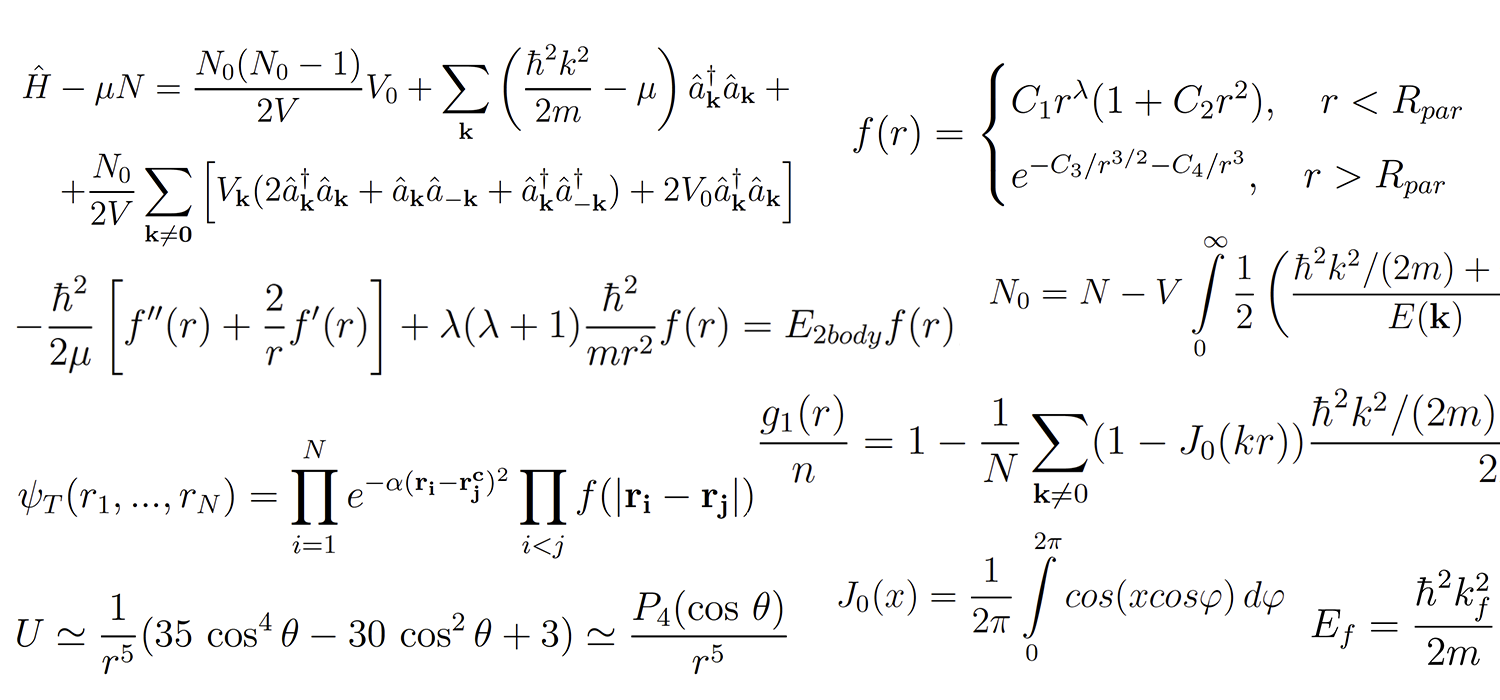
Spesialisasi saya adalah fisika benda terkondensasi. Tentu saja, dalam proses pencelupan di dalamnya, diperlukan untuk mempelajari banyak artikel ilmiah, tetapi dapat mengambil banyak waktu untuk mengurai setidaknya satu. Lebih dari seribu artikel diterbitkan per bulan di
arxiv di bagian
cond-mat . Ada situasi di mana banyak peneliti, terutama pemula, tidak memiliki visi holistik di bidang sains mereka. Alat yang dijelaskan dalam artikel ini merangkum isi basis data artikel ilmiah dan dirancang untuk mempercepat pekerjaan dengan literatur.
Perlu disebutkan bahwa kami menciptakan sepeda, hanya sepeda kami yang akan naik secara gratis (harga untuk
analog yang dibayar sangat tidak senonoh sehingga tidak dapat disebutkan).
Sepeda akan dirakit dalam Python,
Gensim digunakan untuk pemodelan tematik, dan
Plot.ly digunakan untuk visualisasi. Di akhir artikel ada tautan ke laptop Jupyter dan GitHub.
