Amigos y colegas!Uno de nuestros clientes que compró servidores y blades HP, y ahora compró el HP MSA 2040, recientemente hizo una pregunta:
¿Por qué el servidor ve las lunas presentadas como 4 discos separados del mismo tamaño (sistema operativo Linux)?

La respuesta es simple:
En este caso, la conexión al servidor se realiza a través de 4 canales independientes y cada uno de estos discos es un canal separado.
Para obtener un disco al final, debe usar el servicio de E / S de múltiples rutas para trabajar.
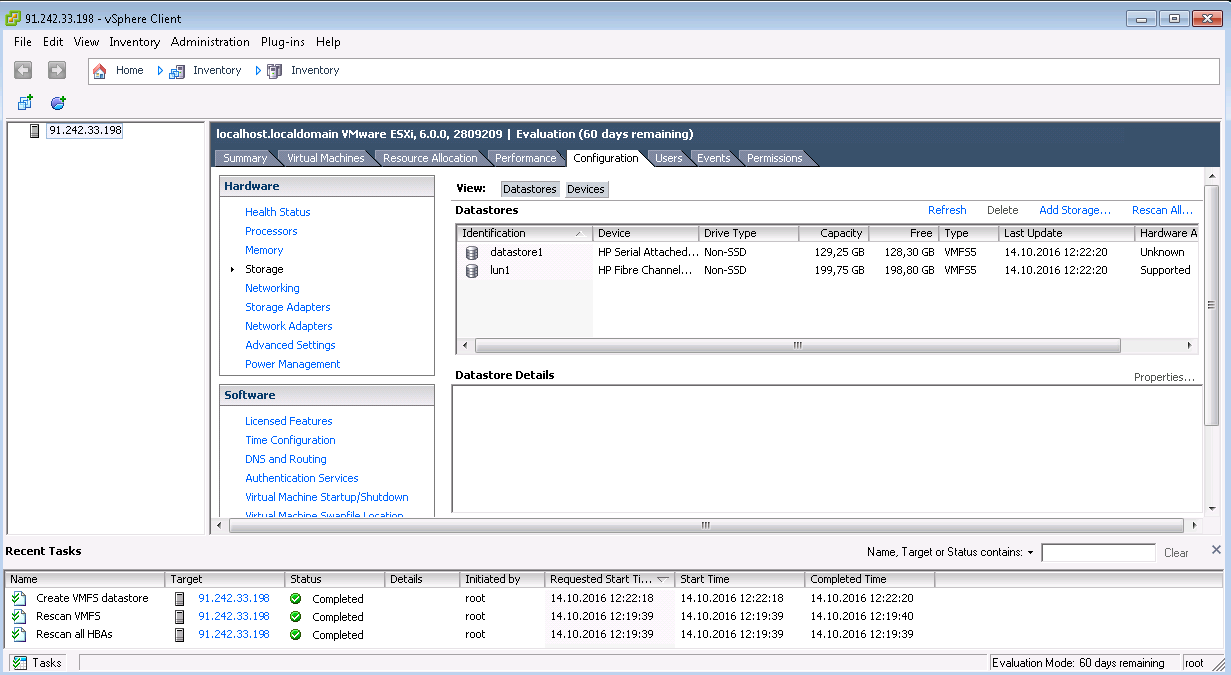
