Si vous devez soudainement déboguer plusieurs microcontrôleurs / microprocesseurs en Crimée, boire des smoothies dans un bureau étouffant à Khimki. Si la carte à microprocesseur est située sur un objet en mouvement et qu'il n'y a aucun moyen d'atteindre le débogueur JTAG (la carte est située sur un ballon / quadricoptère). Si vous avez soudainement juste besoin d'une isolation galvanique entre l'hôte et la carte à déboguer (par exemple, un périphérique haute tension). Et c'est bien qu'il soit toujours bon marché, joyeux et universel pour le fabricant (STM, Broadcom, Xilinx, etc.) ou l'architecture (ARM, MIPS, FPGA, etc.). Ensuite, vous avez besoin d'un routeur, oui, juste un routeur, par exemple, comme celui-ci.
 Image de sagemcom.ru
Image de sagemcom.ruRegardons à l'intérieur:
 wiki.openwrt.org
wiki.openwrt.orgIl s'agit donc de Sagem F @ ST2704 V2, distribué par Rostelecom dans tout le pays. Nous avons un noyau d'architecture SoC BCM6328 MIPS, 320 MHz, une paire de ports USB soudés [1]. Il y a le wifi et ethernet. Et la meilleure partie est la sortie d'openwrt pour ce modèle. Tout ce qui est nécessaire de l'équipement pour les objectifs ci-dessus.
Immédiatement, l'idée surgit de prendre st-link et d'essayer de transférer l'USB sur le réseau. Il ressemble à une béquille, promet très probablement de ne pas fonctionner rapidement et pas très stable, les frais généraux sont énormes. Nous regardons plus loin ce qui peut être fait.
Vous pouvez porter openocd vers openwrt, prendre une puce st-link ou ftdi et démarrer le serveur gdb. Heureusement, openocr était déjà porté sur openwrt. Il semble suffisant de s'attarder sur cette option. Mais je veux voir quelles autres options openocd nous offre. Et ici, dans la documentation, l'interface sysfsgpio apparaît. Ce dont vous avez besoin est possible de contrôler les signaux tck, tdi, tdo, les outils OS Linux réguliers via / sys / class / gpio sur les broches soudées de la puce.
Nous essayons. Pour commencer, collectez openwrt (en utilisant la branche chaos_calmer) avec openocd. Par défaut, sur les GPIO soudés, les fonctions d'indication lumineuse sont fixes, ainsi que les boutons d'interrogation pour exécuter certaines commandes (rfkill, reset et wpsc). Pour qu'ils n'interfèrent pas, je les ai désactivés en supprimant les modules du noyau correspondants de l'assembly.
$cat target/linux/brcm63xx/config-3.18 b/target/linux/brcm63xx/config-3.18 ...
assemblage lui-même:
./scripts/feeds update -a ./scripts/feeds install -a make V=s
Firmware:
mtd -q write openwrt-brcm63xx-generic-F@ST2704V2-squashfs-cfe.bin linux
Pour le test sysfsgpio, nous compilons la configuration:
root@OpenWrt:~
Connectez-vous comme sur la photo:

Nous lançons:
root@OpenWrt:~# openocd -f sysfs.cfg.2.11 Open On-Chip Debugger 0.10.0+dev-00085-gfced6ac6-dirty (2017-03-xx-21:49) Licensed under GNU GPL v2 For bug reports, read http://openocd.org/doc/doxygen/bugs.html SysfsGPIO num: swclk = 482 SysfsGPIO num: swdio = 491 SysfsGPIO num: trst = 481 adapter speed: 1000 kHz adapter_nsrst_delay: 100 none separate cortex_m reset_config sysresetreq Info : SysfsGPIO JTAG/SWD bitbang driver Info : SWD only mode enabled (specify tck, tms, tdi and tdo gpios to add JTAG mode) Warn : gpio 482 is already exported Warn : gpio 491 is already exported Info : This adapter doesn't support configurable speed Info : SWD DPIDR 0x1ba01477 Info : stm32f1x.cpu: hardware has 6 breakpoints, 4 watchpoints
Exécutez le débogage dans l'IDE, tout fonctionne.