Bahan sumber untuk karya ini adalah anotasi dan teks artikel ilmiah. Jika yang pertama tersedia untuk kita dalam bentuk XML "siap pakai", maka file PDF dari artikel perlu dikonversi ke txt, sebagai akibat dari proses ini banyak "sampah" tetap dalam teks, sehingga mereka perlu dibersihkan secara serius.
Anotasi sampel<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <feed xmlns="http://www.w3.org/2005/Atom"> <link href="http://arxiv.org/api/query?search_query%3D%26id_list%3D1706.09062%26start%3D0%26max_results%3D10" rel="self" type="application/atom+xml"/> <title type="html">ArXiv Query: search_query=&id_list=1706.09062&start=0&max_results=10</title> <id>http://arxiv.org/api/ECEwpFhuO79sa+LzMzx6/iStFak</id> <updated>2018-05-01T00:00:00-04:00</updated> <opensearch:totalResults xmlns:opensearch="http://a9.com/-/spec/opensearch/1.1/">1</opensearch:totalResults> <opensearch:startIndex xmlns:opensearch="http://a9.com/-/spec/opensearch/1.1/">0</opensearch:startIndex> <opensearch:itemsPerPage xmlns:opensearch="http://a9.com/-/spec/opensearch/1.1/">10</opensearch:itemsPerPage> <entry> <id>http://arxiv.org/abs/1706.09062v1</id> <updated>2017-06-27T22:03:24Z</updated> <published>2017-06-27T22:03:24Z</published> <title>On Bose-Einstein condensation and superfluidity of trapped photons with coordinate-dependent mass and interactions</title> <summary> The condensate density profile of trapped two-dimensional gas of photons in an optical microcavity, filled by a dye solution, is analyzed taking into account a coordinate-dependent effective mass of cavity photons and photon-photon coupling parameter. The profiles for the densities of the superfluid and normal phases of trapped photons in the different regions of the system at the fixed temperature are analyzed. The radial dependencies of local mean-field phase transition temperature $T_c^0 (r)$ and local Kosterlitz-Thouless transition temperature $T_c (r)$ for trapped microcavity photons are obtained. The coordinate dependence of cavity photon effective mass and photon-photon coupling parameter is important for the mirrors of smaller radius with the high trapping frequency, which provides BEC and superfluidity for smaller critical number of photons at the same temperature. We discuss a possibility of an experimental study of the density profiles for the normal and superfluid components in the system under consideration. </summary> <author> <name>Oleg L. Berman</name> </author> <author> <name>Roman Ya. Kezerashvili</name> </author> <author> <name>Yurii E. Lozovik</name> </author> <arxiv:doi xmlns:arxiv="http://arxiv.org/schemas/atom">10.1364/JOSAB.34.001649</arxiv:doi> <link title="doi" href="http://dx.doi.org/10.1364/JOSAB.34.001649" rel="related"/> <arxiv:comment xmlns:arxiv="http://arxiv.org/schemas/atom">14 page 5, figures</arxiv:comment> <link href="http://arxiv.org/abs/1706.09062v1" rel="alternate" type="text/html"/> <link title="pdf" href="http://arxiv.org/pdf/1706.09062v1" rel="related" type="application/pdf"/> <arxiv:primary_category xmlns:arxiv="http://arxiv.org/schemas/atom" term="cond-mat.mes-hall" scheme="http://arxiv.org/schemas/atom"/> <category term="cond-mat.mes-hall" scheme="http://arxiv.org/schemas/atom"/> </entry> </feed>
Contoh teksOn Bose-Einstein condensation and super¬‚uidity of trapped photons with
coordinate-dependent mass and interactions
Oleg L. Berman1,2, Roman Ya. Kezerashvili1,2, and Yurii E. Lozovik3,4
1Physics Department, New York City College of Technology, The City University of New York,
2The Graduate School and University Center, The City University of New York,
Brooklyn, NY 11201, USA
3Institute of Spectroscopy, Russian Academy of Sciences, 142190 Troitsk, Moscow, Russia
4National Research University Higher School of Economics, Moscow, Russia
New York, NY 10016, USA
(Dated: June 29, 2017)
The condensate density pro¬Ѓle of trapped two-dimensional gas of photons in an optical micro-
cavity, ¬Ѓlled by a dye solution, is analyzed taking into account a coordinate-dependent e¬Ђective
mass of cavity photons and photon-photon coupling parameter. The pro¬Ѓles for the densities of the
super¬‚uid and normal phases of trapped photons in the di¬Ђerent regions of the system at the ¬Ѓxed
temperature are analyzed. The radial dependencies of local mean-¬Ѓeld phase transition temperature
T 0
c (r) and local Kosterlitz-Thouless transition temperature Tc(r) for trapped microcavity photons
are obtained. The coordinate dependence of cavity photon e¬Ђective mass and photon-photon cou-
pling parameter is important for the mirrors of smaller radius with the high trapping frequency,
which provides BEC and super¬‚uidity for smaller critical number of photons at the same temper-
ature. We discuss a possibility of an experimental study of the density pro¬Ѓles for the normal and
super¬‚uid components in the system under consideration.
