Hai
Banyak orang ingin memulai pemrograman di android, tetapi Android Studio dan Java membuat mereka takut. Mengapa Karena itu dalam arti dari meriam pada burung pipit. "Aku hanya ingin membuat ular, itu saja!"
Ayo mulai! (bonus di akhir)
Mengapa membuat tutorial ular lain di Kivy? (opsional untuk membaca)Jika Anda seorang pythonist dan ingin mulai mengembangkan game sederhana untuk android, Anda harus sudah google "snake on android" dan menemukannya
(Eng) atau
terjemahannya (Rus) . Dan saya juga melakukannya. Sayangnya, saya menemukan artikel tersebut tidak berguna karena beberapa alasan:
Kode salah
Kelemahan kecil:
- Penggunaan "tail" dan "head" secara terpisah. Ini tidak perlu, karena di kepala ular adalah bagian pertama dari ekor. Anda tidak boleh membagi seluruh ular menjadi dua bagian, yang kode ini ditulis secara terpisah.
- Clock.schedule dari self.update dipanggil dari ... self.update.
- Kelas level kedua (dengan syarat titik masuk dari kelas pertama) Playground dideklarasikan di awal, tetapi kelas level pertama SnakeApp dideklarasikan di akhir file.
- Nama untuk arah ("atas", "bawah", ...) bukan vektor ((0, 1), (1, 0) ...).
Kerugian serius:
- Objek dinamis (seperti buah) dilampirkan ke file kv, jadi Anda tidak dapat membuat lebih dari satu apel tanpa menulis ulang setengah kode
- Logika yang indah dari menggerakkan ular bukannya sel demi sel.
- 350 baris - kode terlalu panjang.
Artikel ini tidak jelas bagi pemula.
Ini pendapat pribadi saya. Selain itu, saya tidak dapat menjamin bahwa artikel saya akan lebih menarik dan mudah dipahami. Tapi saya akan mencoba, dan saya jamin:
- Kode akan pendek
- Ular cantik (relatif)
- Tutorial akan memiliki pengembangan bertahap.
Hasilnya tidak kome il faut

Tidak ada jarak antara sel, segitiga indah, ular menyentak.
Kenalan
Aplikasi pertama
Pastikan sudah menginstal Kivy (jika tidak, ikuti
instruksi ) dan jalankan
buildozer init dalam folder proyek.
Jalankan program pertama:
main.py
from kivy.app import App from kivy.uix.widget import Widget class WormApp(App): def build(self): return Widget() if __name__ == '__main__': WormApp().run()

Kami telah membuat widget. Demikian pula, kita dapat membuat tombol atau elemen lain dari antarmuka grafis:
from kivy.app import App from kivy.uix.widget import Widget from kivy.uix.button import Button class WormApp(App): def build(self): self.but = Button() self.but.pos = (100, 100) self.but.size = (200, 200) self.but.text = "Hello, cruel world" self.form = Widget() self.form.add_widget(self.but) return self.form if __name__ == '__main__': WormApp().run()