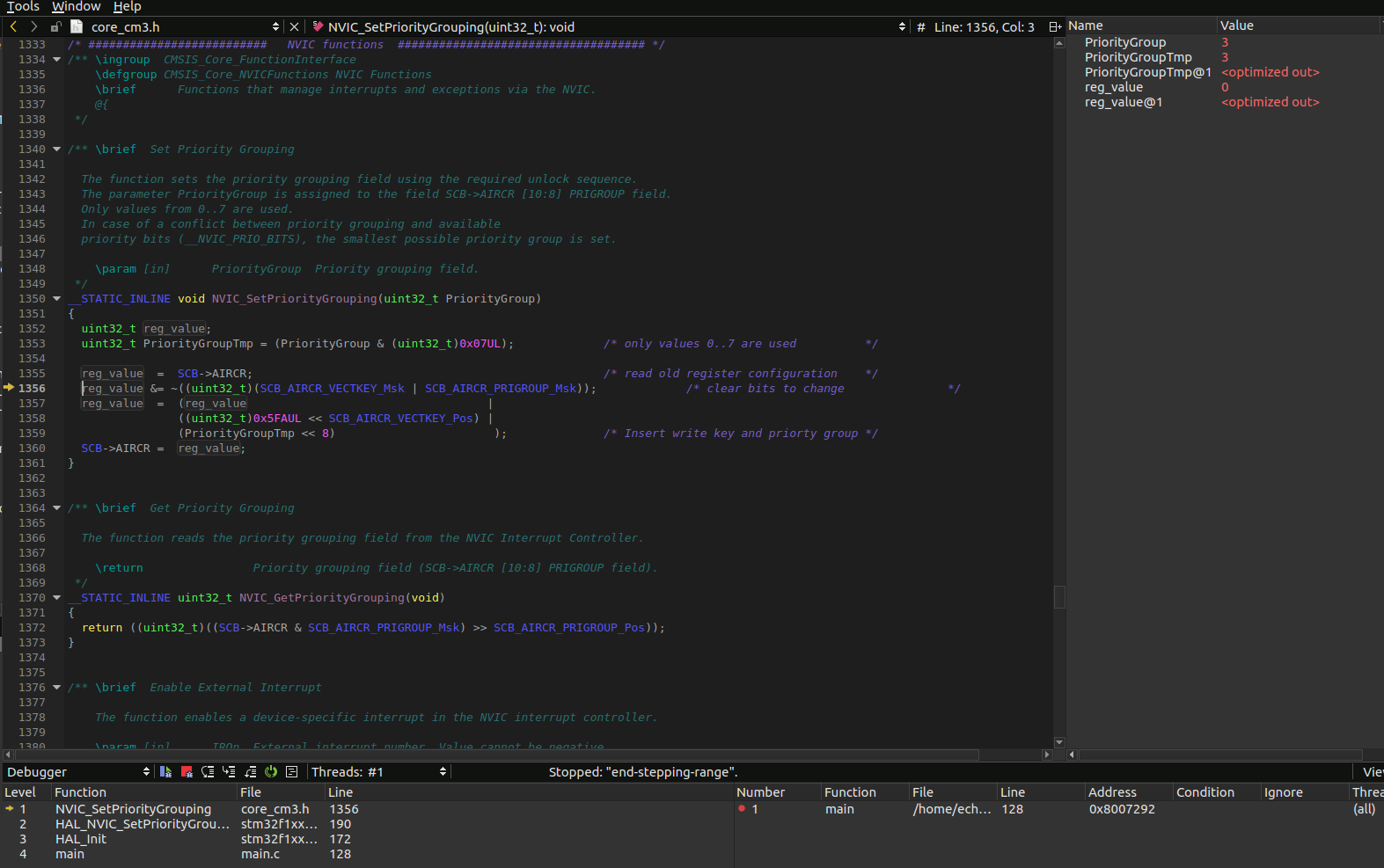
Seulement très lentement.