Key words: Photons in a microcavity; Bose-Einstein condensation of photons; super¬‚uidity of
photons.
PACS numbers: 03.75.Hh, 42.55.Mv, 67.85.Bc, 67.85.Hj
I.
INTRODUCTION
When a system of bosons is cooled to low temperatures, a substantial fraction of the particles spontaneously occupy
the single lowest energy quantum state. This phenomenon is known as Bose-Einstein condensation (BEC) and its
occurs in many-particle systems of bosons with masses m and temperature T when the de Broglie wavelength of the
Bose particle exceeds the mean interparticle distance [1]. The most remarkable consequence of BEC is that there
should be a temperature below which a ¬Ѓnite fraction of all the bosons ЂњcondenseЂќ into the same one-particle state
with macroscopic properties described by a single condensate wavefunction, promoting quantum physics to classical
time- and length scales.
Most recently, the observations at room temperature of the BEC of two-dimensional photon gas con¬Ѓned in an optical
microcavity, formed by spherical mirrors and ¬Ѓlled by a dye solution, were reported [2Ђ“5]. The interaction between
microcavity photons is achieved through the interaction of the photons with the non-linear media of a microcavity,
¬Ѓlled by a dye solution. While the main contribution to the interaction in the experiment, reported in Ref. 2, is
thermooptic, it is not a contact interaction.
It is known that BEC for bosons can exist without particle-particle
interactions [6] (see Ref. 1 for the details), but at least the interactions with the surrounding media are necessary to
achieve thermodynamical equilibrium. For photon BEC it can be achieved by interaction with incoherent phonons [7].
The in¬‚uence of interactions on condensate-number ¬‚uctuations in a BEC of microcavity photons was studied in Ref. 8.
The kinetics of photon thermalization and condensation was analyzed in Refs. 9Ђ“11. The kinetics of trapped photon
gas in a microcavity, ¬Ѓlled by a dye solution, was studied, and, a crossover between driven-dissipative system laser
dynamics and a thermalized Bose-Einstein condensation of photons was observed [12].
In previous theoretical studies the equation of motion for a BEC of photons con¬Ѓned by the axially symmetrical
trap in a microcavity was obtained.
It was assumed that the changes of the cavity width are much smaller than
the width of the trap [13]. This assumption results in the coordinate-independent e¬Ђective photon mass mph and
photon-photon coupling parameter g. In this Paper, we study the local super¬‚uid and normal density pro¬Ѓles for
trapped two-dimensional gas of photons with the coordinate-dependent e¬Ђective mass and photon-photon coupling
parameter in a an optical microcavity, ¬Ѓlled by a dye solution. We propose the approach to study the local BEC
and local super¬‚uidity of cavity photon gas in the framework of local density approximation (LDA) in the traps of
larger size without the assumption, that total changes of the cavity width are much smaller than the size of the trap.
In this case, we study the e¬Ђects of coordinate-dependent e¬Ђective mass and photon-photon coupling parameter on
the super¬‚uid and normal density pro¬Ѓles as well as the pro¬Ѓles of the local temperature of the phase transition for
trapped cavity photons. Such approach is useful for the mirrors of smaller radius with the high trapping frequency,
2
which provide BEC and super¬‚uidity for smaller critical number of photons at the same temperature.
The paper is organized in the following way.
In Sec. II, we obtain the condensate density pro¬Ѓle for trapped
microcavity photon BEC with locally variable mass and interactions. The expression for the number of particles in a
condensate is analyzed in Sec. III. In Sec. IV, the dependence of the condensate parameters on the geometry of the
trap is discussed. In Sec. V, we study the collective excitation spectrum and super¬‚uidity of 2D weakly-interacting
Bose gas of cavity photons. The results of our calculations are discussed in Sec. VI. The proposed experiment for
measuring the distribution of the local density of a photon BEC is described in Sec. VII. The conclusions follow in
Sec. VIII.
II. THE CONDENSATE DENSITY PROFILE
While at ¬Ѓnite temperatures there is no true BEC in any in¬Ѓnite untrapped two-dimensional (2D) system, a true
2D BEC quantum phase transition can be obtained in the presence of a con¬Ѓning potential [14, 15]. In an in¬Ѓnite
translationally invariant two-dimensional system, without a trap, super¬‚uidity occurs via a Kosterlitz€'Thouless
super¬‚uid (KTS) phase transition [16]. While KTS phase transition occurs in systems, characterized by thermal
equilibrium, it survives in a dissipative highly nonequilibrium system driven into a steady state [17].
