LINQ hat .NET als leistungsstarke neue Datenbearbeitungssprache eingeführt. Mit LINQ to SQL als Teil davon können Sie bequem mit dem DBMS kommunizieren, beispielsweise über das Entity Framework. Entwickler vergessen jedoch häufig, zu prüfen, welche bestimmte SQL-Abfrage der abfragbare Anbieter in Ihrem Fall das Entity Framework generiert.
Lassen Sie uns zwei Hauptpunkte anhand eines Beispiels analysieren.
Erstellen Sie dazu die Testdatenbank in SQL Server und erstellen Sie mit der folgenden Abfrage zwei Tabellen darin:
Erstellen Sie TabellenUSE [TEST]
GO
SET ANSI_NULLS ON
GO
SET QUOTED_IDENTIFIER ON
GO
CREATE TABLE [dbo].[Ref](
[ID] [int] NOT NULL,
[ID2] [int] NOT NULL,
[Name] [nvarchar](255) NOT NULL,
[InsertUTCDate] [datetime] NOT NULL,
CONSTRAINT [PK_Ref] PRIMARY KEY CLUSTERED
(
[ID] ASC
)WITH (PAD_INDEX = OFF, STATISTICS_NORECOMPUTE = OFF, IGNORE_DUP_KEY = OFF, ALLOW_ROW_LOCKS = ON, ALLOW_PAGE_LOCKS = ON) ON [PRIMARY]
) ON [PRIMARY]
GO
ALTER TABLE [dbo].[Ref] ADD CONSTRAINT [DF_Ref_InsertUTCDate] DEFAULT (getutcdate()) FOR [InsertUTCDate]
GO
USE [TEST]
GO
SET ANSI_NULLS ON
GO
SET QUOTED_IDENTIFIER ON
GO
CREATE TABLE [dbo].[Customer](
[ID] [int] NOT NULL,
[Name] [nvarchar](255) NOT NULL,
[Ref_ID] [int] NOT NULL,
[InsertUTCDate] [datetime] NOT NULL,
[Ref_ID2] [int] NOT NULL,
CONSTRAINT [PK_Customer] PRIMARY KEY CLUSTERED
(
[ID] ASC
)WITH (PAD_INDEX = OFF, STATISTICS_NORECOMPUTE = OFF, IGNORE_DUP_KEY = OFF, ALLOW_ROW_LOCKS = ON, ALLOW_PAGE_LOCKS = ON) ON [PRIMARY]
) ON [PRIMARY]
GO
ALTER TABLE [dbo].[Customer] ADD CONSTRAINT [DF_Customer_Ref_ID] DEFAULT ((0)) FOR [Ref_ID]
GO
ALTER TABLE [dbo].[Customer] ADD CONSTRAINT [DF_Customer_InsertUTCDate] DEFAULT (getutcdate()) FOR [InsertUTCDate]
GO
Ref :
RefUSE [TEST]
GO
DECLARE @ind INT=1;
WHILE(@ind<1200000)
BEGIN
INSERT INTO [dbo].[Ref]
([ID]
,[ID2]
,[Name])
SELECT
@ind
,@ind
,CAST(@ind AS NVARCHAR(255));
SET @ind=@ind+1;
END
GO
Customer :
CustomerUSE [TEST]
GO
DECLARE @ind INT=1;
DECLARE @ind_ref INT=1;
WHILE(@ind<=12000000)
BEGIN
IF(@ind%3=0) SET @ind_ref=1;
ELSE IF (@ind%5=0) SET @ind_ref=2;
ELSE IF (@ind%7=0) SET @ind_ref=3;
ELSE IF (@ind%11=0) SET @ind_ref=4;
ELSE IF (@ind%13=0) SET @ind_ref=5;
ELSE IF (@ind%17=0) SET @ind_ref=6;
ELSE IF (@ind%19=0) SET @ind_ref=7;
ELSE IF (@ind%23=0) SET @ind_ref=8;
ELSE IF (@ind%29=0) SET @ind_ref=9;
ELSE IF (@ind%31=0) SET @ind_ref=10;
ELSE IF (@ind%37=0) SET @ind_ref=11;
ELSE SET @ind_ref=@ind%1190000;
INSERT INTO [dbo].[Customer]
([ID]
,[Name]
,[Ref_ID]
,[Ref_ID2])
SELECT
@ind,
CAST(@ind AS NVARCHAR(255)),
@ind_ref,
@ind_ref;
SET @ind=@ind+1;
END
GO
, 1 , - 10 .
