierarchien in verschiedenen Ebenen ist besser nacheinander durchzuführen. Dies gilt meiner Meinung nach für alle Dinge, die Routing-Informationen verbergen. Eine Zusammenfassung lässt sich leichter auf einer stabilen Grundlage hierarchischer IGP aufbauen, als diese Stufen zu kombinieren.
Wir haben also einen allgemeinen Plan, und wenn Sie Ihre Meinung noch nicht geändert haben, lassen Sie uns über eine Software-Implementierung auf Pyez nachdenken, so etwas wie diese auf dem Bild.

Jedes schöne Oval kann eine separate Softwareeinheit sein, d.h. eine Sache, die die Arbeit erledigt und die Daten für den nächsten Schritt vorbereitet. Anfangsdaten sind Informationen aus dem Netzwerk. Um beispielsweise die Konfiguration eines neuen OSPF-Bereichs vorzubereiten, müssen Sie die Namen der aktiven Schnittstellen, die zum alten Bereich gehören, und deren Gewicht abrufen. Dies bedeutet, dass wir Kenntnisse in der Arbeit mit Operationstabellen und -ansichten benötigen. Diese Konzepte finden Sie in einem früheren Artikel in der Reihe
„Programmierung für Netzwerktechniker: Der erste Fall“ . In der ersten Phase speichert der Generator in den Dateien die Befehle, die zum Aktivieren des neuen Bereichs erforderlich sind, in der zweiten - um den alten zu löschen und den neuen in den Hauptmodus zu übertragen, in der dritten - den Befehl zum Löschen des alten Bereichs. Mit Blick auf die Zukunft werde ich sagen, dass ich für diesen Artikel absichtlich keine Vorlagenvisualisierer wie Jinja2 verwende. Um nicht vom Zielthema abgelenkt zu werden, wird der Code so einfach wie möglich geschrieben. Wenn sich jemand für die Dokumentation unter dem Link
"Jinja2-Dokumentation" interessiert.
Schritt Konfigurationsgenerierungscodeimport sys import yaml from jnpr.junos.factory.factory_loader import FactoryLoader from jnpr.junos import Device def getConnection(p_host, p_user): acc = {'lab': 'lab123'} try: print ' DEBUG --- getting ssh connection to ' + p_host l_dev = Device(host=p_host, user=p_user, password=acc[p_user], auto_probe=2, gather_facts=True, port=22) l_dev.open() if (l_dev.connected): l_dev.timeout = 900 print ' DEBUG --- ssh cionnection to host ' + p_host + ' established' print ' DEBUG --- connection ' + p_host + ' named ' + l_dev.facts['hostname'] + ' established ' return l_dev else: raise Exception(' DEBUG --- ssh connection to ' + p_host + ' was not established') except Exception as ex: print ' DEBUG --- ERROR --- getConnection : connection to ' + p_host + ' was not established. ex:' + str(ex) return def close_dev(d): try: d.close() except Exception as ex: print ' DEBUG --- ERROR --- close_dev : connection to cant be closed. ex:' + str(ex) yml = ''' --- OSPFInterface: rpc: get-ospf-interface-information args: area: '0.0.0.200' detail: True item: ospf-interface view: OSPFInterfaceView OSPFInterfaceView: fields: name: interface-name type: interface-type cost: interface-cost ''' globals().update(FactoryLoader().load(yaml.load(yml))) node_list = ['10.83.20.68', '10.83.20.69', '10.83.20.70', '10.83.20.71'] abr_list = ['10.83.20.66', '10.83.20.67'] for node in node_list + abr_list: ddev = getConnection(node, 'lab') ospf_interfaces = OSPFInterface(ddev).get() with open('st1-' + node + '.txt', "w") as f_st1: for ospf_interface in ospf_interfaces: if ( 'ge' in ospf_interface.name ): f_st1.write('set protocols ospf area 0.0.0.250 interface ' + ospf_interface.name + ' secondary' + '\n') f_st1.write('set protocols ospf area 0.0.0.250 interface ' + ospf_interface.name + ' interface-type p2p' + '\n') f_st1.write('set protocols ospf area 0.0.0.250 interface ' + ospf_interface.name + ' metric ' + ospf_interface.cost + '\n') with open('st2-' + node + '.txt', "w") as f_st1: f_st1.write('delete protocols ospf area 0.0.0.200' + '\n') f_st1.write('delete protocols ospf area 0.0.0.250' + '\n') for ospf_interface in ospf_interfaces: f_st1.write('set protocols ospf area 0.0.0.250 interface ' + ospf_interface.name + ' interface-type p2p' + '\n') f_st1.write('set protocols ospf area 0.0.0.200 interface ' + ospf_interface.name + ' secondary' + '\n') f_st1.write('set protocols ospf area 0.0.0.200 interface ' + ospf_interface.name + ' interface-type p2p' + '\n') if (ospf_interface.cost != '0'): f_st1.write('set protocols ospf area 0.0.0.250 interface ' + ospf_interface.name + ' metric ' + ospf_interface.cost + '\n') f_st1.write('set protocols ospf area 0.0.0.200 interface ' + ospf_interface.name + ' metric ' + ospf_interface.cost + '\n') with open('st3-' + node + '.txt', "w") as f_st1: f_st1.write('delete protocols ospf area 0.0.0.200' + '\n')
Aus Gründen der Übersichtlichkeit habe ich in einem solchen Netzwerk auf vMX zusammengestellt.
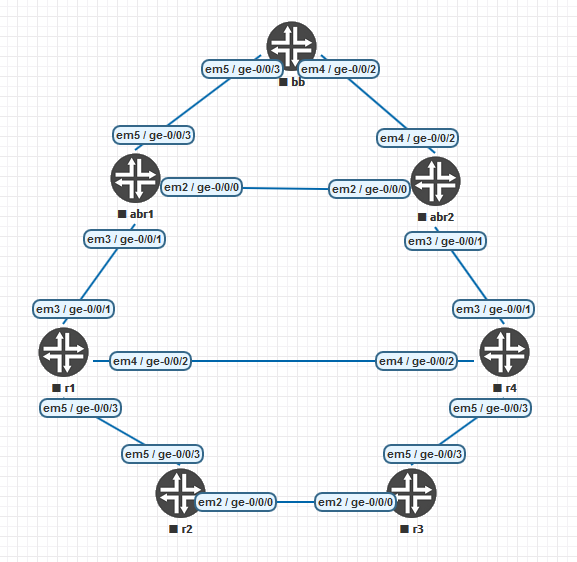
vMX ist ein voll ausgestatteter Software-Router von Juniper Networks, der das Verhalten seines älteren, eisernen Bruders MX weitgehend wiederholt. Nicht dass es ein Produkt war, das eingeführt werden muss, es ist nur nützlich, diese Dinge für Programmierübungen oder Labortests griffbereit zu halten.
Die Testversion kann hier heruntergeladen werden
"vMX Trial Download" und die Installationsanweisungen unter diesem Link
"Vorbereiten des Systems für die Installation von
vMX" .
Die Router bb, abr1 und abr2 bilden den Nullbereich, die Router r1, r2, r3 und r4 - sollten vom 200. Bereich in den 250. Bereich verschoben werden.