The trap for the cavity photons can be formed by the concave spherical mirrors of the microcavity, that provide
the axial symmetry for a trapped gas of photons. Thus the transverse (along xy plane of the cavity) con¬Ѓnement
of photons can be achieved by using an optical microcavity with a variable width. Let us introduce the frame of
reference, where z€'axis is directed along the axis of cavity mirrors, and (x, y) plane is perpendicular to this axis. The
energy spectrum E(k) for small wave vectors k of photons, con¬Ѓned in z direction in an ideal microcavity with the
coordinate-dependent width L(r), is given by [2]
E(k) =
ЇhЂcњn
...
[23] L. Onsager, ЂњStatistical Hydrodynamics,Ђќ Nuovo Cimento Suppl. 6, 279 (1949).
[24] RP Feynman, ЂњApplication of Quantum Mechanics to Liquid Helium,Ђќ Prog. Low Temp. Phys. 1, 17 (1955).
[25] PC Hohenberg and PC Martin, ЂњMicroscopic Theory of Super¬‚uid Helium,Ђќ Ann. Phys. 34, 291 (1965).
[26] G. Blatter, MY FeigelЂman, YB Geshkenbein, AI Larkin, and VM Vinokur, ЂњVortices in high-temperature super-
conductors,Ђќ Rev. Mod. Phys. 66, 1125 (1994).
[27] NS Voronova and Yu. E. Lozovik, ЂњExcitons in cores of exciton-polariton vortices,Ђќ Phys. Rev. B 86, 195305 (2012);
NS Voronova, AA Elistratov, and Yu. E. Lozovik, ЂњDetuning-Controlled Internal Oscillations in an Exciton-Polariton
Condensate,Ђќ Phys. Rev. Lett. 115, 186402 (2015) .
[28] A. Gri¬ѓn, ЂњConserving and gapless approximations for an inhomogeneous Bose gas at ¬Ѓnite temperatures,Ђќ Phys. Rev. B
53, 9341 (1996).
[29] AA Abrikosov, LP Gorkov and IE Dzyaloshinski, Methods of Quantum Field Theory in Statistical Physics (Prentice-
Hall, Englewood Cli¬Ђs. NJ, 1963).
[30] OL Berman, Yu. E. Lozovik, and DW Snoke, ЂњTheory of Bose-Einstein condensation and super¬‚uidity of two-
dimensional polaritons in an in-plane harmonic potential,Ђќ Phys. Rev. B 77, 155317 (2008).
[31] OL Berman, R. Ya. Kezerashvili, and K. Ziegler, ЂњSuper¬‚uidity and collective properties of excitonic polaritons in gapped
graphene in a microcavityЂќ, Phys. Rev. B 86, 235404 (2012).
[32] A. Amo, J. Lefr`ere, S. Pigeon, C. Adrados, C. Ciuti, I. Carusotto, R. Houdrґe, E. Giacobino, and A. Bramati, ЂњSuper¬‚uidity
of polaritons in semiconductor microcavities,Ђќ Nature Physics 5, 805 (2009).
[33] JP Fernґandez and WJ Mullin, ЂњThe Two-Dimensional Bose€'Einstein Condensate,Ђќ J. Low. Temp. Phys. 128, 233
Dari anotasi, kami
hanya memerlukan informasi tentang penulis dan subbagian artikel.
Di bawah ini, sebagai contoh, kami mempertimbangkan berbagai artikel dari bagian cond-mat untuk tahun 2017. Semua yang dijelaskan mudah direproduksi untuk bagian lainnya.
Cara paling sederhana untuk memulai studi teks adalah membuat daftar kata kunci yang menarik bagi kami dan menghitung proporsi artikel di mana mereka muncul.
Mari kita mengevaluasi perubahan dalam pembagian, misalnya, dibandingkan dengan 2010.