Hore! Selamat! Anda telah membuat tombol!
File .Kv
Namun, ada cara lain untuk membuat elemen tersebut. Pertama, nyatakan formulir kami:
from kivy.app import App from kivy.uix.widget import Widget from kivy.uix.button import Button class Form(Widget): def __init__(self): super().__init__() self.but1 = Button() self.but1.pos = (100, 100) self.add_widget(self.but1) class WormApp(App): def build(self): self.form = Form() return self.form if __name__ == '__main__': WormApp().run()
Kemudian buat file "worm.kv".
worm.kv
<Form>: but2: but_id Button: id: but_id pos: (200, 200)
Apa yang terjadi Kami membuat tombol lain dan menetapkan id but_id. Sekarang but_id dikaitkan dengan formulir but2. Ini berarti bahwa kita dapat mengakses tombol menggunakan but2:
class Form(Widget): def __init__(self): super().__init__() self.but1 = Button() self.but1.pos = (100, 100) self.add_widget(self.but1)
Grafik
Selanjutnya, buat elemen grafik. Pertama, nyatakan di worm.kv:
<Form>: <Cell>: canvas: Rectangle: size: self.size pos: self.pos
Kami menghubungkan posisi persegi panjang dengan self.pos dan ukurannya dengan self.size. Jadi sekarang properti ini tersedia dari Cell, misalnya, segera setelah kami membuat sel, kami dapat mengubah ukuran dan posisinya:
class Cell(Widget): def __init__(self, x, y, size): super().__init__() self.size = (size, size)
Oke, kami membuat kandang.
Metode yang Diperlukan
Mari kita coba gerakkan ular. Untuk melakukan ini, kita dapat menambahkan fungsi Form.update dan mengikat ke jadwal menggunakan Clock.schedule.
from kivy.app import App from kivy.uix.widget import Widget from kivy.clock import Clock class Cell(Widget): def __init__(self, x, y, size): super().__init__() self.size = (size, size) self.pos = (x, y) class Form(Widget): def __init__(self): super().__init__() self.cell = Cell(100, 100, 30) self.add_widget(self.cell) def start(self): Clock.schedule_interval(self.update, 0.01) def update(self, _): self.cell.pos = (self.cell.pos[0] + 2, self.cell.pos[1] + 3) class WormApp(App): def build(self): self.form = Form() self.form.start() return self.form if __name__ == '__main__': WormApp().run()
Sel akan bergerak dalam bentuk. Seperti yang Anda lihat, kita dapat mengatur timer untuk fungsi apa pun menggunakan Jam.
Selanjutnya, buat acara sentuh. Formulir Penulisan Ulang:
class Form(Widget): def __init__(self): super().__init__() self.cells = [] def start(self): Clock.schedule_interval(self.update, 0.01) def update(self, _): for cell in self.cells: cell.pos = (cell.pos[0] + 2, cell.pos[1] + 3) def on_touch_down(self, touch): cell = Cell(touch.x, touch.y, 30) self.add_widget(cell) self.cells.append(cell)
Setiap touch_down membuat sel dengan koordinat = (touch.x, touch.y) dan ukuran = 30. Kemudian, kita akan menambahkannya sebagai widget bentuk AND ke array kita sendiri (untuk mengaksesnya nanti).
Sekarang setiap klik pada formulir menghasilkan sel.
Pengaturan yang bagus
Karena kita ingin membuat ular yang indah, kita harus secara logis memisahkan posisi grafik dan nyata.
MengapaAda banyak alasan untuk melakukan ini. Semua logika harus dihubungkan dengan apa yang disebut posisi nyata, tetapi grafik adalah hasil dari masa kini. Misalnya, jika kita ingin membuat indentasi, posisi saat ini adalah (100, 100) sedangkan posisi grafik adalah (102, 102).
PS Kami tidak akan mandi uap jika kami berurusan dengan on_draw. Tapi sekarang kita tidak perlu menggambar ulang bentuknya dengan cakar.
Mari kita ubah file worm.kv:
<Form>: <Cell>: canvas: Rectangle: size: self.graphical_size pos: self.graphical_pos
dan main.py:
... from kivy.properties import * ... class Cell(Widget): graphical_size = ListProperty([1, 1]) graphical_pos = ListProperty([1, 1]) def __init__(self, x, y, size, margin=4): super().__init__() self.actual_size = (size, size) self.graphical_size = (size - margin, size - margin) self.margin = margin self.actual_pos = (x, y) self.graphical_pos_attach() def graphical_pos_attach(self): self.graphical_pos = (self.actual_pos[0] - self.graphical_size[0] / 2, self.actual_pos[1] - self.graphical_size[1] / 2) ... class Form(Widget): def __init__(self): super().__init__() self.cell1 = Cell(100, 100, 30) self.cell2 = Cell(130, 100, 30) self.add_widget(self.cell1) self.add_widget(self.cell2) ...
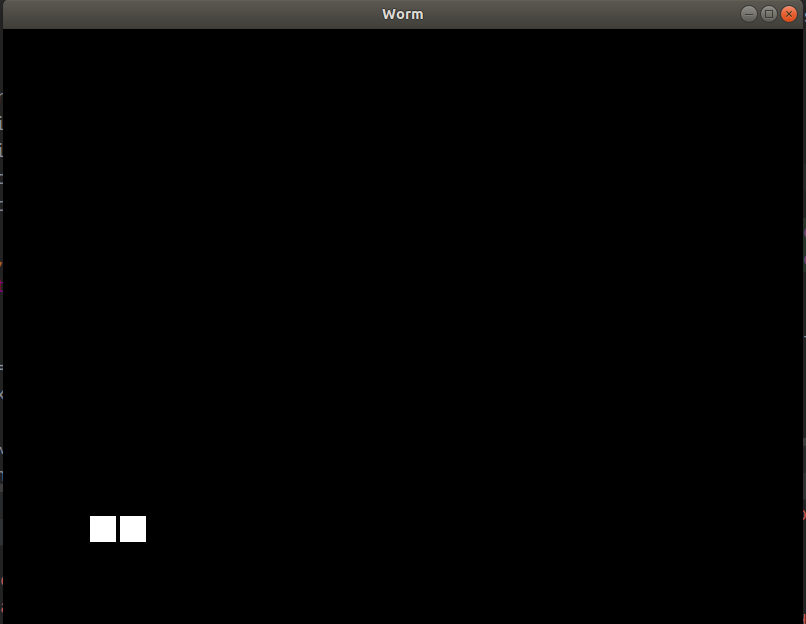
Lekukan telah muncul, sehingga terlihat lebih baik meskipun faktanya kita membuat sel kedua dengan X = 130, bukan 132. Nanti kita akan melakukan gerakan lunak berdasarkan jarak antara actual_pos dan graphical_pos.
Pemrograman Cacing
Pengumuman
Inisialisasi konfigurasi di main.py
class Config: DEFAULT_LENGTH = 20 CELL_SIZE = 25 APPLE_SIZE = 35 MARGIN = 4 INTERVAL = 0.2 DEAD_CELL = (1, 0, 0, 1) APPLE_COLOR = (1, 1, 0, 1)
(Percayalah, kamu akan menyukainya!)
Kemudian tetapkan config ke aplikasi:
class WormApp(App): def __init__(self): super().__init__() self.config = Config() self.form = Form(self.config) def build(self): self.form.start() return self.form
Tulis ulang init dan mulai:
class Form(Widget): def __init__(self, config): super().__init__() self.config = config self.worm = None def start(self): self.worm = Worm(self.config) self.add_widget(self.worm) Clock.schedule_interval(self.update, self.config.INTERVAL)
Lalu, Cell:
class Cell(Widget): graphical_size = ListProperty([1, 1]) graphical_pos = ListProperty([1, 1]) def __init__(self, x, y, size, margin=4): super().__init__() self.actual_size = (size, size) self.graphical_size = (size - margin, size - margin) self.margin = margin self.actual_pos = (x, y) self.graphical_pos_attach() def graphical_pos_attach(self): self.graphical_pos = (self.actual_pos[0] - self.graphical_size[0] / 2, self.actual_pos[1] - self.graphical_size[1] / 2) def move_to(self, x, y): self.actual_pos = (x, y) self.graphical_pos_attach() def move_by(self, x, y, **kwargs): self.move_to(self.actual_pos[0] + x, self.actual_pos[1] + y, **kwargs) def get_pos(self): return self.actual_pos def step_by(self, direction, **kwargs): self.move_by(self.actual_size[0] * direction[0], self.actual_size[1] * direction[1], **kwargs)
Saya harap ini kurang lebih jelas.
Dan akhirnya Worm:
class Worm(Widget): def __init__(self, config): super().__init__() self.cells = [] self.config = config self.cell_size = config.CELL_SIZE self.head_init((100, 100)) for i in range(config.DEFAULT_LENGTH): self.lengthen() def destroy(self): for i in range(len(self.cells)): self.remove_widget(self.cells[i]) self.cells = [] def lengthen(self, pos=None, direction=(0, 1)):
Mari kita buat worm kita.