Nous essayons de quantifier la vitesse, allez sur le routeur telnet:
telnet 10.65.9.239 4444
Nous faisons un vidage de mémoire.
> dump_image dump.bin 0x08000000 0x1ffff dumped 131071 bytes in 55.013523s (2.327 KiB/s)
Hmm, par exemple, st-linkv2 sur mon hôte donne une vitesse d'environ 45 Ko / s. 20 fois la différence!

Le point, bien sûr, est dû au travail lent avec les fichiers dans / sys / class / gpio. Fouiller dans openocd. Recherchez le pilote d'interface pour RaspberryPi (src / jtag / drivers / bcm2835gpio.c). A en juger par les tests [5], il devrait avoir une vitesse similaire à celle du st-link. Ceci est réalisé, en grande partie, grâce à l'accès direct aux registres GPIO. Nous ferons de même pour notre SoC, et cela sera également vrai pour toute la famille de puces bcm63xx.
cette interface s'est avérée #ifdef HAVE_CONFIG_H #include "config.h" #endif #include <jtag/interface.h> #include "bitbang.h" #include <sys/mman.h> /* * Helper func to determine if gpio number valid * * Assume here that there will be less than 1000 gpios on a system */ static int is_gpio_valid(int gpio) { return gpio >= 0 && gpio < 32; } off_t address_dir = NULL; off_t address_val = NULL; static int dev_mem_fd = -1; static volatile uint32_t *pio_base = NULL; static volatile uint32_t *pval_base = NULL; static volatile uint32_t *pads_base = NULL; static unsigned int jtag_delay = 0; static void set_dir_gpio(const int gpio, const int direction) { if(direction) *pio_base |= 1 << gpio; else *pio_base &= ~(1 << gpio); } static void set_value_gpio(const int gpio, const int value) { if(value) *pval_base |= 1 << gpio; else *pval_base &= ~(1 << gpio); for (unsigned int i = 0; i < jtag_delay; i++) asm volatile (""); } static int read_gpio(const int gpio) { uint32_t val = *pval_base & (1 << gpio); val = val ? 1 : 0; return val; } static int setup_bcm63xx_gpio(int gpio, int is_output, int init_high) { char buf[40]; char gpiostr[4]; int ret; if (!is_gpio_valid(gpio)) return ERROR_OK; if((address_dir == NULL) || (address_val == NULL)){ perror("address of gpio register don't set"); return ERROR_FAIL; } if( dev_mem_fd < 0 ) { dev_mem_fd = open("/dev/mem", O_RDWR | O_SYNC); if (dev_mem_fd < 0) { perror("open"); return ERROR_FAIL; } const uint32_t mapped_size = getpagesize(); const off_t target_mmap = address_dir & ~(off_t)(mapped_size - 1); pads_base = mmap(NULL, mapped_size, PROT_READ | PROT_WRITE, MAP_SHARED, dev_mem_fd, target_mmap); if (pads_base == MAP_FAILED) { perror("mmap. Check correct register address."); close(dev_mem_fd); return ERROR_FAIL; } pio_base = (char*)pads_base + (unsigned)(address_dir - target_mmap); pval_base = (char*)pads_base + (unsigned)(address_val - target_mmap); } set_dir_gpio(gpio, is_output); set_value_gpio(gpio, init_high); return 0; } /* gpio numbers for each gpio. Negative values are invalid */ static int tck_gpio = -1; static int tms_gpio = -1; static int tdi_gpio = -1; static int tdo_gpio = -1; static int trst_gpio = -1; static int srst_gpio = -1; static int swclk_gpio = -1; static int swdio_gpio = -1; /* * file descriptors for /sys/class/gpio/gpioXX/value * Set up during init. */ static int tck_fd = -1; static int tms_fd = -1; static int tdi_fd = -1; static int tdo_fd = -1; static int trst_fd = -1; static int srst_fd = -1; static int swclk_fd = -1; static int swdio_fd = -1; static int last_swclk; static int last_swdio; static bool last_stored; static bool swdio_input; static void bcm63xx_gpio_swdio_drive(bool is_output) { set_dir_gpio(swdio_gpio, is_output ? 1 : 0); last_stored = false; swdio_input = !is_output; } static int bcm63xx_gpio_swdio_read(void) { return read_gpio(swdio_gpio); } static void bcm63xx_gpio_swdio_write(int swclk, int swdio) { const char one[] = "1"; const char zero[] = "0"; size_t bytes_written; if (!swdio_input) { if (!last_stored || (swdio != last_swdio)) { set_value_gpio(swdio_gpio, swdio ? 1 : 0); } } /* write swclk last */ if (!last_stored || (swclk != last_swclk)) { set_value_gpio(swclk_gpio, swclk ? 1 : 0); } last_swdio = swdio; last_swclk = swclk; last_stored = true; } /* * Bitbang interface read of TDO * * The bcm63xx value will read back either '0' or '1'. The trick here is to call * lseek to bypass buffering in the bcm63xx kernel driver. */ static int bcm63xx_gpio_read(void) { return read_gpio(tdo_gpio); } /* * Bitbang interface write of TCK, TMS, TDI * * Seeing as this is the only function where the outputs are changed, * we can cache the old value to avoid needlessly writing it. */ static void bcm63xx_gpio_write(int tck, int tms, int tdi) { if (swd_mode) { bcm63xx_gpio_swdio_write(tck, tdi); return; } const char one[] = "1"; const char zero[] = "0"; static int last_tck; static int last_tms; static int last_tdi; static int first_time; size_t bytes_written; if (!first_time) { last_tck = !tck; last_tms = !tms; last_tdi = !tdi; first_time = 1; } if (tdi != last_tdi) { set_value_gpio(tdi_gpio,tdi); } if (tms != last_tms) { set_value_gpio(tms_gpio,tms); } /* write clk last */ if (tck != last_tck) { set_value_gpio(tck_gpio,tck); } last_tdi = tdi; last_tms = tms; last_tck = tck; } /* * Bitbang interface to manipulate reset lines SRST and TRST * * (1) assert or (0) deassert reset lines */ static void bcm63xx_gpio_reset(int trst, int srst) { LOG_DEBUG("bcm63xx_gpio_reset"); const char one[] = "1"; const char zero[] = "0"; size_t bytes_written; /* assume active low */ if (srst_fd >= 0) { set_value_gpio(srst_gpio,srst); } /* assume active low */ if (trst_fd >= 0) { set_value_gpio(trst_gpio,trst); } } COMMAND_HANDLER(bcm63xx_gpio_handle_jtag_gpionums) { if (CMD_ARGC == 4) { COMMAND_PARSE_NUMBER(int, CMD_ARGV[0], tck_gpio); COMMAND_PARSE_NUMBER(int, CMD_ARGV[1], tms_gpio); COMMAND_PARSE_NUMBER(int, CMD_ARGV[2], tdi_gpio); COMMAND_PARSE_NUMBER(int, CMD_ARGV[3], tdo_gpio); } else