Decidí vacaciones para estudiar el desarrollo de Vive en Unity3D. Busqué en Google un par de ejemplos y comencé a intentarlo, pero por alguna razón no funcionó. Después de comenzar a comprender con más detalle y descubrir que Valve lanzó recientemente una actualización de complemento para Unity3D, una nueva versión muy rediseñada. Aparecieron un par de innovaciones fundamentales que hicieron que los antiguos tutoriales no fueran relevantes. Decidí escribir uno nuevo

Necesitaremos Unity> = 5.4.0 y el nuevo complemento SteamVR Plugin ( GitHub )
En el complemento en sí hay tres archivos PDF útiles para familiarizarse.
\ Assets \ SteamVR \ SteamVR Unity Plugin.pdf
\ Assets \ SteamVR \ SteamVR Unity Plugin - Input System.pdf
\ Assets \ SteamVR \ InteractionSystem \ InteractionSystem.pdf
Y dos ejemplos:
\ Assets \ SteamVR \ Simple Sample.unity
\ Assets \ SteamVR \ InteractionSystem \ Samples \ Interactions_Example.unity
El complemento admite el modo de simulación: se enciende si el casco no está encendido
Bueno, ahora paso a paso;
Cree un nuevo proyecto de plantilla 3D con el complemento SteamVR Plugin
Estamos de acuerdo con la configuración

Ahora el punto clave es que necesita configurar la administración. Seleccione el elemento de menú Window \ SteamVR Imput