lab @ bb> Konfigurationsprotokolle anzeigen bgp { group int { type internal; local-address 10.0.0.65; neighbor 10.0.0.66; neighbor 10.0.0.67; neighbor 10.0.0.68; neighbor 10.0.0.69; neighbor 10.0.0.70; neighbor 10.0.0.71; } } ospf { area 0.0.0.0 { interface lo0.0 { passive; } interface ge-0/0/3.0 { interface-type p2p; } interface ge-0/0/2.0 { interface-type p2p; } } }
lab @ abr1> Konfigurationsprotokolle anzeigen bgp { group int { type internal; local-address 10.0.0.66; neighbor 10.0.0.65; neighbor 10.0.0.67; neighbor 10.0.0.68; neighbor 10.0.0.69; neighbor 10.0.0.70; neighbor 10.0.0.71; } } ospf { area 0.0.0.0 { interface lo0.0 { interface-type p2p; } interface ge-0/0/3.0 { interface-type p2p; } interface ge-0/0/0.0 { interface-type p2p; } } area 0.0.0.200 { interface ge-0/0/1.0 { interface-type p2p; } } }
lab @ abr2> Konfigurationsprotokolle anzeigen bgp { group int { type internal; local-address 10.0.0.67; neighbor 10.0.0.65; neighbor 10.0.0.66; neighbor 10.0.0.68; neighbor 10.0.0.69; neighbor 10.0.0.70; neighbor 10.0.0.71; } } ospf { area 0.0.0.0 { interface lo0.0 { interface-type p2p; } interface ge-0/0/0.0 { interface-type p2p; } interface ge-0/0/2.0 { interface-type p2p; } } area 0.0.0.200 { interface ge-0/0/1.0 { interface-type p2p; } } }
lab @ r1> Konfigurationsprotokolle anzeigen bgp { group int { type internal; local-address 10.0.0.68; neighbor 10.0.0.65; neighbor 10.0.0.66; neighbor 10.0.0.67; neighbor 10.0.0.69; neighbor 10.0.0.70; neighbor 10.0.0.71; } } ospf { area 0.0.0.200 { interface ge-0/0/1.0 { interface-type p2p; } interface ge-0/0/2.0 { interface-type p2p; } interface ge-0/0/3.0 { interface-type p2p; } interface lo0.0 { interface-type p2p; } } }
lab @ r2> Konfigurationsprotokolle anzeigen bgp { group int { type internal; local-address 10.0.0.69; neighbor 10.0.0.65; neighbor 10.0.0.66; neighbor 10.0.0.67; neighbor 10.0.0.68; neighbor 10.0.0.70; neighbor 10.0.0.71; } } ospf { area 0.0.0.200 { interface ge-0/0/0.0 { interface-type p2p; } interface ge-0/0/3.0 { interface-type p2p; } interface lo0.0 { interface-type p2p; } } }
lab @ r3> Konfigurationsprotokolle anzeigen bgp { group int { type internal; local-address 10.0.0.70; neighbor 10.0.0.65; neighbor 10.0.0.66; neighbor 10.0.0.67; neighbor 10.0.0.68; neighbor 10.0.0.69; neighbor 10.0.0.71; } } ospf { area 0.0.0.200 { interface ge-0/0/0.0 { interface-type p2p; } interface ge-0/0/3.0 { interface-type p2p; } interface lo0.0 { interface-type p2p; } } }
lab @ r4> Konfigurationsprotokolle anzeigen bgp { group int { type internal; local-address 10.0.0.71; neighbor 10.0.0.65; neighbor 10.0.0.66; neighbor 10.0.0.67; neighbor 10.0.0.68; neighbor 10.0.0.69; neighbor 10.0.0.70; } } ospf { area 0.0.0.200 { interface ge-0/0/1.0 { interface-type p2p; } interface ge-0/0/2.0 { interface-type p2p; } interface ge-0/0/3.0 { interface-type p2p; } interface lo0.0 { interface-type p2p; } } }
Für den r2-Router werden die folgenden Befehle generiert.
Für die erste Stufesetze protokolle ospf bereich 0.0.0.250 schnittstelle ge-0/0 / 1.0 sekundär
Protokolle einstellen ospf area 0.0.0.250 Schnittstelle ge-0/0 / 1.0 Schnittstellentyp p2p
setze Protokolle ospf Bereich 0.0.0.250 Schnittstelle ge-0/0 / 1.0 Metrik 1
Protokolle einstellen ospf area 0.0.0.250 Schnittstelle ge-0/0 / 2.0 sekundär
Protokolle einstellen ospf area 0.0.0.250 interface ge-0/0 / 2.0 schnittstellentyp p2p
setze Protokolle ospf Bereich 0.0.0.250 Schnittstelle ge-0/0 / 2.0 Metrik 1
Protokolle einstellen ospf area 0.0.0.250 Schnittstelle ge-0/0 / 3.0 sekundär
Protokolle einstellen ospf area 0.0.0.250 Schnittstelle ge-0/0 / 3.0 Schnittstellentyp p2p
setze Protokolle ospf Bereich 0.0.0.250 Schnittstelle ge-0/0 / 3.0 Metrik 1
Für die zweite StufeProtokolle löschen ospf area 0.0.0.200
Protokolle löschen ospf area 0.0.0.250
Protokolle einstellen ospf area 0.0.0.250 Schnittstelle ge-0/0 / 1.0 Schnittstellentyp p2p
Protokolle einstellen ospf area 0.0.0.200 Schnittstelle ge-0/0 / 1.0 sekundär
setze Protokolle ospf Bereich 0.0.0.200 Schnittstelle ge-0/0 / 1.0 Schnittstellentyp p2p
setze Protokolle ospf Bereich 0.0.0.250 Schnittstelle ge-0/0 / 1.0 Metrik 1
Protokolle einstellen ospf area 0.0.0.200 Schnittstelle ge-0/0 / 1.0 Metrik 1
Protokolle einstellen ospf area 0.0.0.250 interface ge-0/0 / 2.0 schnittstellentyp p2p
Protokolle einstellen ospf area 0.0.0.200 Schnittstelle ge-0/0 / 2.0 sekundär
setze Protokolle ospf Bereich 0.0.0.200 Schnittstelle ge-0/0 / 2.0 Schnittstellentyp p2p
setze Protokolle ospf Bereich 0.0.0.250 Schnittstelle ge-0/0 / 2.0 Metrik 1
Protokolle einstellen ospf area 0.0.0.200 Schnittstelle ge-0/0 / 2.0 Metrik 1
Protokolle einstellen ospf area 0.0.0.250 Schnittstelle ge-0/0 / 3.0 Schnittstellentyp p2p
setze protokolle ospf bereich 0.0.0.200 schnittstelle ge-0/0 / 3.0 sekundär
Protokolle einstellen ospf area 0.0.0.200 Schnittstelle ge-0/0 / 3.0 Schnittstellentyp p2p
setze Protokolle ospf Bereich 0.0.0.250 Schnittstelle ge-0/0 / 3.0 Metrik 1
Protokolle einstellen ospf area 0.0.0.200 Schnittstelle ge-0/0 / 3.0 Metrik 1
setze Protokolle ospf Bereich 0.0.0.250 Schnittstelle lo0.0 Schnittstellentyp p2p
setze Protokolle ospf Bereich 0.0.0.200 Schnittstelle lo0.0 sekundär
setze Protokolle ospf Bereich 0.0.0.200 Schnittstelle lo0.0 Schnittstellentyp p2p
Für die dritte StufeProtokolle löschen ospf area 0.0.0.200
Wie ich bereits geschrieben habe, haben die Elemente des Netzwerks einen internen Zustand, um und in ihnen passiert ständig etwas, unabhängig davon, ob wir es wollen oder nicht. Das Auftreten von Ereignissen wie Transceiverausfall, Stromausfall an einem Knoten oder Unterbrechung eines optischen Kanals muss bei der Arbeit als selbstverständlich angesehen und berücksichtigt werden. Ich schlage vor, diese Tatsache im Zusammenhang mit der Wahl der Überprüfung des Erfolgs der Migrationsphasen zu berücksichtigen. Egal wie paradox dies klingen mag, in diesem Fall müssen wir nicht prüfen, ob die OSPF-Nachbarschaft auf dieser oder jener Schnittstelle aufgetreten ist, da die Gründe für ihre Abwesenheit in einer völlig anderen Ebene liegen können. Darüber hinaus kann ein Fehler oder eine Ungenauigkeit immer in die Quelldaten gelangen, beispielsweise in Form einer vergessenen Schnittstelle, die gelöscht werden muss, aber derzeit die "Leere" untersucht. Bei der Erstellung von Überprüfungen ist es hilfreich, eine Ebene nach oben zu gehen, um das Netzwerk unter dem Gesichtspunkt der bereitgestellten Dienste und der auferlegten Protokolle zu betrachten, da letztendlich nur der Status dieser Dinge es Ihnen ermöglicht, eine fundierte Entscheidung über den Erfolg einer bestimmten Phase zu treffen. Nur wenige Kunden stimmen öffentlichen Artikeln zu, die auf den Ergebnissen ihrer Arbeit basieren. Deshalb habe ich eine virtuelle Umgebung zur Demonstration zusammengestellt. In dieser Umgebung beschränke ich mich darauf, den Status von BGP-Sitzungen zu überprüfen, die eins zu eins zwischen Routern erstellt werden. Dies sind unsere auferlegten Dienste und Dienste. Wenn nach der Arbeit die Voraussetzungen für ihre Leistung in Form einer IP-Konnektivität erfüllt sind, besteht Grund zu der Annahme, dass die Arbeit erfolgreich ausgeführt wurde. In realen Projekten beschränken sich Überprüfungen normalerweise auf das Volumen der auferlegten Dienste und Protokolle, das in einem bestimmten Netzwerk als geschäftskritisch eingestuft wird. Dies gilt nicht für die Programmierung, ich kann mich jedoch nur auf dieses Thema konzentrieren, da die Wahl des Erfolgskriteriums der Schlüssel zu einem guten Schlaf nach getaner Arbeit ist.