Visual Studio Visual C# Console App (.NET Framework):
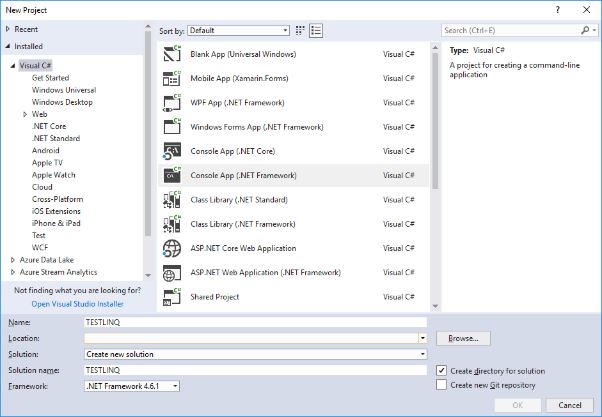
, Entity Framework.
, Manage NuGet Packages:
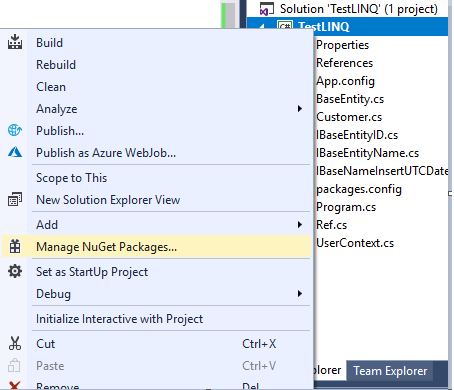
NuGet- «Entity Framework» Entity Framework :

App.config configSections :
<connectionStrings>
<add name="DBConnection" connectionString="data source=__MSSQL;Initial Catalog=TEST;Integrated Security=True;" providerName="System.Data.SqlClient" />
</connectionStrings>
connectionString .
3 :
IBaseEntityIDnamespace TestLINQ
{
public interface IBaseEntityID
{
int ID { get; set; }
}
}
IBaseEntityNamenamespace TestLINQ
{
public interface IBaseEntityName
{
string Name { get; set; }
}
}
IBaseNameInsertUTCDatenamespace TestLINQ
{
public interface IBaseNameInsertUTCDate
{
DateTime InsertUTCDate { get; set; }
}
}
BaseEntity , :
BaseEntitynamespace TestLINQ
{
public class BaseEntity : IBaseEntityID, IBaseEntityName, IBaseNameInsertUTCDate
{
public int ID { get; set; }
public string Name { get; set; }
public DateTime InsertUTCDate { get; set; }
}
}
:
Refusing System.ComponentModel.DataAnnotations.Schema;
namespace TestLINQ
{
[Table("Ref")]
public class Ref : BaseEntity
{
public int ID2 { get; set; }
}
}
Customerusing System.ComponentModel.DataAnnotations.Schema;
namespace TestLINQ
{
[Table("Customer")]
public class Customer: BaseEntity
{
public int Ref_ID { get; set; }
public int Ref_ID2 { get; set; }
}
}
UserContext:
UserContexusing System.Data.Entity;
namespace TestLINQ
{
public class UserContext : DbContext
{
public UserContext()
: base("DbConnection")
{
Database.SetInitializer<UserContext>(null);
}
public DbSet<Customer> Customer { get; set; }
public DbSet<Ref> Ref { get; set; }
}
}
LINQ to SQL EF MS SQL Server:
Program.cs :
Program.csusing System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
namespace TestLINQ
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
using (UserContext db = new UserContext())
{
var dblog = new List<string>();
db.Database.Log = dblog.Add;
var query = from e1 in db.Customer
from e2 in db.Ref
where (e1.Ref_ID == e2.ID)
&& (e1.Ref_ID2 == e2.ID2)
select new { Data1 = e1.Name, Data2 = e2.Name };
var result = query.Take(1000).ToList();
Console.WriteLine(dblog[1]);
Console.ReadKey();
}
}
}
}
.
:
SQL-SELECT TOP (1000)
[Extent1].[Ref_ID] AS [Ref_ID],
[Extent1].[Name] AS [Name],
[Extent2].[Name] AS [Name1]
FROM [dbo].[Customer] AS [Extent1]
INNER JOIN [dbo].[Ref] AS [Extent2] ON ([Extent1].[Ref_ID] = [Extent2].[ID]) AND ([Extent1].[Ref_ID2] = [Extent2].[ID2])
. . LINQ- SQL- MS SQL Server.
LINQ-:
LINQ-var query = from e1 in db.Customer
from e2 in db.Ref
where (e1.Ref_ID == e2.ID)
|| (e1.Ref_ID2 == e2.ID2)
select new { Data1 = e1.Name, Data2 = e2.Name };
.