if (CMD_ARGC != 0) { return ERROR_COMMAND_SYNTAX_ERROR; } command_print(CMD_CTX, "bcm63xx_GPIO nums: tck = %d, tms = %d, tdi = %d, tdo = %d", tck_gpio, tms_gpio, tdi_gpio, tdo_gpio); return ERROR_OK; } COMMAND_HANDLER(bcm63xx_gpio_handle_jtag_gpionum_tck) { if (CMD_ARGC == 1) COMMAND_PARSE_NUMBER(int, CMD_ARGV[0], tck_gpio); command_print(CMD_CTX, "bcm63xx_GPIO num: tck = %d", tck_gpio); return ERROR_OK; } COMMAND_HANDLER(bcm63xx_gpio_handle_jtag_gpionum_tms) { if (CMD_ARGC == 1) COMMAND_PARSE_NUMBER(int, CMD_ARGV[0], tms_gpio); command_print(CMD_CTX, "bcm63xx_GPIO num: tms = %d", tms_gpio); return ERROR_OK; } COMMAND_HANDLER(bcm63xx_gpio_handle_jtag_gpionum_tdo) { if (CMD_ARGC == 1) COMMAND_PARSE_NUMBER(int, CMD_ARGV[0], tdo_gpio); command_print(CMD_CTX, "bcm63xx_GPIO num: tdo = %d", tdo_gpio); return ERROR_OK; } COMMAND_HANDLER(bcm63xx_gpio_handle_jtag_gpionum_tdi) { if (CMD_ARGC == 1) COMMAND_PARSE_NUMBER(int, CMD_ARGV[0], tdi_gpio); command_print(CMD_CTX, "bcm63xx_GPIO num: tdi = %d", tdi_gpio); return ERROR_OK; } COMMAND_HANDLER(bcm63xx_gpio_handle_jtag_gpionum_srst) { if (CMD_ARGC == 1) COMMAND_PARSE_NUMBER(int, CMD_ARGV[0], srst_gpio); command_print(CMD_CTX, "bcm63xx_GPIO num: srst = %d", srst_gpio); return ERROR_OK; } COMMAND_HANDLER(bcm63xx_gpio_handle_jtag_gpionum_trst) { if (CMD_ARGC == 1) COMMAND_PARSE_NUMBER(int, CMD_ARGV[0], trst_gpio); command_print(CMD_CTX, "bcm63xx_GPIO num: trst = %d", trst_gpio); return ERROR_OK; } COMMAND_HANDLER(bcm63xx_gpio_handle_swd_gpionums) { if (CMD_ARGC == 2) { COMMAND_PARSE_NUMBER(int, CMD_ARGV[0], swclk_gpio); COMMAND_PARSE_NUMBER(int, CMD_ARGV[1], swdio_gpio); } else if (CMD_ARGC != 0) { return ERROR_COMMAND_SYNTAX_ERROR; } command_print(CMD_CTX, "bcm63xx_GPIO nums: swclk = %d, swdio = %d", swclk_gpio, swdio_gpio); return ERROR_OK; } COMMAND_HANDLER(bcm63xx_gpio_handle_swd_gpionum_swclk) { if (CMD_ARGC == 1) COMMAND_PARSE_NUMBER(int, CMD_ARGV[0], swclk_gpio); command_print(CMD_CTX, "bcm63xx_GPIO num: swclk = %d", swclk_gpio); return ERROR_OK; } COMMAND_HANDLER(bcm63xx_gpio_handle_swd_gpionum_swdio) { if (CMD_ARGC == 1) COMMAND_PARSE_NUMBER(int, CMD_ARGV[0], swdio_gpio); command_print(CMD_CTX, "bcm63xx_GPIO num: swdio = %d", swdio_gpio); return ERROR_OK; } COMMAND_HANDLER(bcm63xx_gpio_jtag_delay) { if (CMD_ARGC == 1) COMMAND_PARSE_NUMBER(int, CMD_ARGV[0], jtag_delay); command_print(CMD_CTX, "bcm63xx_GPIO jtag_delay:= %d tics", jtag_delay); return ERROR_OK; } COMMAND_HANDLER(bcm63xx_gpio_adresses) { if (CMD_ARGC == 2) { COMMAND_PARSE_NUMBER(u32, CMD_ARGV[0], address_dir); COMMAND_PARSE_NUMBER(u32, CMD_ARGV[1], address_val); } else if (CMD_ARGC != 0) { return ERROR_COMMAND_SYNTAX_ERROR; } command_print(CMD_CTX, "bcm63xx_GPIO address: direction = %x, value = %x", address_dir, address_val); return ERROR_OK; } static const struct command_registration