BGP-Sitzungsüberprüfungscode import sys import yaml from jnpr.junos.factory.factory_loader import FactoryLoader from jnpr.junos import Device def getConnection(p_host, p_user): acc = {'lab': 'lab123'} try: print ' DEBUG --- getting ssh connection to ' + p_host l_dev = Device(host=p_host, user=p_user, password=acc[p_user], auto_probe=2, gather_facts=True, port=22) l_dev.open() if (l_dev.connected): l_dev.timeout = 900 print ' DEBUG --- ssh cionnection to host ' + p_host + ' established' print ' DEBUG --- connection ' + p_host + ' named ' + l_dev.facts['hostname'] + ' established ' return l_dev else: raise Exception(' DEBUG --- ssh connection to ' + p_host + ' was not established') except Exception as ex: print ' DEBUG --- ERROR --- getConnection : connection to ' + p_host + ' was not established. ex:' + str(ex) return def close_dev(d): try: d.close() except Exception as ex: print ' DEBUG --- ERROR --- close_dev : connection to cant be closed. ex:' + str(ex) ip_f_name = 'ip-list-1.txt' yml = ''' --- BGPGroup: rpc: get-bgp-group-information args: group-name: 'int' item: bgp-group view: BGPGroupView BGPGroupView: fields: count: peer-count established: established-count ''' globals().update(FactoryLoader().load(yaml.load(yml))) node_list = ['10.83.20.68', '10.83.20.69', '10.83.20.70', '10.83.20.71'] abr_list = ['10.83.20.66', '10.83.20.67'] for node in node_list + abr_list: ddev = getConnection(node, 'lab') bgp_group = BGPGroup(ddev).get() for group in bgp_group: if (group.count != group.established): print 'bgp connection lost' else: print 'dont panic!'
Ergebnisse seiner ArbeitDEBUG - SSH-Verbindung zu 10.83.20.68 erhalten
DEBUG - SSH-Verbindung zum Host 10.83.20.68 hergestellt
DEBUG - Verbindung 10.83.20.68 mit dem Namen r1 hergestellt
Keine Panik!
DEBUG - SSH-Verbindung zu 10.83.20.69 erhalten
DEBUG - SSH-Verbindung zum Host 10.83.20.69 hergestellt
DEBUG - Verbindung 10.83.20.69 mit dem Namen r2 hergestellt
Keine Panik!
DEBUG - SSH-Verbindung zu 10.83.20.70 erhalten
DEBUG - SSH-Verbindung zum Host 10.83.20.70 hergestellt
DEBUG - Verbindung 10.83.20.70 mit dem Namen r3 hergestellt
Keine Panik!
DEBUG - SSH-Verbindung zu 10.83.20.71 erhalten
DEBUG - SSH-Verbindung zum Host 10.83.20.71 hergestellt
DEBUG - Verbindung 10.83.20.71 mit dem Namen r4 hergestellt
Keine Panik!
DEBUG - SSH-Verbindung zu 10.83.20.66 erhalten
DEBUG - SSH-Verbindung zum Host 10.83.20.66 hergestellt
DEBUG - Verbindung 10.83.20.66 mit dem Namen abr1 hergestellt
Keine Panik!
DEBUG - SSH-Verbindung zu 10.83.20.67 erhalten
DEBUG - SSH-Verbindung zum Host 10.83.20.67 hergestellt
DEBUG - Verbindung 10.83.20.67 mit dem Namen abr2 hergestellt
Keine Panik!
Bisher haben wir hauptsächlich über Netzwerk-Dinge gesprochen, aber ich habe noch kein Wort über den Programmcode erwähnt, der in einem Artikel mit diesem Namen im Mittelpunkt der Aufmerksamkeit zu stehen scheint. Erstens scheint es mir, dass Gedanken viel wichtiger sind als Code. Wenn formalisierte Entitäten im Kopf sind, kann ein Ingenieur sie in ein Werkzeug verwandeln und sie in Form von Code angeben. Zweitens möchte ich mich nicht wiederholen. Alles, was in diesen Beispielen nicht offensichtlich erscheint, sowie das erforderliche Mindestwissen, um mit Python und Pyez zu arbeiten, sind im vorherigen Artikel der Serie enthalten. Drittens führt der Konfigurationsvorbereitungscode seine Arbeit aus, die als offline bezeichnet wird und keine unmittelbaren Auswirkungen auf das Netzwerk hat, sodass es unwahrscheinlich ist, dass Interesse entsteht. Mit dem Implementierungscode der Implementierungsphase sieht es etwas anders aus. Die Entwicklung dieser Verfahren wirft die folgenden Fragen auf:
- Wie kann überprüft werden, ob das gesamte Befehlsvolumen vom Dolmetscher angemessen wahrgenommen wird?
- Wie kann ich überprüfen, ob Änderungen an der Konfiguration übernommen wurden?
- Wie implementiere ich ein Transaktionskonfigurationsschema?
- Wie kann die Konfiguration bei Kontrollverlust zurückgesetzt werden?
- Wie bereinige ich, wenn der Interpreter während der Übertragung von Befehlen einen Fehler meldet?
Je mehr Aufmerksamkeit diesen Themen gewidmet wird, desto seltener werden Überraschungen in der Ausführungsphase serviert. Stellen Sie sich den Ärger eines Syntaxfehlers vor, der eine Routing-Richtlinie beschreibt, wenn Klassifizierer dieser Richtlinie vom Interpreter nur teilweise genehmigt werden. Wenn Sie den Vorgang des Zusammenführens dieser Richtlinie mit der aktuellen Konfiguration nicht zeilenweise steuern, können Sie den Gerätestapel mit einem Klick auf eine Schaltfläche in einen unzureichenden Zustand versetzen. Daher halte ich mich ungefähr an einen solchen Block des Ausführungsstufendiagramms.
 Ausgerüstet
Ausgerüstet mit der
Pyez- Dokumentation wurde der folgende universelle Konfigurationsladecode kompiliert, den Sie in Ihrer täglichen Arbeit genauso verwenden können, wie ich ihn in meiner verwende.