, 30 :
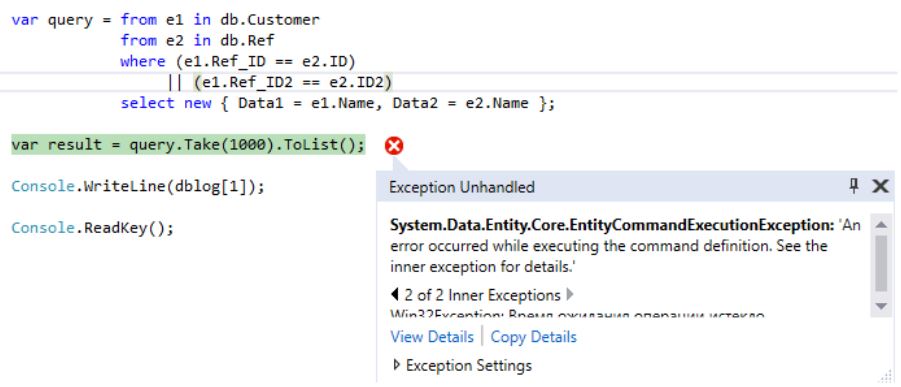
LINQ:
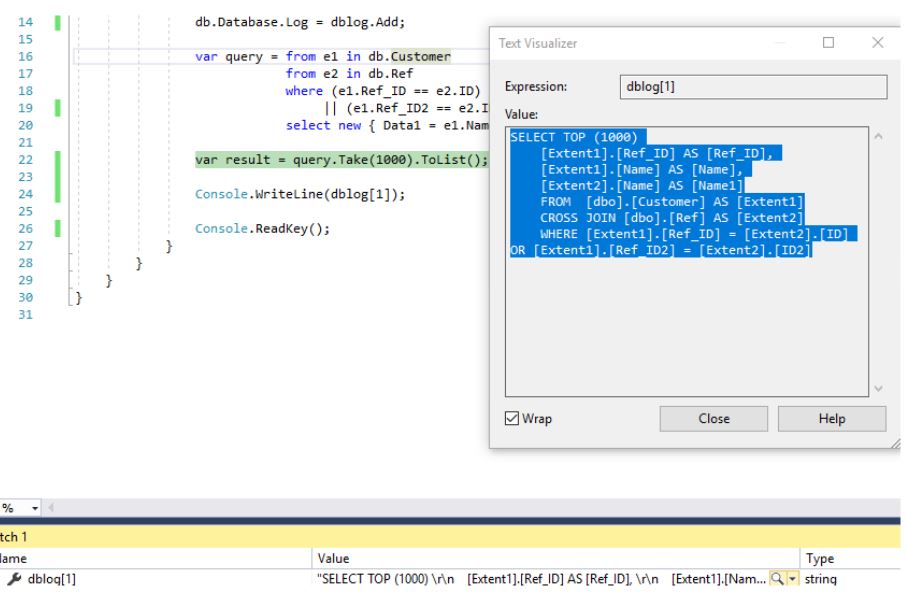
, , ():
SQL-SELECT TOP (1000)
[Extent1].[Ref_ID] AS [Ref_ID],
[Extent1].[Name] AS [Name],
[Extent2].[Name] AS [Name1]
FROM [dbo].[Customer] AS [Extent1]
CROSS JOIN [dbo].[Ref] AS [Extent2]
WHERE [Extent1].[Ref_ID] = [Extent2].[ID] OR [Extent1].[Ref_ID2] = [Extent2].[ID2]
LINQ- :
LINQ-var query = (from e1 in db.Customer
join e2 in db.Ref
on e1.Ref_ID equals e2.ID
select new { Data1 = e1.Name, Data2 = e2.Name }).Union(
from e1 in db.Customer
join e2 in db.Ref
on e1.Ref_ID2 equals e2.ID2
select new { Data1 = e1.Name, Data2 = e2.Name });
SQL-:
SQL-SELECT
[Limit1].[C1] AS [C1],
[Limit1].[C2] AS [C2],
[Limit1].[C3] AS [C3]
FROM ( SELECT DISTINCT TOP (1000)
[UnionAll1].[C1] AS [C1],
[UnionAll1].[Name] AS [C2],
[UnionAll1].[Name1] AS [C3]
FROM (SELECT
1 AS [C1],
[Extent1].[Name] AS [Name],
[Extent2].[Name] AS [Name1]
FROM [dbo].[Customer] AS [Extent1]
INNER JOIN [dbo].[Ref] AS [Extent2] ON [Extent1].[Ref_ID] = [Extent2].[ID]
UNION ALL
SELECT
1 AS [C1],
[Extent3].[Name] AS [Name],
[Extent4].[Name] AS [Name1]
FROM [dbo].[Customer] AS [Extent3]
INNER JOIN [dbo].[Ref] AS [Extent4] ON [Extent3].[Ref_ID2] = [Extent4].[ID2]) AS [UnionAll1]
) AS [Limit1]
, LINQ- , Union .
, , . , .