Unity preguntará acerca de las acciones faltantes. Json y ofrecerá copiar el archivo de ejemplo (se encuentra en \ Assets \ SteamVR \ Input \ ExampleJSON). Le aconsejo que acepte.

Los archivos json muestran que el complemento está diseñado no solo para Vive, sino también para Oculus y Windows MR, así como nuevos controladores de nudillos. Los principales cambios están asociados con esto.
En la ventana que se abre, simplemente haga clic en "Guardar y generar"

Ahora debe agregar el reproductor (reproductor de \ Assets \ SteamVR \ InteractionSystem \ Core \ Prefabs) a la escena y eliminar la cámara principal
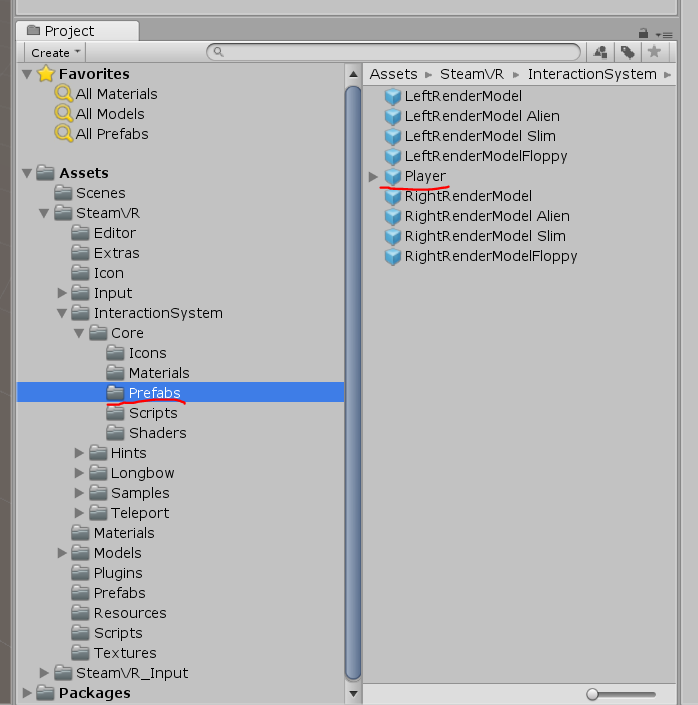
para que funcione el modo de simulación: debe estar habilitado en las propiedades del reproductor
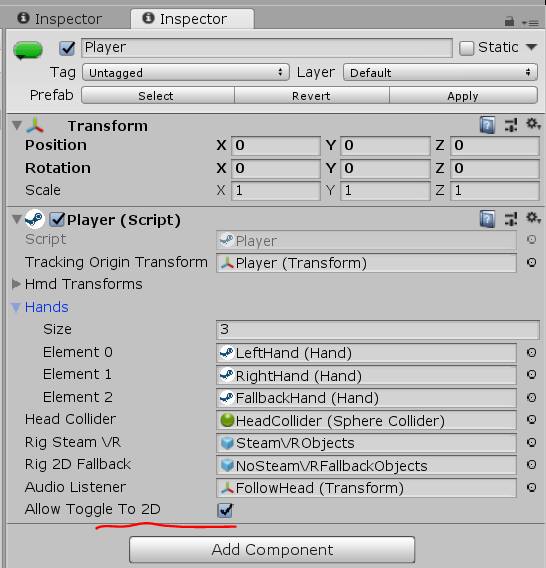
También es útil copiar la carpeta \ Assets \ SteamVR \ InteractionSystem \ Core \ Icons en \ Assets y cambiarle el nombre a Gizmos
Puede hacer clic en Reproducir, pero solo una mano falsa en la simulación no funcionará, debe copiar el script desde aquí y colgarlo en Player-> NoSteamVRFallbackObjects-> FallbackHand
Código de script de mano falsousing System.Collections.Generic; using UnityEngine; using Valve.VR; public class VrSimulatorHandFixer156 : SteamVR_Behaviour_Pose { Valve.VR.InteractionSystem.Hand _hand; protected