conf_change.py import sys import yaml from jnpr.junos.factory.factory_loader import FactoryLoader from jnpr.junos import Device from jnpr.junos.utils.config import Config import copy import re import traceback import time import random from jnpr.junos.exception import * import os.path yml = ''' --- VersionInfo: rpc: get-software-information item: software-information view: VersionInfoView VersionInfoView: fields: name: host-name ''' Device.auto_probe = 3 ip_f_name = 'ip-list-1.txt' cur_stage='2' globals().update(FactoryLoader().load(yaml.load(yml))) def doTestOSPF(p_dev, p_node, f_do): print ' DEBUG --- doTestOSPF : at ' + p_node if ( p_dev == None ): print ' DEBUG --- ERROR --- doTestOSPF : connection to ' + p_node + ' is None' return else: try: d_conf = p_dev.cli("show configuration | display set").split('\n') ret_val = True set_found = 0 c_path = 'st' + cur_stage + '-' + p_node + '.txt' with open(c_path, "r") as f: for line in f: c_line = line.replace('\n', '').replace('\r\n', '') if ('delete ' not in c_line): set_found = 1 if ( (c_line not in d_conf) and (c_line != '')): print ' DEBUG --- doTestOSPF found missing line ' + c_line ret_val = False f.close() if ( (set_found == 0) and (f_do == True) ): return False return ret_val except Exception as ex: print ' DEBUG --- ERROR --- doTestOSPF : connection to ' + p_node + ' was not established. ex:' + str(ex) return def doTest(p_dev, p_node, f_do): return doTestOSPF(p_dev, p_node, f_do) def close_dev(d): try: d.close() except Exception as ex: print ' DEBUG --- ERROR --- close_dev : connection to cant be closed. ex:' + str(ex) def getConnection(p_host, p_user): acc = {'lab': 'lab123'} try: print ' DEBUG --- getting ssh connection to ' + p_host l_dev = Device(host=p_host, user=p_user, password=acc[p_user], auto_probe=2, gather_facts=True, port=22) l_dev.open() if (l_dev.connected): l_dev.timeout = 900 print ' DEBUG --- ssh cionnection to host ' + p_host + ' established' v = VersionInfo(l_dev).get() print ' DEBUG --- connection ' + p_host + ' named ' + l_dev.facts['hostname'] + ' established ' return l_dev else: raise Exception(' DEBUG --- ssh connection to ' + p_host + ' was not established') except Exception as ex: print ' DEBUG --- ERROR --- getConnection : connection to ' + p_host + ' was not established. ex:' + str(ex) traceback.print_exc() return def doCompare(p_conf, p_node): try: print ' DEBUG --- doCompare at ' + p_node if ( p_conf.diff() == None ): return False else: return True except Exception as ex: print ' DEBUG --- ERROR --- doCompare : conf.diff at ' + p_node + ' ex:' + str(ex) return def doLoad(p_conf, p_node): try: print ' DEBUG --- doLoad at ' + p_node c_path = 'st' + cur_stage + '-' + p_node + '.txt' if (os.path.isfile(c_path)): p_conf.load(path=c_path, format='set') return True except Exception as ex: print ' DEBUG --- ERROR --- doLoad : cant load config to ' + p_node + ' ex:' + str(ex) return def doRollback(p_conf, p_node, p_r): try: print ' DEBUG --- doRollback at ' + p_node if ( p_conf.rollback(rb_id=p_r) == True ): return True else: return False except Exception as ex: print ' DEBUG --- ERROR --- doRollback : cant rollback config to ' + p_node + ' ex:' + str(ex) return None def doCommitCheck(p_conf, p_node): try: print ' DEBUG --- doCommitCheck at ' + p_node p_conf.commit_check() return True except Exception as ex: print ' DEBUG --- ERROR --- doCommitCheck : cant config commit check config to ' + p_node + ' ex:' + str(ex) return None def doCommit(p_conf, p_node, p_confirm_m=None): try: print ' DEBUG --- doCommit at ' + p_node commit_res = None if (p_confirm_m == None): commit_res = p_conf.commit(timeout=30) else: commit_res = p_conf.commit(confirm=p_confirm_m, timeout=30) if (commit_res == True): return True else: return False except CommitError as c_ex: print ' DEBUG --- ERROR --- doCommit : cant config commit at ' + p_node + ' ex:' + str(c_ex) return None except RpcTimeoutError as t_ex: print ' DEBUG --- ERROR --- doCommit : config was commited at ' + p_node + ' with the following ex:' + str(t_ex) return True def doJob(p_dev, p_node): print ' DEBUG --- doJob at ' + p_node if ( p_dev == None ): print ' DEBUG --- ERROR --- doJob : connection to ' + p_node + ' is None' return else: try: with Config(p_dev) as conf: is_compare = doCompare(conf, node) if ( is_compare == None ): print ' DEBUG --- ERROR --- doJob : at config compare ' + node return if ( is_compare == True ): print ' DEBUG --- ERROR --- doJob : configuration locked at ' + node return False print ' DEBUG --- starting to do config changes at ' + node if ( doLoad(conf, node) != True ): print ' DEBUG --- ERROR --- doJob : conf.load ' + node if ( doCompare(conf, node) != False ): print ' DEBUG --- doJob : doing rollback after load at ' + node + ' deleting :' + str(conf.diff()) doRollback(conf, node, 0) return print ' DEBUG --- commit check at ' + node if (doCommitCheck(conf, node) != True): print ' DEBUG --- ERROR --- doJob : conf.doCommitCheck failed at ' + node if ( doCompare(conf, node) != False ): print ' DEBUG --- doJob : doing rollback after load at ' + node + ' deleting :' + str(conf.diff()) doRollback(conf, node, 0) return commit_m = 5 print ' DEBUG --- commiting changes at ' + node if (doCommit(conf, node, commit_m) != True): print ' DEBUG --- ERROR --- doJob : conf.commit ' + node if ( doCompare(conf, node) != False ): print ' DEBUG --- doJob : doing rollback after commit at ' + node + ' deleting :' + str(conf.diff()) doRollback(conf, node, 0) return True except Exception as ex: print ' DEBUG --- ERROR --- doJob : cant do job ' + node + ' ex:' + str(ex) return node_list = [] result_list = {} with open(ip_f_name, "r") as f_ip: for line in f_ip: c_ip_line = line.replace('\n', '').replace('\r\n', '') if (c_ip_line != ''): node_list.append(c_ip_line) for node in node_list: print 'FLOW -- ************************************ ' print 'FLOW -- checking ' + node result_list.setdefault(node, {}) cur_dev = getConnection(node, 'lab') is_test = doTest(cur_dev, node, True) if( is_test == None): print 'FLOW -- error' result_list.setdefault(node, {}).setdefault('status', 'error') break if( is_test == True): print 'FLOW -- conf exist' result_list.setdefault(node, {}).setdefault('status', 'nn') if( is_test == False): print 'FLOW -- conf not exist, doing change' is_job = doJob(cur_dev, node) if( is_job == None): print 'FLOW -- cant do job at ' + node result_list.setdefault(node, {}).setdefault('status', 'error') break if( is_job == False): print 'FLOW -- cant do job at ' + node result_list.setdefault(node, {}).setdefault('status', 'not_done') if( is_job == True): print 'FLOW -- done job at ' + node print 'FLOW -- going sleep at ' + node time.sleep(5) print 'FLOW -- checking job status ' + node cur_dev_confirm = getConnection(node, 'lab') if ( cur_dev_confirm != None ): if (doTest(cur_dev, node, False) == True): print 'FLOW -- commiting the configuration at ' + node if (doCommit(Config(cur_dev_confirm), node) != True): print 'FLOW -- ERROR cant commit the configuration at ' + node result_list.setdefault(node, {}).setdefault('status', 'not_done') break else: print 'FLOW -- configuration commited at ' + node result_list.setdefault(node, {}).setdefault('status', 'done') else: print 'FLOW -- ERROR cant find conf after job ' + node result_list.setdefault(node, {}).setdefault('status', 'not_done') close_dev(cur_dev_confirm) else: print 'FLOW -- ERROR cant access ' + node + ' for commiting' result_list.setdefault(node, {}).setdefault('status', 'not_done') close_dev(cur_dev) print result_list
Und die Ergebnisse seiner Arbeit in drei Schritten
Versteckter TextPython 2.7.14 (v2.7.14:84471935ed, Sep 16 2017, 20:19:30) [MSC v.1500 32 bit (Intel)] on win32
Type "copyright", "credits" or "license()" for more information.