bcm63xx_gpio_command_handlers[] = { { .name = "bcm63xx_gpio_jtag_nums", .handler = &bcm63xx_gpio_handle_jtag_gpionums, .mode = COMMAND_CONFIG, .help = "gpio numbers for tck, tms, tdi, tdo. (in that order)", .usage = "(tck tms tdi tdo)* ", }, { .name = "bcm63xx_gpio_tck_num", .handler = &bcm63xx_gpio_handle_jtag_gpionum_tck, .mode = COMMAND_CONFIG, .help = "gpio number for tck.", }, { .name = "bcm63xx_gpio_tms_num", .handler = &bcm63xx_gpio_handle_jtag_gpionum_tms, .mode = COMMAND_CONFIG, .help = "gpio number for tms.", }, { .name = "bcm63xx_gpio_tdo_num", .handler = &bcm63xx_gpio_handle_jtag_gpionum_tdo, .mode = COMMAND_CONFIG, .help = "gpio number for tdo.", }, { .name = "bcm63xx_gpio_tdi_num", .handler = &bcm63xx_gpio_handle_jtag_gpionum_tdi, .mode = COMMAND_CONFIG, .help = "gpio number for tdi.", }, { .name = "bcm63xx_gpio_srst_num", .handler = &bcm63xx_gpio_handle_jtag_gpionum_srst, .mode = COMMAND_CONFIG, .help = "gpio number for srst.", }, { .name = "bcm63xx_gpio_trst_num", .handler = &bcm63xx_gpio_handle_jtag_gpionum_trst, .mode = COMMAND_CONFIG, .help = "gpio number for trst.", }, { .name = "bcm63xx_gpio_swd_nums", .handler = &bcm63xx_gpio_handle_swd_gpionums, .mode = COMMAND_CONFIG, .help = "gpio numbers for swclk, swdio. (in that order)", .usage = "(swclk swdio)* ", }, { .name = "bcm63xx_gpio_swclk_num", .handler = &bcm63xx_gpio_handle_swd_gpionum_swclk, .mode = COMMAND_CONFIG, .help = "gpio number for swclk.", }, { .name = "bcm63xx_gpio_swdio_num", .handler = &bcm63xx_gpio_handle_swd_gpionum_swdio, .mode = COMMAND_CONFIG, .help = "gpio number for swdio.", }, { .name = "bcm63xx_gpio_jtag_delay", .handler = &bcm63xx_gpio_jtag_delay, .mode = COMMAND_CONFIG, .help = "qty tics gpio delay.", }, { .name = "bcm63xx_gpio_adresses", .handler = &bcm63xx_gpio_adresses, .mode = COMMAND_CONFIG, .help = "addresses for direction and value setup. (in that order)", .usage = "(address_dir address_val)* ", }, COMMAND_REGISTRATION_DONE }; static int bcm63xx_gpio_init(void); static int bcm63xx_gpio_quit(void); static const char * const bcm63xx_gpio_transports[] = { "jtag", "swd", NULL }; struct jtag_interface bcm63xxgpio_interface = { .name = "bcm63xxgpio", .supported = DEBUG_CAP_TMS_SEQ, .execute_queue = bitbang_execute_queue, .transports = bcm63xx_gpio_transports, .swd = &bitbang_swd, .commands = bcm63xx_gpio_command_handlers, .init = bcm63xx_gpio_init, .quit = bcm63xx_gpio_quit, }; static struct bitbang_interface bcm63xx_gpio_bitbang = { .read = bcm63xx_gpio_read, .write = bcm63xx_gpio_write, .reset = bcm63xx_gpio_reset, .swdio_read = bcm63xx_gpio_swdio_read, .swdio_drive = bcm63xx_gpio_swdio_drive, .blink = 0 }; static void unusing_all_gpio(void) { munmap(pads_base, sysconf(_SC_PAGE_SIZE)); close(dev_mem_fd); LOG_INFO("unusing_all_gpio\n"); } static bool bcm63xx_gpio_jtag_mode_possible(void) { if (!is_gpio_valid(tck_gpio)) return 0; if (!is_gpio_valid(tms_gpio)) return 