override void Start() { base.Start(); _hand = this.gameObject.GetComponent<Valve.VR.InteractionSystem.Hand>(); _hand.handType = SteamVR_Input_Sources.RightHand; GameObject broHand = GameObject.Instantiate(_hand.gameObject); Destroy(broHand.GetComponent<VrSimulatorHandFixer156>()); broHand.SetActive(false); _hand.otherHand = broHand.GetComponent<Valve.VR.InteractionSystem.Hand>(); _hand.otherHand.handType = SteamVR_Input_Sources.LeftHand; var spoofMouse = new SpoofMouseAction(); _hand.grabGripAction = spoofMouse; spoofMouse.InitializeDictionariesExposed(_hand.handType); this.poseAction = new Poser_SteamVR_Action_Pose(); } protected override void OnEnable() { } protected override void Update() { _hand.grabGripAction.UpdateValue(SteamVR_Input_Sources.RightHand); } protected override void OnDisable() { } protected override void CheckDeviceIndex() { }
En modo VR con los controladores encendidos, serán visibles
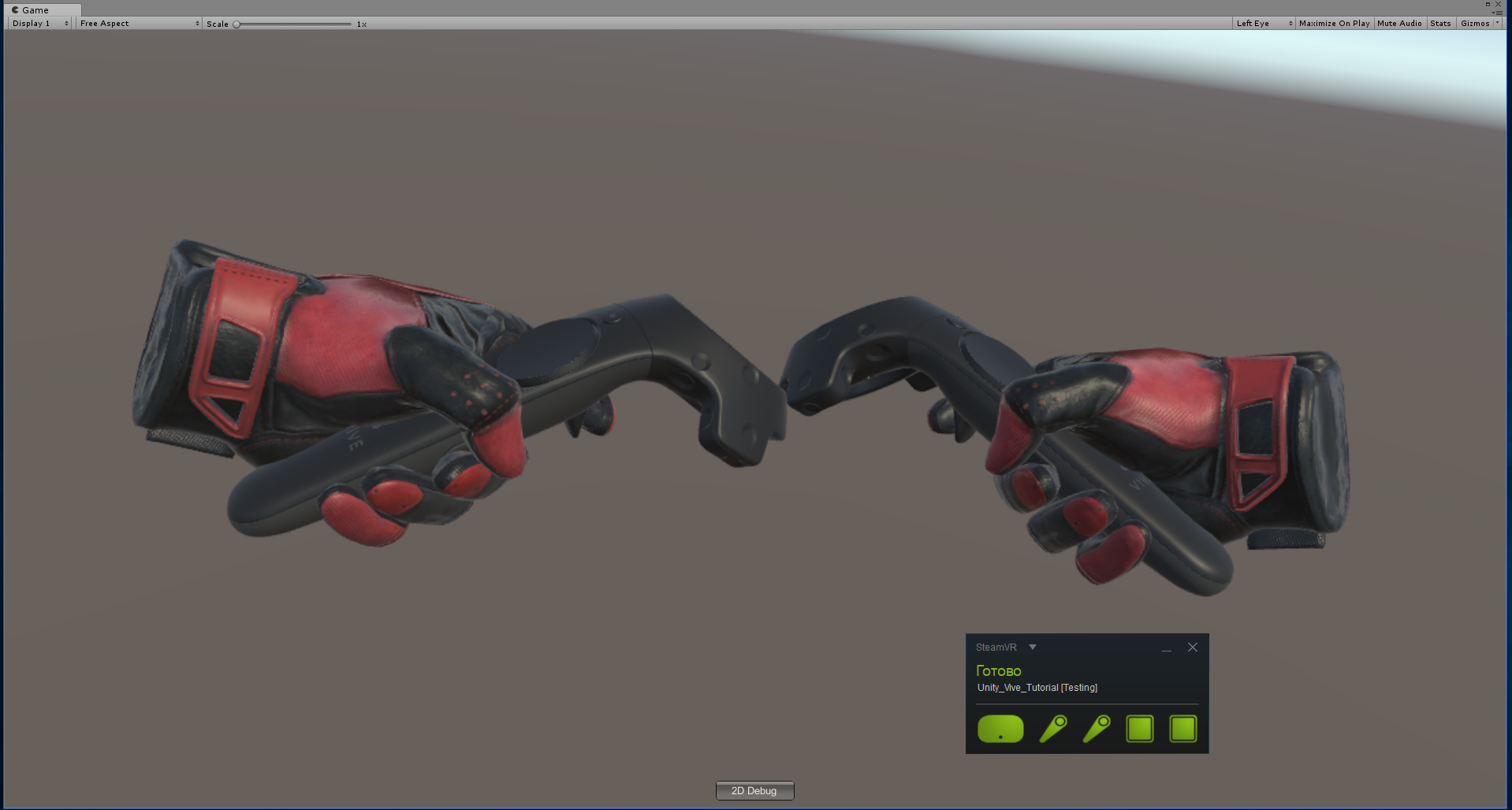
Agregamos VR, pero ni siquiera podemos movernos. El complemento tiene una implementación de teletransportación
para habilitarlo, debe agregar a la escena de Teletransporte desde \ Assets \ SteamVR \ InteractionSystem \ Teleport \ Prefabs
y también organizar TeleportPoint desde allí

También puede teletransportarse en imitación con la tecla T.