>>>
==== RESTART: C:\Users\and_andreev\Desktop\tools\lab-case2\conf_change.py ====
FLOW -- ************************************
FLOW -- checking 10.83.20.66
DEBUG --- getting ssh connection to 10.83.20.66
DEBUG --- ssh cionnection to host 10.83.20.66 established
DEBUG --- connection 10.83.20.66 named abr1 established
DEBUG --- doTestOSPF : at 10.83.20.66
DEBUG --- doTestOSPF found missing line set protocols ospf area 0.0.0.250 interface ge-0/0/1.0 secondary
DEBUG --- doTestOSPF found missing line set protocols ospf area 0.0.0.250 interface ge-0/0/1.0 interface-type p2p
DEBUG --- doTestOSPF found missing line set protocols ospf area 0.0.0.250 interface ge-0/0/1.0 metric 1
FLOW -- conf not exist, doing change
DEBUG --- doJob at 10.83.20.66
DEBUG --- doCompare at 10.83.20.66
DEBUG --- starting to do config changes at 10.83.20.66
DEBUG --- doLoad at 10.83.20.66
DEBUG --- commit check at 10.83.20.66
DEBUG --- doCommitCheck at 10.83.20.66
DEBUG --- commiting changes at 10.83.20.66
DEBUG --- doCommit at 10.83.20.66
FLOW -- done job at 10.83.20.66
FLOW -- going sleep at 10.83.20.66
FLOW -- checking job status 10.83.20.66
DEBUG --- getting ssh connection to 10.83.20.66
DEBUG --- ssh cionnection to host 10.83.20.66 established
DEBUG --- connection 10.83.20.66 named abr1 established
DEBUG --- doTestOSPF : at 10.83.20.66
FLOW -- commiting the configuration at 10.83.20.66
DEBUG --- doCommit at 10.83.20.66
FLOW -- configuration commited at 10.83.20.66
FLOW -- ************************************
FLOW -- checking 10.83.20.67
DEBUG --- getting ssh connection to 10.83.20.67
DEBUG --- ssh cionnection to host 10.83.20.67 established
DEBUG --- connection 10.83.20.67 named abr2 established
DEBUG --- doTestOSPF : at 10.83.20.67
DEBUG --- doTestOSPF found missing line set protocols ospf area 0.0.0.250 interface ge-0/0/1.0 secondary
DEBUG --- doTestOSPF found missing line set protocols ospf area 0.0.0.250 interface ge-0/0/1.0 interface-type p2p
DEBUG --- doTestOSPF found missing line set protocols ospf area 0.0.0.250 interface ge-0/0/1.0 metric 1
FLOW -- conf not exist, doing change
DEBUG --- doJob at 10.83.20.67
DEBUG --- doCompare at 10.83.20.67
DEBUG --- starting to do config changes at 10.83.20.67
DEBUG --- doLoad at 10.83.20.67
DEBUG --- commit check at 10.83.20.67
DEBUG --- doCommitCheck at 10.83.20.67
DEBUG --- commiting changes at 10.83.20.67
DEBUG --- doCommit at 10.83.20.67
FLOW -- done job at 10.83.20.67
FLOW -- going sleep at 10.83.20.67
FLOW -- checking job status 10.83.20.67
DEBUG --- getting ssh connection to 10.83.20.67
DEBUG --- ssh cionnection to host 10.83.20.67 established
DEBUG --- connection 10.83.20.67 named abr2 established
DEBUG --- doTestOSPF : at 10.83.20.67
FLOW -- commiting the configuration at 10.83.20.67
DEBUG --- doCommit at 10.83.20.67
FLOW -- configuration commited at 10.83.20.67
FLOW -- ************************************
FLOW -- checking 10.83.20.68
DEBUG --- getting ssh connection to 10.83.20.68
DEBUG --- ssh cionnection to host 10.83.20.68 established
DEBUG --- connection 10.83.20.68 named r1 established
DEBUG --- doTestOSPF : at 10.83.20.68
DEBUG --- doTestOSPF found missing line set protocols ospf area 0.0.0.250 interface ge-0/0/1.0 secondary
DEBUG --- doTestOSPF found missing line set protocols ospf area 0.0.0.250 interface ge-0/0/1.0 interface-type p2p
DEBUG --- doTestOSPF found missing line set protocols ospf area 0.0.0.250 interface ge-0/0/1.0 metric 1
DEBUG --- doTestOSPF found missing line set protocols ospf area 0.0.0.250 interface ge-0/0/2.0 secondary
DEBUG --- doTestOSPF found missing line set protocols ospf area 0.0.0.250 interface ge-0/0/2.0 interface-type p2p
DEBUG --- doTestOSPF found missing line set protocols ospf area 0.0.0.250 interface ge-0/0/2.0 metric 1
DEBUG --- doTestOSPF found missing line set protocols ospf area 0.0.0.250 interface ge-0/0/3.0 secondary
DEBUG --- doTestOSPF found missing line set protocols ospf area 0.0.0.250 interface ge-0/0/3.0 interface-type p2p
DEBUG --- doTestOSPF found missing line set protocols ospf area 0.0.0.250 interface ge-0/0/3.0 metric 1
FLOW -- conf not exist, doing change
DEBUG --- doJob at 10.83.20.68
DEBUG --- doCompare at 10.83.20.68
DEBUG --- starting to do config changes at 10.83.20.68
DEBUG --- doLoad at 10.83.20.68
DEBUG --- commit check at 10.83.20.68
DEBUG --- doCommitCheck at 10.83.20.68
DEBUG --- commiting changes at 10.83.20.68
DEBUG --- doCommit at 10.83.20.68
FLOW -- done job at 10.83.20.68
FLOW -- going sleep at 10.83.20.68
FLOW -- checking job status 10.83.20.68
DEBUG --- getting ssh connection to 10.83.20.68
DEBUG --- ssh cionnection to host 10.83.20.68 established
DEBUG --- connection 10.83.20.68 named r1 established
DEBUG --- doTestOSPF : at 10.83.20.68
FLOW -- commiting the configuration at 10.83.20.68
DEBUG --- doCommit at 10.83.20.68
FLOW -- configuration commited at 10.83.20.68
FLOW -- ************************************
FLOW -- checking 10.83.20.69
DEBUG --- getting ssh connection to 10.83.20.69
DEBUG --- ssh cionnection to host 10.83.20.69 established
DEBUG --- connection 10.83.20.69 named r2 established
DEBUG --- doTestOSPF : at 10.83.20.69
DEBUG --- doTestOSPF found missing line set protocols ospf area 0.0.0.250 interface ge-0/0/0.0 secondary
DEBUG --- doTestOSPF found missing line set protocols ospf area 0.0.0.250 interface ge-0/0/0.0 interface-type p2p
DEBUG --- doTestOSPF found missing line set protocols ospf area 0.0.0.250 interface ge-0/0/0.0 metric 1
DEBUG --- doTestOSPF found missing line set protocols ospf area 0.0.0.250 interface ge-0/0/3.0 secondary
DEBUG --- doTestOSPF found missing line set protocols ospf area 0.0.0.250 interface ge-0/0/3.0 interface-type p2p
DEBUG --- doTestOSPF found missing line set protocols ospf area 0.0.0.250 interface ge-0/0/3.0 metric 1
FLOW -- conf not exist, doing change
DEBUG --- doJob at 10.83.20.69
DEBUG --- doCompare at 10.83.20.69
DEBUG --- starting to do config changes at 10.83.20.69
DEBUG --- doLoad at 10.83.20.69
DEBUG --- commit check at 10.83.20.69
DEBUG --- doCommitCheck at 10.83.20.69
DEBUG --- commiting changes at 10.83.20.69
DEBUG --- doCommit at 10.83.20.69
FLOW -- done job at 10.83.20.69
FLOW -- going sleep at 10.83.20.69
FLOW -- checking job status 10.83.20.69
DEBUG --- getting ssh connection to 10.83.20.69
DEBUG --- ssh cionnection to host 10.83.20.69 established
DEBUG --- connection 10.83.20.69 named r2 established
DEBUG --- doTestOSPF : at 10.83.20.69
FLOW -- commiting the configuration at 10.83.20.69
DEBUG --- doCommit at 10.83.20.69
FLOW -- configuration commited at 10.83.20.69
FLOW -- ************************************
FLOW -- checking 10.83.20.70
DEBUG --- getting ssh connection to 10.83.20.70
DEBUG --- ssh cionnection to host 10.83.20.70 established
DEBUG --- connection 10.83.20.70 named r3 established
DEBUG --- doTestOSPF : at 10.83.20.70