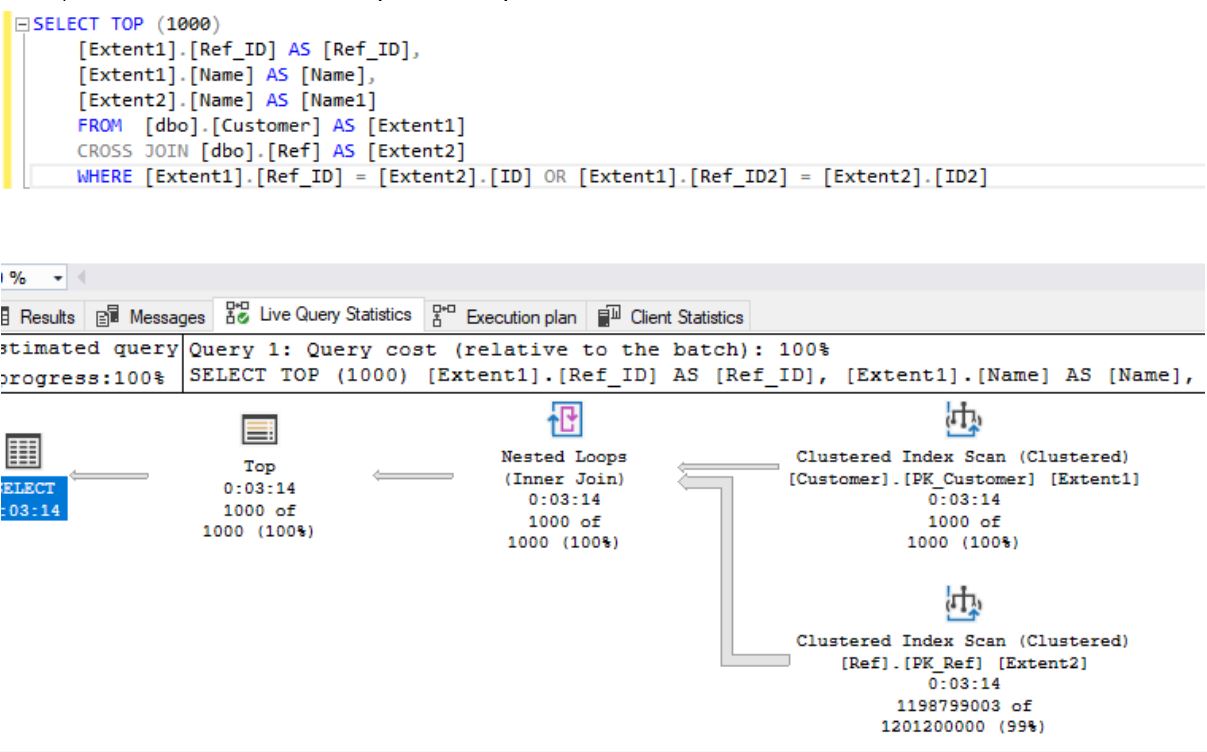
:
- CROSS JOIN 195 :
- INNER JOIN-UNION 24 :
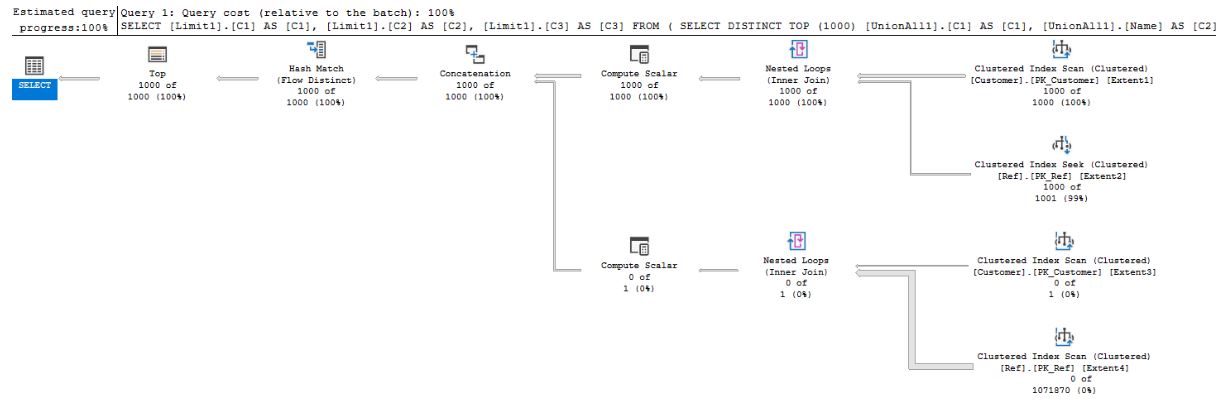
.
Plans .