Puede crear una superficie de teletransportación: cree un plano y cuelgue el script TeleportArea.cs desde \ Assets \ SteamVR \ InteractionSystem \ Teleport \ Scripts en él

Intentemos interactuar con objetos: cree un cubo y cuelgue el script Interactable.cs de \ Assets \ SteamVR \ InteractionSystem \ Core \ Scripts en él
ahora está resaltado, pero no le pasa nada

Necesitamos registrar la interacción: crearemos un nuevo script para Cube
Código para la interacción using System.Collections; using System.Collections.Generic; using UnityEngine; using Valve.VR.InteractionSystem; public class NewBehaviourScript : MonoBehaviour { private Hand.AttachmentFlags attachmentFlags = Hand.defaultAttachmentFlags & (~Hand.AttachmentFlags.SnapOnAttach) & (~Hand.AttachmentFlags.DetachOthers) & (~Hand.AttachmentFlags.VelocityMovement); private Interactable interactable; // Use this for initialization void Start () { interactable = this.GetComponent<Interactable>(); } private void HandHoverUpdate(Hand hand) { GrabTypes startingGrabType = hand.GetGrabStarting(); bool isGrabEnding = hand.IsGrabEnding(this.gameObject); if (startingGrabType != GrabTypes.None) { // Call this to continue receiving HandHoverUpdate messages, // and prevent the hand from hovering over anything else hand.HoverLock(interactable); // Attach this object to the hand hand.AttachObject(gameObject, startingGrabType, attachmentFlags); } else if (isGrabEnding) { // Detach this object from the hand hand.DetachObject(gameObject); // Call this to undo HoverLock hand.HoverUnlock(interactable); } } }
Se pueden encontrar más detalles sobre la interacción en los ejemplos para el complemento, en particular en \ Assets \ SteamVR \ InteractionSystem \ Samples \ Scripts \ InteractableExample.cs
Y luego intentaremos hacer lo que no está en los ejemplos: agregar nuevas acciones
Abra el script Player.cs y agregue los campos.
[SteamVR_DefaultAction("PlayerMove", "default")] public SteamVR_Action_Vector2 a_move; [SteamVR_DefaultAction("PlayerRotate", "default")] public SteamVR_Action_Vector2 a_rotate; [SteamVR_DefaultAction("MenuClick", "default")] public SteamVR_Action_Boolean a_menu;
Los tipos de devolución válidos se pueden encontrar en \ Assets \ SteamVR \ Input
Y el método de actualización:
private void Update() { bool st = a_menu.GetStateDown(SteamVR_Input_Sources.Any); if (st) { this.transform.position = new Vector3(0, 0, 0); } else { Camera camera = this.GetComponentInChildren<Camera>(); Quaternion cr = Quaternion.Euler(0, 0, 0); if (camera != null) { Vector2 r = a_rotate.GetAxis(SteamVR_Input_Sources.RightHand); Quaternion qp = this.transform.rotation; qp.eulerAngles += new Vector3(0, rx, 0); this.transform.rotation = qp; cr = camera.transform.rotation; } Vector2 m = a_move.GetAxis(SteamVR_Input_Sources.LeftHand); m = Quaternion.Euler(0, 0, -cr.eulerAngles.y) * m; this.transform.position += new Vector3(mx / 10, 0, my / 10); } }
Código Player.cs completo //======= Copyright (c) Valve Corporation, All rights reserved. =============== // // Purpose: Player interface used to query HMD transforms and VR hands // //============================================================================= using UnityEngine; using System.Collections; using System.Collections.Generic; namespace Valve.VR.InteractionSystem { //------------------------------------------------------------------------- // Singleton representing the local VR player/user, with methods for getting // the player's hands, head, tracking origin, and guesses for various properties. //------------------------------------------------------------------------- public class Player : MonoBehaviour { [Tooltip( "Virtual transform corresponding to the meatspace tracking origin. Devices are tracked relative to this." )] public Transform trackingOriginTransform; [Tooltip( "List of possible transforms for the head/HMD, including the no-SteamVR fallback camera." )] public Transform[] hmdTransforms; [Tooltip( "List of possible Hands, including no-SteamVR fallback Hands." )] public Hand[] hands; [Tooltip( "Reference to the physics collider that follows the player's HMD position." )] public Collider headCollider; [Tooltip( "These objects are enabled when SteamVR is available" )] public GameObject rigSteamVR; [Tooltip( "These objects are enabled when SteamVR is not available, or when the user toggles out of VR" )] public GameObject rig2DFallback; [Tooltip( "The audio listener for this player" )] public Transform audioListener; public bool allowToggleTo2D = true; [SteamVR_DefaultAction("PlayerMove", "default")] public SteamVR_Action_Vector2 a_move; [SteamVR_DefaultAction("PlayerRotate", "default")] public SteamVR_Action_Vector2 a_rotate; [SteamVR_DefaultAction("MenuClick", "default")] public SteamVR_Action_Boolean a_menu; //------------------------------------------------- // Singleton instance of the Player. Only one can exist at a time. //------------------------------------------------- private static Player _instance; public static Player instance { get { if ( _instance == null ) { _instance = FindObjectOfType<Player>(); } return _instance; } } //------------------------------------------------- // Get the number