DEBUG --- doTestOSPF found missing line set protocols ospf area 0.0.0.250 interface ge-0/0/0.0 secondary
DEBUG --- doTestOSPF found missing line set protocols ospf area 0.0.0.250 interface ge-0/0/0.0 interface-type p2p
DEBUG --- doTestOSPF found missing line set protocols ospf area 0.0.0.250 interface ge-0/0/0.0 metric 1
DEBUG --- doTestOSPF found missing line set protocols ospf area 0.0.0.250 interface ge-0/0/3.0 secondary
DEBUG --- doTestOSPF found missing line set protocols ospf area 0.0.0.250 interface ge-0/0/3.0 interface-type p2p
DEBUG --- doTestOSPF found missing line set protocols ospf area 0.0.0.250 interface ge-0/0/3.0 metric 1
FLOW -- conf not exist, doing change
DEBUG --- doJob at 10.83.20.70
DEBUG --- doCompare at 10.83.20.70
DEBUG --- starting to do config changes at 10.83.20.70
DEBUG --- doLoad at 10.83.20.70
DEBUG --- commit check at 10.83.20.70
DEBUG --- doCommitCheck at 10.83.20.70
DEBUG --- commiting changes at 10.83.20.70
DEBUG --- doCommit at 10.83.20.70
FLOW -- done job at 10.83.20.70
FLOW -- going sleep at 10.83.20.70
FLOW -- checking job status 10.83.20.70
DEBUG --- getting ssh connection to 10.83.20.70
DEBUG --- ssh cionnection to host 10.83.20.70 established
DEBUG --- connection 10.83.20.70 named r3 established
DEBUG --- doTestOSPF : at 10.83.20.70
FLOW -- commiting the configuration at 10.83.20.70
DEBUG --- doCommit at 10.83.20.70
FLOW -- configuration commited at 10.83.20.70
FLOW -- ************************************
FLOW -- checking 10.83.20.71
DEBUG --- getting ssh connection to 10.83.20.71
DEBUG --- ssh cionnection to host 10.83.20.71 established
DEBUG --- connection 10.83.20.71 named r4 established
DEBUG --- doTestOSPF : at 10.83.20.71
DEBUG --- doTestOSPF found missing line set protocols ospf area 0.0.0.250 interface ge-0/0/1.0 secondary
DEBUG --- doTestOSPF found missing line set protocols ospf area 0.0.0.250 interface ge-0/0/1.0 interface-type p2p
DEBUG --- doTestOSPF found missing line set protocols ospf area 0.0.0.250 interface ge-0/0/1.0 metric 1
DEBUG --- doTestOSPF found missing line set protocols ospf area 0.0.0.250 interface ge-0/0/2.0 secondary
DEBUG --- doTestOSPF found missing line set protocols ospf area 0.0.0.250 interface ge-0/0/2.0 interface-type p2p
DEBUG --- doTestOSPF found missing line set protocols ospf area 0.0.0.250 interface ge-0/0/2.0 metric 1
DEBUG --- doTestOSPF found missing line set protocols ospf area 0.0.0.250 interface ge-0/0/3.0 secondary
DEBUG --- doTestOSPF found missing line set protocols ospf area 0.0.0.250 interface ge-0/0/3.0 interface-type p2p
DEBUG --- doTestOSPF found missing line set protocols ospf area 0.0.0.250 interface ge-0/0/3.0 metric 1
FLOW -- conf not exist, doing change
DEBUG --- doJob at 10.83.20.71
DEBUG --- doCompare at 10.83.20.71
DEBUG --- starting to do config changes at 10.83.20.71
DEBUG --- doLoad at 10.83.20.71
DEBUG --- commit check at 10.83.20.71
DEBUG --- doCommitCheck at 10.83.20.71
DEBUG --- commiting changes at 10.83.20.71
DEBUG --- doCommit at 10.83.20.71
FLOW -- done job at 10.83.20.71
FLOW -- going sleep at 10.83.20.71
FLOW -- checking job status 10.83.20.71
DEBUG --- getting ssh connection to 10.83.20.71
DEBUG --- ssh cionnection to host 10.83.20.71 established
DEBUG --- connection 10.83.20.71 named r4 established
DEBUG --- doTestOSPF : at 10.83.20.71
FLOW -- commiting the configuration at 10.83.20.71
DEBUG --- doCommit at 10.83.20.71
FLOW -- configuration commited at 10.83.20.71
{'10.83.20.70': {'status': 'done'}, '10.83.20.71': {'status': 'done'}, '10.83.20.67': {'status': 'done'}, '10.83.20.66': {'status': 'done'}, '10.83.20.69': {'status': 'done'}, '10.83.20.68': {'status': 'done'}}
>>>
>>>
>>>
==== RESTART: C:\Users\and_andreev\Desktop\tools\lab-case2\conf_change.py ====
FLOW -- ************************************
FLOW -- checking 10.83.20.66
DEBUG --- getting ssh connection to 10.83.20.66
DEBUG --- ssh cionnection to host 10.83.20.66 established
DEBUG --- connection 10.83.20.66 named abr1 established
DEBUG --- doTestOSPF : at 10.83.20.66
DEBUG --- doTestOSPF found missing line set protocols ospf area 0.0.0.200 interface ge-0/0/1.0 secondary
DEBUG --- doTestOSPF found missing line set protocols ospf area 0.0.0.200 interface ge-0/0/1.0 metric 1
FLOW -- conf not exist, doing change
DEBUG --- doJob at 10.83.20.66
DEBUG --- doCompare at 10.83.20.66
DEBUG --- starting to do config changes at 10.83.20.66
DEBUG --- doLoad at 10.83.20.66
DEBUG --- commit check at 10.83.20.66
DEBUG --- doCommitCheck at 10.83.20.66
DEBUG --- commiting changes at 10.83.20.66
DEBUG --- doCommit at 10.83.20.66
FLOW -- done job at 10.83.20.66
FLOW -- going sleep at 10.83.20.66
FLOW -- checking job status 10.83.20.66
DEBUG --- getting ssh connection to 10.83.20.66
DEBUG --- ssh cionnection to host 10.83.20.66 established
DEBUG --- connection 10.83.20.66 named abr1 established
DEBUG --- doTestOSPF : at 10.83.20.66
FLOW -- commiting the configuration at 10.83.20.66
DEBUG --- doCommit at 10.83.20.66
FLOW -- configuration commited at 10.83.20.66
FLOW -- ************************************
FLOW -- checking 10.83.20.67
DEBUG --- getting ssh connection to 10.83.20.67
DEBUG --- ssh cionnection to host 10.83.20.67 established
DEBUG --- connection 10.83.20.67 named abr2 established
DEBUG --- doTestOSPF : at 10.83.20.67
DEBUG --- doTestOSPF found missing line set protocols ospf area 0.0.0.200 interface ge-0/0/1.0 secondary
DEBUG --- doTestOSPF found missing line set protocols ospf area 0.0.0.200 interface ge-0/0/1.0 metric 1
FLOW -- conf not exist, doing change
DEBUG --- doJob at 10.83.20.67
DEBUG --- doCompare at 10.83.20.67
DEBUG --- starting to do config changes at 10.83.20.67
DEBUG --- doLoad at 10.83.20.67
DEBUG --- commit check at 10.83.20.67
DEBUG --- doCommitCheck at 10.83.20.67
DEBUG --- commiting changes at 10.83.20.67
DEBUG --- doCommit at 10.83.20.67
FLOW -- done job at 10.83.20.67
FLOW -- going sleep at 10.83.20.67
FLOW -- checking job status 10.83.20.67
DEBUG --- getting ssh connection to 10.83.20.67
DEBUG --- ssh cionnection to host 10.83.20.67 established
DEBUG --- connection 10.83.20.67 named abr2 established
DEBUG --- doTestOSPF : at 10.83.20.67
FLOW -- commiting the configuration at 10.83.20.67
DEBUG --- doCommit at 10.83.20.67
FLOW -- configuration commited at 10.83.20.67
FLOW -- ************************************
FLOW -- checking 10.83.20.68
DEBUG --- getting ssh connection to 10.83.20.68
DEBUG --- ssh cionnection to host 10.83.20.68 established
DEBUG --- connection 10.83.20.68 named r1 established
DEBUG --- doTestOSPF : at 10.83.20.68
DEBUG --- doTestOSPF found missing line set protocols ospf area 0.0.0.200 interface ge-0/0/1.0 secondary
DEBUG --- doTestOSPF found missing line set protocols ospf area 0.0.0.200 interface ge-0/0/1.0 metric 1
DEBUG --- doTestOSPF found missing line set protocols ospf area 0.0.0.200 interface ge-0/0/2.0 secondary