0; if (!is_gpio_valid(tdi_gpio)) return 0; if (!is_gpio_valid(tdo_gpio)) return 0; return 1; } static bool bcm63xx_gpio_swd_mode_possible(void) { if (!is_gpio_valid(swclk_gpio)) return 0; if (!is_gpio_valid(swdio_gpio)) return 0; return 1; } static int bcm63xx_gpio_init(void) { bitbang_interface = &bcm63xx_gpio_bitbang; LOG_INFO("bcm63xx_gpio JTAG/SWD bitbang driver"); if (bcm63xx_gpio_jtag_mode_possible()) { if (bcm63xx_gpio_swd_mode_possible()) LOG_INFO("JTAG and SWD modes enabled"); else LOG_INFO("JTAG only mode enabled (specify swclk and swdio gpio to add SWD mode)"); if (!is_gpio_valid(trst_gpio) && !is_gpio_valid(srst_gpio)) { LOG_ERROR("Require at least one of trst or srst gpios to be specified"); return ERROR_JTAG_INIT_FAILED; } } else if (bcm63xx_gpio_swd_mode_possible()) { LOG_INFO("SWD only mode enabled (specify tck, tms, tdi and tdo gpios to add JTAG mode)"); } else { LOG_ERROR("Require tck, tms, tdi and tdo gpios for JTAG mode and/or swclk and swdio gpio for SWD mode"); return ERROR_JTAG_INIT_FAILED; } /* * Configure TDO as an input, and TDI, TCK, TMS, TRST, SRST * as outputs. Drive TDI and TCK low, and TMS/TRST/SRST high. * For SWD, SWCLK and SWDIO are configures as output high. */ if (tck_gpio >= 0) { tck_fd = setup_bcm63xx_gpio(tck_gpio, 1, 0); if (tck_fd < 0) goto out_error; } if (tms_gpio >= 0) { tms_fd = setup_bcm63xx_gpio(tms_gpio, 1, 1); if (tms_fd < 0) goto out_error; } if (tdi_gpio >= 0) { tdi_fd = setup_bcm63xx_gpio(tdi_gpio, 1, 0); if (tdi_fd < 0) goto out_error; } if (tdo_gpio >= 0) { tdo_fd = setup_bcm63xx_gpio(tdo_gpio, 0, 0); if (tdo_fd < 0) goto out_error; } /* assume active low*/ if (trst_gpio >= 0) { trst_fd = setup_bcm63xx_gpio(trst_gpio, 1, 1); if (trst_fd < 0) goto out_error; } /* assume active low*/ if (srst_gpio >= 0) { srst_fd = setup_bcm63xx_gpio(srst_gpio, 1, 1); if (srst_fd < 0) goto out_error; } if (swclk_gpio >= 0) { swclk_fd = setup_bcm63xx_gpio(swclk_gpio, 1, 0); if (swclk_fd < 0) goto out_error; } if (swdio_gpio >= 0) { swdio_fd = setup_bcm63xx_gpio(swdio_gpio, 1, 0); if (swdio_fd < 0) goto out_error; } if (bcm63xx_gpio_swd_mode_possible()) { if (swd_mode) bitbang_swd_switch_seq(JTAG_TO_SWD); else bitbang_swd_switch_seq(SWD_TO_JTAG); } return ERROR_OK; out_error: unusing_all_gpio(); return ERROR_JTAG_INIT_FAILED; } static int bcm63xx_gpio_quit(void) { unusing_all_gpio(); return ERROR_OK; }
Comparé à sysfsgpio, il a ajouté quelques options:
- bcm63xx_gpio_jtag_delay
- bcm63xx_gpio_adresses
Le premier paramètre définit le délai entre la commutation des broches, il s'agit d'un analogue indirect de bcm2835gpio_speed_coeffs pour le pilote RaspberryPi, qui définit la fréquence jtag. Par exemple, avec un retard nul, la fréquence de commutation était d'environ un mégahertz, tout fonctionnait de manière assez stable, mais pour la fiabilité, il est préférable de pouvoir régler ce paramètre.