of active Hands. //------------------------------------------------- public int handCount { get { int count = 0; for ( int i = 0; i < hands.Length; i++ ) { if ( hands[i].gameObject.activeInHierarchy ) { count++; } } return count; } } //------------------------------------------------- // Get the i-th active Hand. // // i - Zero-based index of the active Hand to get //------------------------------------------------- public Hand GetHand( int i ) { for ( int j = 0; j < hands.Length; j++ ) { if ( !hands[j].gameObject.activeInHierarchy ) { continue; } if ( i > 0 ) { i--; continue; } return hands[j]; } return null; } //------------------------------------------------- public Hand leftHand { get { for ( int j = 0; j < hands.Length; j++ ) { if ( !hands[j].gameObject.activeInHierarchy ) { continue; } if ( hands[j].handType != SteamVR_Input_Sources.LeftHand) { continue; } return hands[j]; } return null; } } //------------------------------------------------- public Hand rightHand { get { for ( int j = 0; j < hands.Length; j++ ) { if ( !hands[j].gameObject.activeInHierarchy ) { continue; } if ( hands[j].handType != SteamVR_Input_Sources.RightHand) { continue; } return hands[j]; } return null; } } //------------------------------------------------- // Get Player scale. Assumes it is scaled equally on all axes. //------------------------------------------------- public float scale { get { return transform.lossyScale.x; } } //------------------------------------------------- // Get the HMD transform. This might return the fallback camera transform if SteamVR is unavailable or disabled. //------------------------------------------------- public Transform hmdTransform { get { if (hmdTransforms != null) { for (int i = 0; i < hmdTransforms.Length; i++) { if (hmdTransforms[i].gameObject.activeInHierarchy) return hmdTransforms[i]; } } return null; } } //------------------------------------------------- // Height of the eyes above the ground - useful for estimating player height. //------------------------------------------------- public float eyeHeight { get { Transform hmd = hmdTransform; if ( hmd ) { Vector3 eyeOffset = Vector3.Project( hmd.position - trackingOriginTransform.position, trackingOriginTransform.up ); return eyeOffset.magnitude / trackingOriginTransform.lossyScale.x; } return 0.0f; } } //------------------------------------------------- // Guess for the world-space position of the player's feet, directly beneath the HMD. //------------------------------------------------- public Vector3 feetPositionGuess { get { Transform hmd = hmdTransform; if ( hmd ) { return trackingOriginTransform.position + Vector3.ProjectOnPlane( hmd.position - trackingOriginTransform.position, trackingOriginTransform.up ); } return trackingOriginTransform.position; } } //------------------------------------------------- // Guess for the world-space direction of the player's hips/torso. This is effectively just the gaze direction projected onto the floor plane. //------------------------------------------------- public Vector3 bodyDirectionGuess { get { Transform hmd = hmdTransform; if ( hmd ) { Vector3 direction = Vector3.ProjectOnPlane( hmd.forward, trackingOriginTransform.up ); if ( Vector3.Dot( hmd.up, trackingOriginTransform.up ) < 0.0f ) { // The HMD is upside-down. Either // -The player is bending over backwards // -The player is bent over looking through their legs direction = -direction; } return direction; } return trackingOriginTransform.forward; } } //------------------------------------------------- void Awake() { SteamVR.Initialize(true); //force openvr if ( trackingOriginTransform == null ) { trackingOriginTransform = this.transform; } } //------------------------------------------------- private IEnumerator Start() { _instance = this; while (SteamVR_Behaviour.instance.forcingInitialization) yield return null; if ( SteamVR.instance != null ) { ActivateRig( rigSteamVR ); } else {
Ejecute Window \ SteamVR Imput, cree nuestras acciones en el conjunto predeterminado y guárdelas, ahora seleccione "Abrir interfaz de usuario de enlace" (SteamVR debe estar ejecutándose y al menos un controlador está encendido)
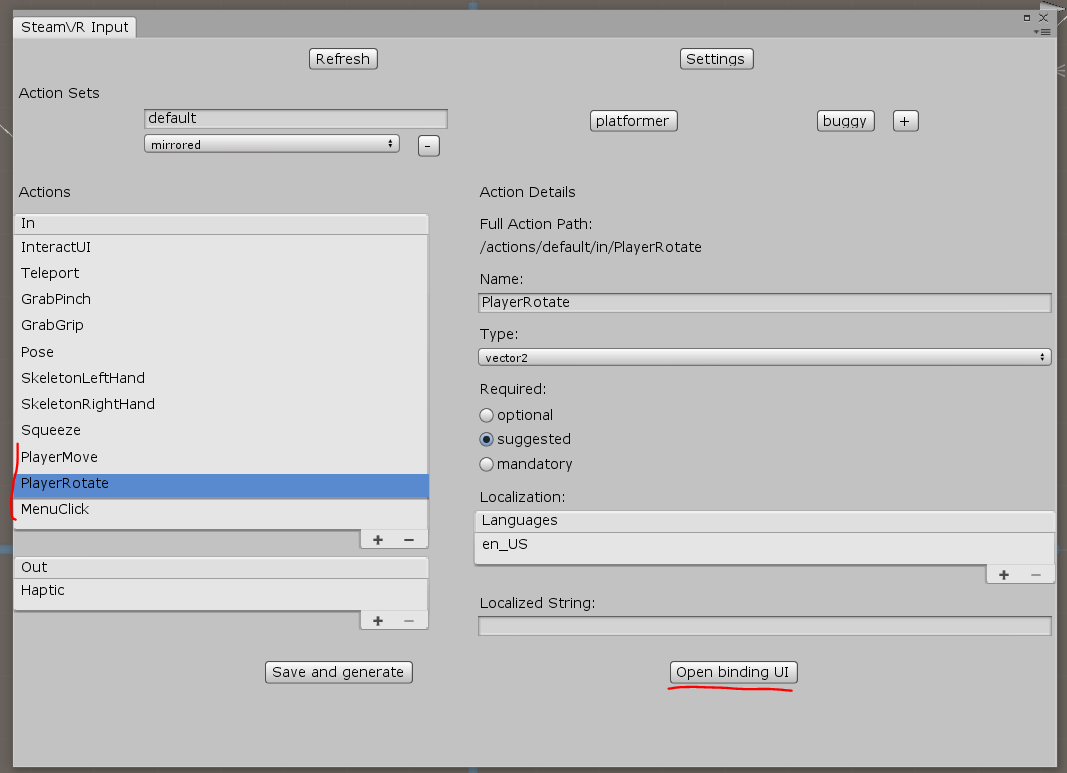
La pestaña Vinculación del controlador se abre en el navegador; en ella debe configurar la conexión de nuestras acciones con los controladores: colgaremos PlayerMove en el TRACKPAD izquierdo (no olvide desactivar el modo espejo), PlayerRotate en el TRACKPAD derecho y cuelgue MenuClick en las teclas de menú
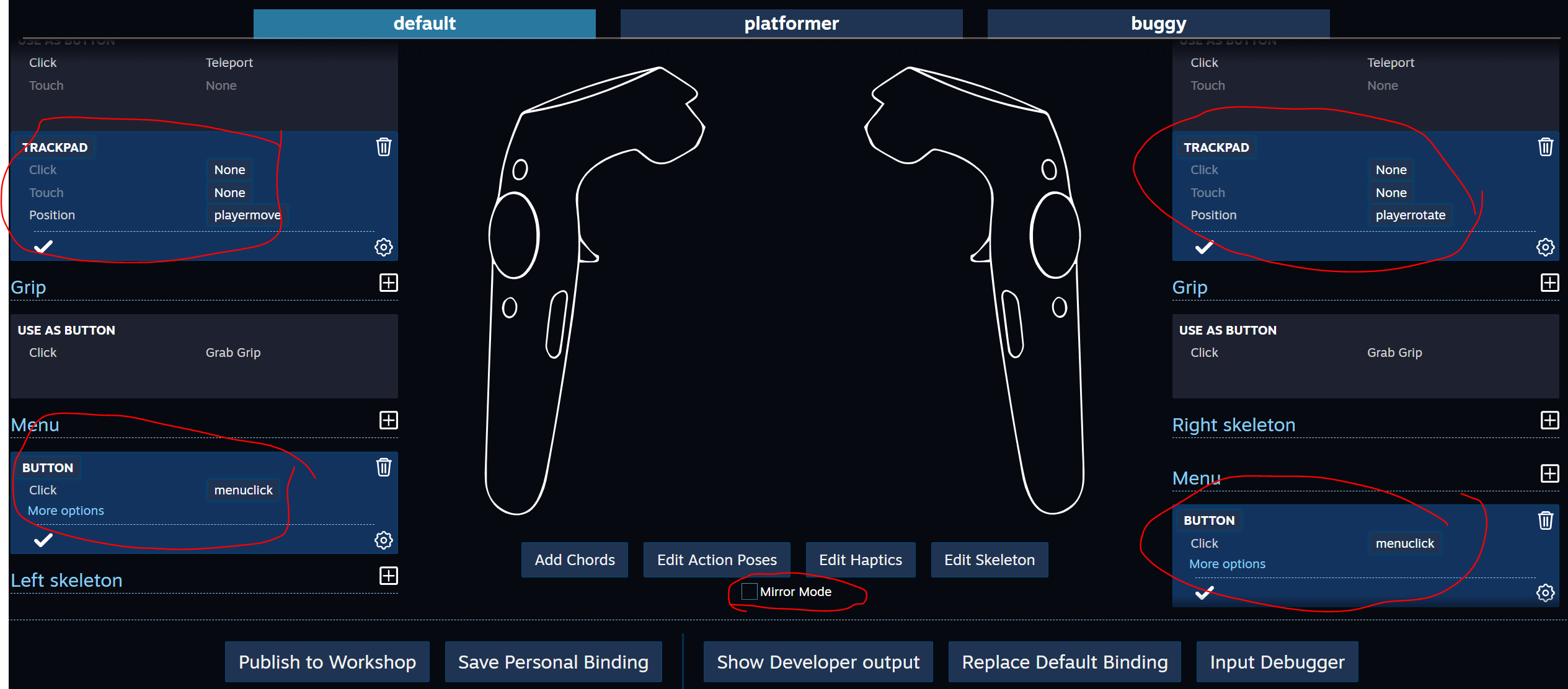
Cierre el enlace del controlador y guarde los cambios.
En las propiedades del jugador conectaremos las nuevas acciones.

Lanzar Play
Proyecto
Conclusión
Algunos puntos deben tenerse en cuenta. Algunas acciones en SteamVR Imput pueden hacer que Unity piense durante mucho tiempo, en principio, puede realizar estos cambios usted mismo en el código y, en lugar de usar Controller Binding, puede editar directamente archivos json, pero existe un gran riesgo de errores que pueden ser difíciles de detectar.
Para un estudio más profundo del complemento, es útil estudiar ejemplos en detalle y, por supuesto, leer la documentación.