DEBUG --- doTestOSPF found missing line set protocols ospf area 0.0.0.200 interface ge-0/0/2.0 metric 1
DEBUG --- doTestOSPF found missing line set protocols ospf area 0.0.0.200 interface ge-0/0/3.0 secondary
DEBUG --- doTestOSPF found missing line set protocols ospf area 0.0.0.200 interface ge-0/0/3.0 metric 1
DEBUG --- doTestOSPF found missing line set protocols ospf area 0.0.0.250 interface lo0.0 interface-type p2p
DEBUG --- doTestOSPF found missing line set protocols ospf area 0.0.0.200 interface lo0.0 secondary
FLOW -- conf not exist, doing change
DEBUG --- doJob at 10.83.20.68
DEBUG --- doCompare at 10.83.20.68
DEBUG --- starting to do config changes at 10.83.20.68
DEBUG --- doLoad at 10.83.20.68
DEBUG --- commit check at 10.83.20.68
DEBUG --- doCommitCheck at 10.83.20.68
DEBUG --- commiting changes at 10.83.20.68
DEBUG --- doCommit at 10.83.20.68
FLOW -- done job at 10.83.20.68
FLOW -- going sleep at 10.83.20.68
FLOW -- checking job status 10.83.20.68
DEBUG --- getting ssh connection to 10.83.20.68
DEBUG --- ssh cionnection to host 10.83.20.68 established
DEBUG --- connection 10.83.20.68 named r1 established
DEBUG --- doTestOSPF : at 10.83.20.68
FLOW -- commiting the configuration at 10.83.20.68
DEBUG --- doCommit at 10.83.20.68
FLOW -- configuration commited at 10.83.20.68
FLOW -- ************************************
FLOW -- checking 10.83.20.69
DEBUG --- getting ssh connection to 10.83.20.69
DEBUG --- ssh cionnection to host 10.83.20.69 established
DEBUG --- connection 10.83.20.69 named r2 established
DEBUG --- doTestOSPF : at 10.83.20.69
DEBUG --- doTestOSPF found missing line set protocols ospf area 0.0.0.200 interface ge-0/0/0.0 secondary
DEBUG --- doTestOSPF found missing line set protocols ospf area 0.0.0.200 interface ge-0/0/0.0 metric 1
DEBUG --- doTestOSPF found missing line set protocols ospf area 0.0.0.200 interface ge-0/0/3.0 secondary
DEBUG --- doTestOSPF found missing line set protocols ospf area 0.0.0.200 interface ge-0/0/3.0 metric 1
DEBUG --- doTestOSPF found missing line set protocols ospf area 0.0.0.250 interface lo0.0 interface-type p2p
DEBUG --- doTestOSPF found missing line set protocols ospf area 0.0.0.200 interface lo0.0 secondary
FLOW -- conf not exist, doing change
DEBUG --- doJob at 10.83.20.69
DEBUG --- doCompare at 10.83.20.69
DEBUG --- starting to do config changes at 10.83.20.69
DEBUG --- doLoad at 10.83.20.69
DEBUG --- commit check at 10.83.20.69
DEBUG --- doCommitCheck at 10.83.20.69
DEBUG --- commiting changes at 10.83.20.69
DEBUG --- doCommit at 10.83.20.69
FLOW -- done job at 10.83.20.69
FLOW -- going sleep at 10.83.20.69
FLOW -- checking job status 10.83.20.69
DEBUG --- getting ssh connection to 10.83.20.69
DEBUG --- ssh cionnection to host 10.83.20.69 established
DEBUG --- connection 10.83.20.69 named r2 established
DEBUG --- doTestOSPF : at 10.83.20.69
FLOW -- commiting the configuration at 10.83.20.69
DEBUG --- doCommit at 10.83.20.69
FLOW -- configuration commited at 10.83.20.69
FLOW -- ************************************
FLOW -- checking 10.83.20.70
DEBUG --- getting ssh connection to 10.83.20.70
DEBUG --- ssh cionnection to host 10.83.20.70 established
DEBUG --- connection 10.83.20.70 named r3 established
DEBUG --- doTestOSPF : at 10.83.20.70
DEBUG --- doTestOSPF found missing line set protocols ospf area 0.0.0.200 interface ge-0/0/0.0 secondary
DEBUG --- doTestOSPF found missing line set protocols ospf area 0.0.0.200 interface ge-0/0/0.0 metric 1
DEBUG --- doTestOSPF found missing line set protocols ospf area 0.0.0.200 interface ge-0/0/3.0 secondary
DEBUG --- doTestOSPF found missing line set protocols ospf area 0.0.0.200 interface ge-0/0/3.0 metric 1
DEBUG --- doTestOSPF found missing line set protocols ospf area 0.0.0.250 interface lo0.0 interface-type p2p
DEBUG --- doTestOSPF found missing line set protocols ospf area 0.0.0.200 interface lo0.0 secondary
FLOW -- conf not exist, doing change
DEBUG --- doJob at 10.83.20.70
DEBUG --- doCompare at 10.83.20.70
DEBUG --- starting to do config changes at 10.83.20.70
DEBUG --- doLoad at 10.83.20.70
DEBUG --- commit check at 10.83.20.70
DEBUG --- doCommitCheck at 10.83.20.70
DEBUG --- commiting changes at 10.83.20.70
DEBUG --- doCommit at 10.83.20.70
FLOW -- done job at 10.83.20.70
FLOW -- going sleep at 10.83.20.70
FLOW -- checking job status 10.83.20.70
DEBUG --- getting ssh connection to 10.83.20.70
DEBUG --- ssh cionnection to host 10.83.20.70 established
DEBUG --- connection 10.83.20.70 named r3 established
DEBUG --- doTestOSPF : at 10.83.20.70
FLOW -- commiting the configuration at 10.83.20.70
DEBUG --- doCommit at 10.83.20.70
FLOW -- configuration commited at 10.83.20.70
FLOW -- ************************************
FLOW -- checking 10.83.20.71
DEBUG --- getting ssh connection to 10.83.20.71
DEBUG --- ssh cionnection to host 10.83.20.71 established
DEBUG --- connection 10.83.20.71 named r4 established
DEBUG --- doTestOSPF : at 10.83.20.71
DEBUG --- doTestOSPF found missing line set protocols ospf area 0.0.0.200 interface ge-0/0/1.0 secondary
DEBUG --- doTestOSPF found missing line set protocols ospf area 0.0.0.200 interface ge-0/0/1.0 metric 1
DEBUG --- doTestOSPF found missing line set protocols ospf area 0.0.0.200 interface ge-0/0/2.0 secondary
DEBUG --- doTestOSPF found missing line set protocols ospf area 0.0.0.200 interface ge-0/0/2.0 metric 1
DEBUG --- doTestOSPF found missing line set protocols ospf area 0.0.0.200 interface ge-0/0/3.0 secondary
DEBUG --- doTestOSPF found missing line set protocols ospf area 0.0.0.200 interface ge-0/0/3.0 metric 1
DEBUG --- doTestOSPF found missing line set protocols ospf area 0.0.0.250 interface lo0.0 interface-type p2p
DEBUG --- doTestOSPF found missing line set protocols ospf area 0.0.0.200 interface lo0.0 secondary
FLOW -- conf not exist, doing change
DEBUG --- doJob at 10.83.20.71
DEBUG --- doCompare at 10.83.20.71
DEBUG --- starting to do config changes at 10.83.20.71
DEBUG --- doLoad at 10.83.20.71
DEBUG --- commit check at 10.83.20.71
DEBUG --- doCommitCheck at 10.83.20.71
DEBUG --- commiting changes at 10.83.20.71
DEBUG --- doCommit at 10.83.20.71
FLOW -- done job at 10.83.20.71
FLOW -- going sleep at 10.83.20.71
FLOW -- checking job status 10.83.20.71
DEBUG --- getting ssh connection to 10.83.20.71
DEBUG --- ssh cionnection to host 10.83.20.71 established
DEBUG --- connection 10.83.20.71 named r4 established
DEBUG --- doTestOSPF : at 10.83.20.71
FLOW -- commiting the configuration at 10.83.20.71
DEBUG --- doCommit at 10.83.20.71
FLOW -- configuration commited at 10.83.20.71
{'10.83.20.70': {'status': 'done'}, '10.83.20.71': {'status': 'done'}, '10.83.20.67': {'status': 'done'}, '10.83.20.66': {'status': 'done'}, '10.83.20.69': {'status': 'done'}, '10.83.20.68': {'status': 'done'}}
>>>
==== RESTART: C:\Users\and_andreev\Desktop\tools\lab-case2\conf_change.py ====