Perbedaan dalam saham untuk tahun 2017 dan 2010. (catatan: Hadiah Nobel dalam Fisika pada tahun 2016 dianugerahi untuk studi fase topologi materi)Selanjutnya, berdasarkan konten teks, kami membangun model
word2vec (untuk visualisasi lebih baik mengambil jendela yang lebih luas, 20 kata). Untuk setiap kunci, kami mengambil N tetangga terdekat dan dengan bantuan t-SNE kami menghitung koordinat 2D mereka. Kami melihat bagaimana kata kunci saling terkait:
Awan kata kunci dan satelitnya, N = 100. Semakin jauh tetangga ke-N, semakin banyak kata yang disorot. Pasangan yang relevan: Graphene + Semiconductor, Qubit + Dot, Topological + Hall, Bose + KondensasiPada arxiv ada subbagian untuk setiap bagian. Kami menemukan di bagian mana kata kunci ditemukan:
Decoding nama-nama subdivisi dari cond-matDi atas dijelaskan bekerja dengan sekumpulan kata kunci yang ingin Anda buat secara manual, tetapi beberapa topik mungkin telah dilewati. Mari kita membangun model
LDA dan melihat topik:
Untuk setiap topik, kami mendapatkan daftar artikel yang sesuai dengannya:
Seperti yang Anda ketahui, saat membaca artikel selalu bermanfaat untuk mempelajari tautan. Bisakah kita mengumpulkan beberapa informasi tentang mereka? Kita bisa! Mari kita lihat bagian belakang teks.
Buntut[23] L. Onsager, ЂњStatistical Hydrodynamics,Ђќ Nuovo Cimento Suppl. 6, 279 (1949).
[24] RP Feynman, ЂњApplication of Quantum Mechanics to Liquid Helium,Ђќ Prog. Low Temp. Phys. 1, 17 (1955).
[25] PC Hohenberg and PC Martin, ЂњMicroscopic Theory of Super¬‚uid Helium,Ђќ Ann. Phys. 34, 291 (1965).
[26] G. Blatter, MY FeigelЂman, YB Geshkenbein, AI Larkin, and VM Vinokur, ЂњVortices in high-temperature super-
conductors,Ђќ Rev. Mod. Phys. 66, 1125 (1994).
[27] NS Voronova and Yu. E. Lozovik, ЂњExcitons in cores of exciton-polariton vortices,Ђќ Phys. Rev. B 86, 195305 (2012);
NS Voronova, AA Elistratov, and Yu. E. Lozovik, ЂњDetuning-Controlled Internal Oscillations in an Exciton-Polariton
Condensate,Ђќ Phys. Rev. Lett. 115, 186402 (2015) .
[28] A. Gri¬ѓn, ЂњConserving and gapless approximations for an inhomogeneous Bose gas at ¬Ѓnite temperatures,Ђќ Phys. Rev. B
53, 9341 (1996).
[29] AA Abrikosov, LP Gorkov and IE Dzyaloshinski, Methods of Quantum Field Theory in Statistical Physics (Prentice-
Hall, Englewood Cli¬Ђs. NJ, 1963).
[30] OL Berman, Yu. E. Lozovik, and DW Snoke, ЂњTheory of Bose-Einstein condensation and super¬‚uidity of two-
dimensional polaritons in an in-plane harmonic potential,Ђќ Phys. Rev. B 77, 155317 (2008).
[31] OL Berman, R. Ya. Kezerashvili, and K. Ziegler, ЂњSuper¬‚uidity and collective properties of excitonic polaritons in gapped
graphene in a microcavityЂќ, Phys. Rev. B 86, 235404 (2012).
[32] A. Amo, J. Lefr`ere, S. Pigeon, C. Adrados, C. Ciuti, I. Carusotto, R. Houdrґe, E. Giacobino, and A. Bramati, ЂњSuper¬‚uidity
of polaritons in semiconductor microcavities,Ђќ Nature Physics 5, 805 (2009).
[33] JP Fernґandez and WJ Mullin, ЂњThe Two-Dimensional Bose€'Einstein Condensate,Ђќ J. Low. Temp. Phys. 128, 233
Konverter PDF menangani bagian dengan bibliografi dengan baik. Ini berarti bahwa tautan dapat diambil dengan beberapa ekspresi reguler. Sebagai hasilnya, kami mendapatkan daftar artikel yang sering dikutip, harus dibaca.
Lihat tautan ini di
Google Cendekia :
Buat daftar penulis paling aktif untuk setiap subbagian - kami mengekstrak dan menghitung konten tag penulis dari anotasi. Jumlah artikel yang diterbitkan oleh penulis tertentu adalah karakteristik yang dapat dimengerti, tetapi tidak dapat diandalkan, dapat ditambah dengan median jumlah penulis bersama (lihat buku catatan).
Penulis dari mes-hall tidak tertandingi: kecepatan kerja rata-rata mereka lebih dari satu artikel per minggu ...Akhirnya, kami memperkirakan proporsi subbagian:
Demo laptop:
cond-mat.17 ,
astro-ph.17 ,
cs.17 ,
math.17Github :
ilovescience