Et la deuxième option est un analogue de bcm2835gpio_peripheral_base, seulement pour cela, vous devez enregistrer deux adresses pour le registre, qui définit la fonction d'entrée / sortie des broches, et le registre, qui est responsable de la valeur logique d'entrée / sortie sur gpio. Au début, il prenait des valeurs de registre dans les fichiers d'en-tête du noyau. Mais rien n'a fonctionné avec ces valeurs. Il s'est avéré que les registres périphériques ne sont pas directement accessibles depuis l'espace utilisateur, c'est-à-dire un remappage doit être effectué dans le noyau. Il est bon que le pilote gpio l’ait déjà implémenté et que les valeurs nécessaires puissent être extraites de / proc / iomem.
Ajoutez notre interface à l'assembly openocdN'oubliez pas d'ajouter --enable-bcm63xxgpio à CONFIGURE_ARGS dans le fichier feeds / packages / utils / openocd / Makefile.
Nous reconstruisons, installons et exécutons sur le routeur:
root@OpenWrt:~# openocd -f interface/bcm63xx-swd.cfg -f target/stm32f1x.cfg Open On-Chip Debugger 0.10.0+dev-00085-gfced6ac6-dirty (2017-03-xx-21:49) Licensed under GNU GPL v2 For bug reports, read http://openocd.org/doc/doxygen/bugs.html bcm63xx_GPIO num: swclk = 2 bcm63xx_GPIO num: swdio = 11 bcm63xx_GPIO jtag_delay:= 10 tics bcm63xx_GPIO address: direction = 10000084, value = 1000008c adapter speed: 1000 kHz adapter_nsrst_delay: 100 none separate cortex_m reset_config sysresetreq Info : bcm63xx_gpio JTAG/SWD bitbang driver Info : SWD only mode enabled (specify tck, tms, tdi and tdo gpios to add JTAG mode) Info : This adapter doesn't support configurable speed Info : SWD DPIDR 0x1ba01477 Info : stm32f1x.cpu: hardware has 6 breakpoints, 4 watchpoints
Vérifiez la vitesse du vidage.
> dump_image dump.bin 0x08000000 0x1ffff dumped 131071 bytes in 4.729815s (27.062 KiB/s)
Très bien, on perd deux fois quelque part en st-link et framboise, mais à l'oeil la différence n'est pas perceptible. Il n'y a pas de frises pendant le débogage, et attendez quelques secondes pour flasher pendant le firmware - "show off".
Tous les tests ont été effectués sur le microcontrôleur STM32F103C8T6 et, malheureusement, il n'y avait pas de jtag sur la carte déboguée uniquement sur l'interface SWD, sur la carte déboguée. Par conséquent, je ne peux donc pas garantir un travail complet sur jtag. De plus, il ne faut pas oublier la coordination des niveaux de signal (en particulier pour MK AVR).
Le routeur lui-même a été tiré d'un tas d'ordures, parmi lesquelles était plein de Sagem F @ st 2704V2 et V7. Malheureusement, tous les appareils étaient hors service. Mais il a été possible de restaurer la carte sans problème (voir [2]).
Si quelqu'un est prêt à créer un débogueur / programmeur à partir de ce constructeur, alors il est prêt à partager ses stocks avec le public sans frais, en retirant toutes les responsabilités et les fonds pour l'envoi (depuis la ville par défaut).
Mise à jour du firmware
ici .
Je vous avertis que les paramètres par défaut du réseau et du pare-feu ont été modifiés.
C'est tout, bon débogage!
Liste des ressources utiles
- wiki.openwrt.org/toh/sagem/fast2704
- radiohlam.ru/forum/viewtopic.php?f=54&t=3749
- openocd.org
- developer.mbed.org/handbook/CMSIS-DAP
- github.com/rogerclarkmelbourne/Arduino_STM32/wiki/Programming-an-STM32F103XXX-with-a-generic-ST-Link-V2-programmer-from-Linux