Almacenamiento LUN de múltiples rutas para VMware ESXi
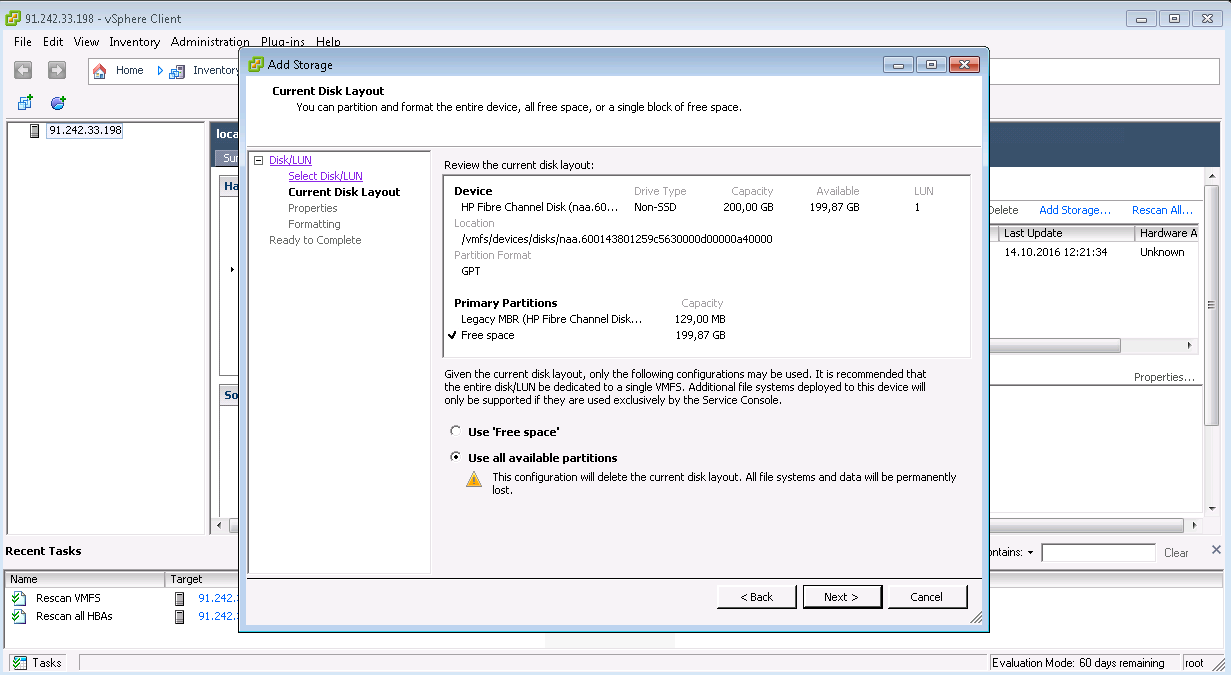
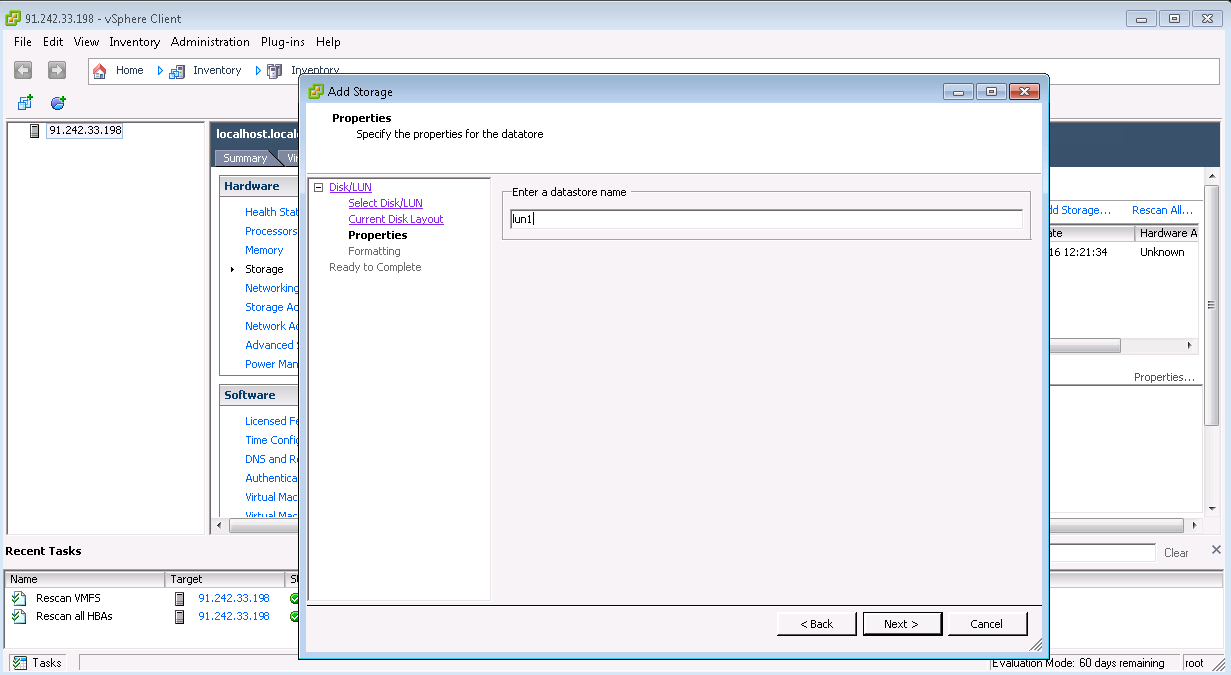
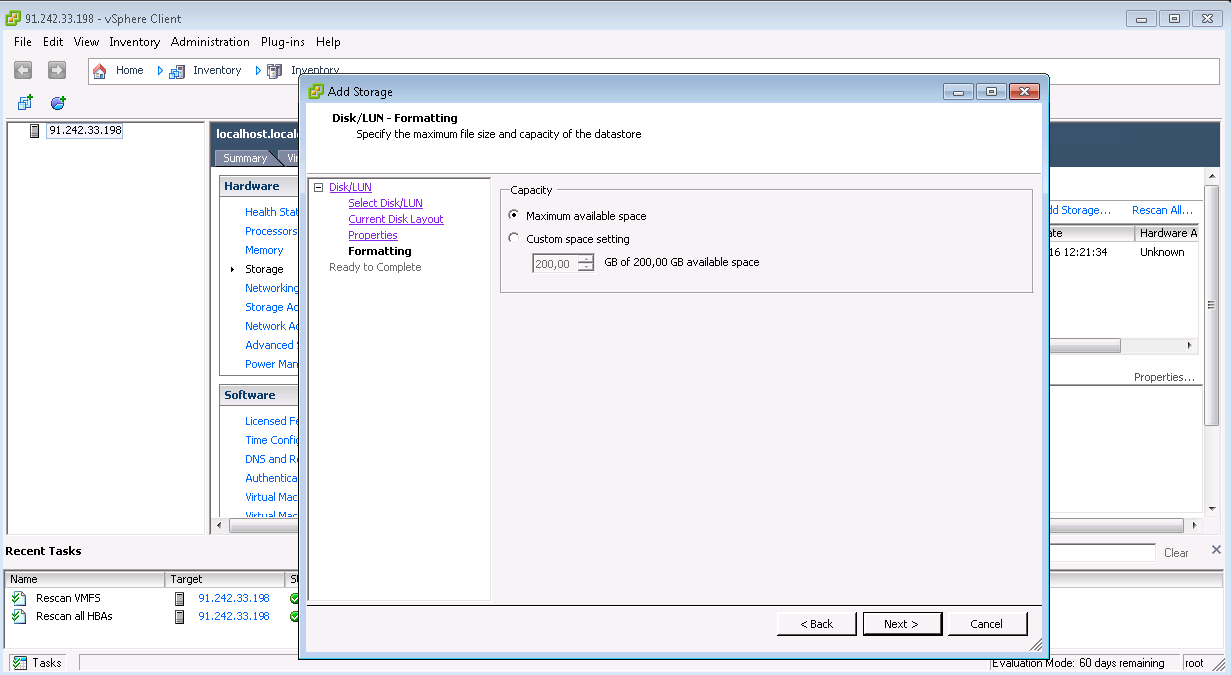
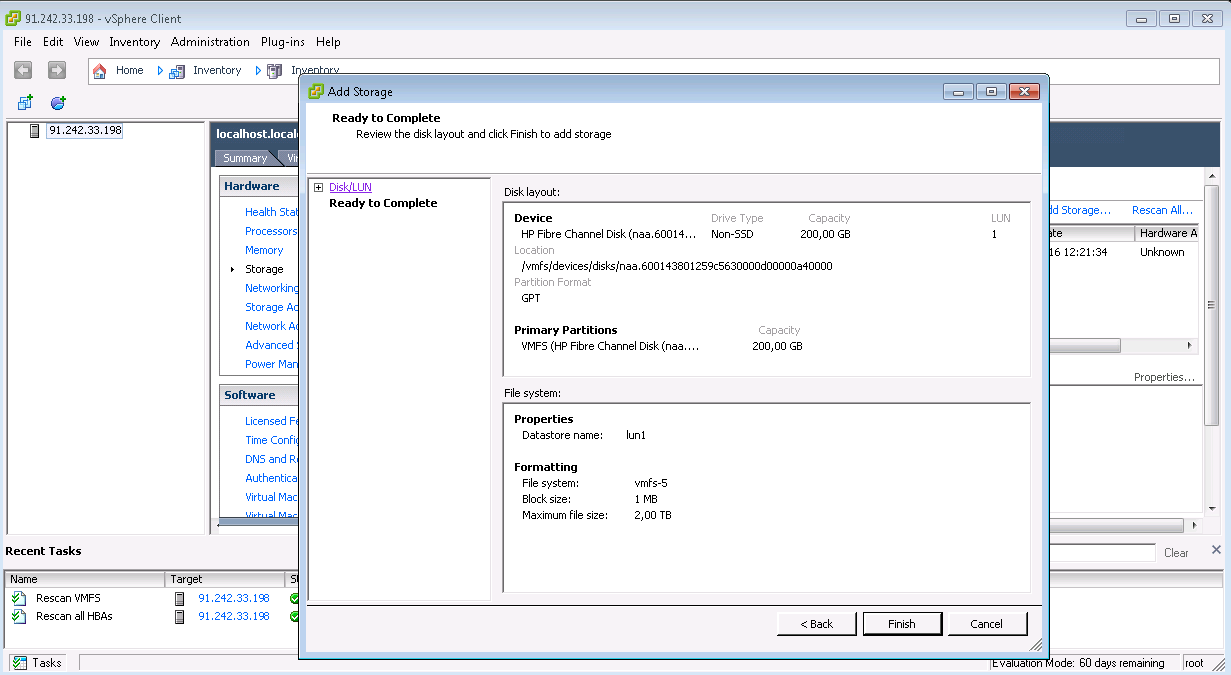
 Almacenamiento LUN de múltiples rutas para Debian GNU / LinuxUn poco más complicado:
Almacenamiento LUN de múltiples rutas para Debian GNU / LinuxUn poco más complicado:
En la etapa inicial de instalación de Debian GNU / Linux, podemos encontrar el problema de la imposibilidad de detectar el sistema de firmware ql2400_fw.bin. Se resuelve simplemente:
En un sistema Linux en funcionamiento, descargue el paquete firmware-qlogic, descomprímalo, escríbalo en la imagen y móntelo a través de la OIT (las acciones se realizan en el servidor HP Proliant). Se parece a esto:
#apt-get --download-only install firmware-qlogic #cp /var/cache/apt/archives/firmware-qlogic_* . #ar x firmware-qlogic* #tar cJpfv data.tar.xz #dd if=/dev/zero of=qlfw.raw bs=1M count=50 #mkdir fw #mount -o loop qlfw.raw fw #cp -r lib/firmware/* fw #umount fw
Conectamos qlfw.raw a través del menú Dispositivo virtual-> Archivo extraíble de imagen. Si el instalador aún no puede encontrar el firmware, puede hacerlo manualmente montando la imagen en el directorio / lib / firmware y reiniciando el módulo qla2xxx. Cambie a la consola de texto (las siguientes acciones se realizan en OIT. Teclado-> CTRL-ALT-Fn-> menú CTRL-ALT-F2):
#fdisk -l| grep 50 Disk /dev/sdr: 50 MiB, 52428800 bytes, 102400 sectors #mkdir /lib/firmware #mount /dev/sdr /lib/firmware #rmmod qla2xxx #modprobe qla2xxx
Después de eso, volvemos al instalador (Menú Teclado-> CTRL-ALT-Fn-> CTRL-ALT-F5), y reinstalamos el sistema en modo normal.