FLOW -- ************************************
FLOW -- checking 10.83.20.66
DEBUG --- getting ssh connection to 10.83.20.66
DEBUG --- ssh cionnection to host 10.83.20.66 established
DEBUG --- connection 10.83.20.66 named abr1 established
DEBUG --- doTestOSPF : at 10.83.20.66
FLOW -- conf not exist, doing change
DEBUG --- doJob at 10.83.20.66
DEBUG --- doCompare at 10.83.20.66
DEBUG --- starting to do config changes at 10.83.20.66
DEBUG --- doLoad at 10.83.20.66
DEBUG --- commit check at 10.83.20.66
DEBUG --- doCommitCheck at 10.83.20.66
DEBUG --- commiting changes at 10.83.20.66
DEBUG --- doCommit at 10.83.20.66
FLOW -- done job at 10.83.20.66
FLOW -- going sleep at 10.83.20.66
FLOW -- checking job status 10.83.20.66
DEBUG --- getting ssh connection to 10.83.20.66
DEBUG --- ssh cionnection to host 10.83.20.66 established
DEBUG --- connection 10.83.20.66 named abr1 established
DEBUG --- doTestOSPF : at 10.83.20.66
FLOW -- commiting the configuration at 10.83.20.66
DEBUG --- doCommit at 10.83.20.66
FLOW -- configuration commited at 10.83.20.66
FLOW -- ************************************
FLOW -- checking 10.83.20.67
DEBUG --- getting ssh connection to 10.83.20.67
DEBUG --- ssh cionnection to host 10.83.20.67 established
DEBUG --- connection 10.83.20.67 named abr2 established
DEBUG --- doTestOSPF : at 10.83.20.67
FLOW -- conf not exist, doing change
DEBUG --- doJob at 10.83.20.67
DEBUG --- doCompare at 10.83.20.67
DEBUG --- starting to do config changes at 10.83.20.67
DEBUG --- doLoad at 10.83.20.67
DEBUG --- commit check at 10.83.20.67
DEBUG --- doCommitCheck at 10.83.20.67
DEBUG --- commiting changes at 10.83.20.67
DEBUG --- doCommit at 10.83.20.67
FLOW -- done job at 10.83.20.67
FLOW -- going sleep at 10.83.20.67
FLOW -- checking job status 10.83.20.67
DEBUG --- getting ssh connection to 10.83.20.67
DEBUG --- ssh cionnection to host 10.83.20.67 established
DEBUG --- connection 10.83.20.67 named abr2 established
DEBUG --- doTestOSPF : at 10.83.20.67
FLOW -- commiting the configuration at 10.83.20.67
DEBUG --- doCommit at 10.83.20.67
FLOW -- configuration commited at 10.83.20.67
FLOW -- ************************************
FLOW -- checking 10.83.20.68
DEBUG --- getting ssh connection to 10.83.20.68
DEBUG --- ssh cionnection to host 10.83.20.68 established
DEBUG --- connection 10.83.20.68 named r1 established
DEBUG --- doTestOSPF : at 10.83.20.68
FLOW -- conf not exist, doing change
DEBUG --- doJob at 10.83.20.68
DEBUG --- doCompare at 10.83.20.68
DEBUG --- starting to do config changes at 10.83.20.68
DEBUG --- doLoad at 10.83.20.68
DEBUG --- commit check at 10.83.20.68
DEBUG --- doCommitCheck at 10.83.20.68
DEBUG --- commiting changes at 10.83.20.68
DEBUG --- doCommit at 10.83.20.68
FLOW -- done job at 10.83.20.68
FLOW -- going sleep at 10.83.20.68
FLOW -- checking job status 10.83.20.68
DEBUG --- getting ssh connection to 10.83.20.68
DEBUG --- ssh cionnection to host 10.83.20.68 established
DEBUG --- connection 10.83.20.68 named r1 established
DEBUG --- doTestOSPF : at 10.83.20.68
FLOW -- commiting the configuration at 10.83.20.68
DEBUG --- doCommit at 10.83.20.68
FLOW -- configuration commited at 10.83.20.68
FLOW -- ************************************
FLOW -- checking 10.83.20.69
DEBUG --- getting ssh connection to 10.83.20.69
DEBUG --- ssh cionnection to host 10.83.20.69 established
DEBUG --- connection 10.83.20.69 named r2 established
DEBUG --- doTestOSPF : at 10.83.20.69
FLOW -- conf not exist, doing change
DEBUG --- doJob at 10.83.20.69
DEBUG --- doCompare at 10.83.20.69
DEBUG --- starting to do config changes at 10.83.20.69
DEBUG --- doLoad at 10.83.20.69
DEBUG --- commit check at 10.83.20.69
DEBUG --- doCommitCheck at 10.83.20.69
DEBUG --- commiting changes at 10.83.20.69
DEBUG --- doCommit at 10.83.20.69
FLOW -- done job at 10.83.20.69
FLOW -- going sleep at 10.83.20.69
FLOW -- checking job status 10.83.20.69
DEBUG --- getting ssh connection to 10.83.20.69
DEBUG --- ssh cionnection to host 10.83.20.69 established
DEBUG --- connection 10.83.20.69 named r2 established
DEBUG --- doTestOSPF : at 10.83.20.69
FLOW -- commiting the configuration at 10.83.20.69
DEBUG --- doCommit at 10.83.20.69
FLOW -- configuration commited at 10.83.20.69
FLOW -- ************************************
FLOW -- checking 10.83.20.70
DEBUG --- getting ssh connection to 10.83.20.70
DEBUG --- ssh cionnection to host 10.83.20.70 established
DEBUG --- connection 10.83.20.70 named r3 established
DEBUG --- doTestOSPF : at 10.83.20.70
FLOW -- conf not exist, doing change
DEBUG --- doJob at 10.83.20.70
DEBUG --- doCompare at 10.83.20.70
DEBUG --- starting to do config changes at 10.83.20.70
DEBUG --- doLoad at 10.83.20.70
DEBUG --- commit check at 10.83.20.70
DEBUG --- doCommitCheck at 10.83.20.70
DEBUG --- commiting changes at 10.83.20.70
DEBUG --- doCommit at 10.83.20.70
FLOW -- done job at 10.83.20.70
FLOW -- going sleep at 10.83.20.70
FLOW -- checking job status 10.83.20.70
DEBUG --- getting ssh connection to 10.83.20.70
DEBUG --- ssh cionnection to host 10.83.20.70 established
DEBUG --- connection 10.83.20.70 named r3 established
DEBUG --- doTestOSPF : at 10.83.20.70
FLOW -- commiting the configuration at 10.83.20.70
DEBUG --- doCommit at 10.83.20.70
FLOW -- configuration commited at 10.83.20.70
FLOW -- ************************************
FLOW -- checking 10.83.20.71
DEBUG --- getting ssh connection to 10.83.20.71
DEBUG --- ssh cionnection to host 10.83.20.71 established
DEBUG --- connection 10.83.20.71 named r4 established
DEBUG --- doTestOSPF : at 10.83.20.71
FLOW -- conf not exist, doing change
DEBUG --- doJob at 10.83.20.71
DEBUG --- doCompare at 10.83.20.71
DEBUG --- starting to do config changes at 10.83.20.71
DEBUG --- doLoad at 10.83.20.71
DEBUG --- commit check at 10.83.20.71
DEBUG --- doCommitCheck at 10.83.20.71
DEBUG --- commiting changes at 10.83.20.71
DEBUG --- doCommit at 10.83.20.71
FLOW -- done job at 10.83.20.71
FLOW -- going sleep at 10.83.20.71
FLOW -- checking job status 10.83.20.71
DEBUG --- getting ssh connection to 10.83.20.71
DEBUG --- ssh cionnection to host 10.83.20.71 established
DEBUG --- connection 10.83.20.71 named r4 established
DEBUG --- doTestOSPF : at 10.83.20.71
FLOW -- commiting the configuration at 10.83.20.71
DEBUG --- doCommit at 10.83.20.71
FLOW -- configuration commited at 10.83.20.71
{'10.83.20.70': {'status': 'done'}, '10.83.20.71': {'status': 'done'}, '10.83.20.67': {'status': 'done'}, '10.83.20.66': {'status': 'done'}, '10.83.20.69': {'status': 'done'}, '10.83.20.68': {'status': 'done'}}
>>>
- Das vollständige IS-IS-Routing-Protokoll - Hannes Gredler, Walter Goralski
- OSPF Anatomie eines Internet-Routing-Protokolls - John T. Moy
- Netzwerkfusionen und -migrationen: Junos Design und Implementierung - Gonzalo Gomez Herrero, Jan Anton Bernal Van Der Ven
- OSPF Multi-Area Adjacency - tools.ietf.org/html/rfc5185