En un sistema que funcione, necesitamos instalar el paquete de herramientas multitrayecto con todas las dependencias:
#apt-get install multipath-tools … … : multipath-tools-boot , : multipath-tools 0, 1 , 0 , 0 . 0 B/185 kB . , 632 kB. multipath-tools. ( … 30895 .) …/multipath-tools_0.5.0-6+deb8u2_amd64.deb … multipath-tools (0.5.0-6+deb8u2) … systemd (215-17+deb8u5) … man-db (2.7.0.2-5) … multipath-tools (0.5.0-6+deb8u2) … libc-bin (2.19-18+deb8u6) …
Determine el inicio del servicio:
#systemctl enable multipath-tools Synchronizing state for multipath-tools.service with sysvinit using update-rc.d... Executing /usr/sbin/update-rc.d multipath-tools defaults Executing /usr/sbin/update-rc.d multipath-tools enable
Veamos cómo se agrupan los dispositivos:
# multipath -l 36001438005dea4600001a000000f0000 dm-0 HP,HSV450 size=100G features='1 queue_if_no_path' hwhandler='0' wp=rw |-+- policy='service-time 0' prio=0 status=active | |- 0:0:2:1 sdd 8:48 active undef running | |- 0:0:3:1 sde 8:64 active undef running | |- 2:0:0:1 sdj 8:144 active undef running | `- 2:0:1:1 sdk 8:160 active undef running `-+- policy='service-time 0' prio=0 status=enabled |- 0:0:0:1 sdb 8:16 active undef running |- 0:0:1:1 sdc 8:32 active undef running |- 2:0:2:1 sdl 8:176 active undef running `- 2:0:3:1 sdm 8:192 active undef running 3600143801259c5630000d00000a40000 dm-1 HP,HSV360 size=200G features='1 queue_if_no_path' hwhandler='0' wp=rw |-+- policy='service-time 0' prio=0 status=active | |- 0:0:4:1 sdf 8:80 active undef running | |- 0:0:5:1 sdg 8:96 active undef running | |- 2:0:4:1 sdn 8:208 active undef running | `- 2:0:5:1 sdo 8:224 active undef running `-+- policy='service-time 0' prio=0 status=enabled |- 0:0:6:1 sdh 8:112 active undef running |- 0:0:7:1 sdi 8:128 active undef running |- 2:0:6:1 sdp 8:240 active undef running `- 2:0:7:1 sdq 65:0 active undef running
Cree un sistema de archivos en el LUN que necesitamos:
# mkfs.ext4 /dev/dm-0 mke2fs 1.42.12 (29-Aug-2014) Creating filesystem with 26214400 4k blocks and 6553600 inodes Filesystem UUID: ae98a176-55d4-484a-b637-6a57a9212d3c Superblock backups stored on blocks: 32768, 98304, 163840, 229376, 294912, 819200, 884736, 1605632, 2654208, 4096000, 7962624, 11239424, 20480000, 23887872 Allocating group tables: done Writing inode tables: done Creating journal (32768 blocks): done Writing superblocks and filesystem accounting information: done
Monte y vea lo que sucedió:
# mount /dev/dm-0 /mnt/ # df -h /mnt % C /dev/mapper/36001438005dea4600001a000000f0000 99G 60M 94G 1% /mnt
LUN está montado y listo para usar. Queda por agregar una línea a fstab:
#echo '/dev/dm-0 /mnt/ext4 defaults 0 0'>>/etc/fstab
En este caso, vimos un ejemplo de conexión a VMware ESXi y Debian GNU / Linux.
También utilizamos un sistema para asignar LUN a servidores en nuestro
alojamientoEn este caso, utilizamos:
1. Chasis blade HP C7000 como máximo, con dos módulos administrativos.
2. Conmutadores FC en el chasis C7000 para conectar sistemas de almacenamiento externo - Conmutador HP Brocade 8Gb 8 / 24c SAN. Switches FC externos: puertos HP StorageWorks 8/40 Base 24, (24) Full Fabric SAN Switch.
3. Almacenamiento HPE 3PAR StorServ 7400 (4 nodos), almacenamiento HPE 3PAR StorServ 7450c (4 nodos), HPE 3PAR StorServ 7400c (2 nodos) y almacenamiento HPE EVA P6550.
Donde destacamos la luna:
ALLFlash: solo SSD
AO - SSD mixto + SAS
NL - solo SAS
En el próximo artículo, veremos la conexión del almacenamiento LUN de múltiples rutas a Windows Server 2008 y Windows Server 2012.