Gerakan
Sekarang kami memindahkannya.
Sederhana:
class Worm(Widget): ... def move(self, direction): for i in range(len(self.cells) - 1, 0, -1): self.cells[i].move_to(*self.cells[i - 1].get_pos()) self.cells[0].step_by(direction)
class Form(Widget): def __init__(self, config): super().__init__() self.config = config self.worm = None self.cur_dir = (0, 0) def start(self): self.worm = Worm(self.config) self.add_widget(self.worm) self.cur_dir = (1, 0) Clock.schedule_interval(self.update, self.config.INTERVAL) def update(self, _): self.worm.move(self.cur_dir)

Itu hidup! Itu hidup!
Manajemen
Seperti yang Anda dapat menilai dari gambar pertama, kendali ular akan seperti ini:
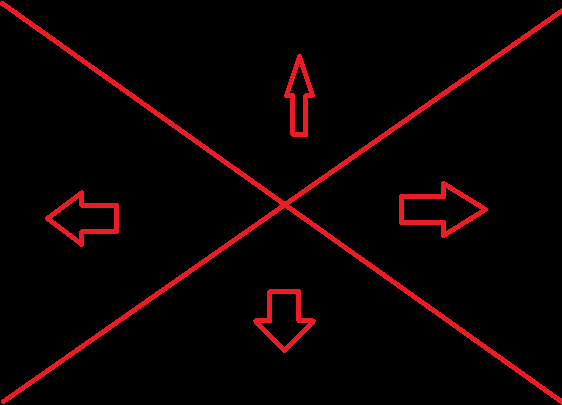
class Form(Widget): ... def on_touch_down(self, touch): ws = touch.x / self.size[0] hs = touch.y / self.size[1] aws = 1 - ws if ws > hs and aws > hs: cur_dir = (0, -1)

Wow
Membuat buah
Pertama mendeklarasikan.
class Form(Widget): ... def __init__(self, config): super().__init__() self.config = config self.worm = None self.cur_dir = (0, 0) self.fruit = None ... def random_cell_location(self, offset): x_row = self.size[0] // self.config.CELL_SIZE x_col = self.size[1] // self.config.CELL_SIZE return random.randint(offset, x_row - offset), random.randint(offset, x_col - offset) def random_location(self, offset): x_row, x_col = self.random_cell_location(offset) return self.config.CELL_SIZE * x_row, self.config.CELL_SIZE * x_col def fruit_dislocate(self): x, y = self.random_location(2) self.fruit.move_to(x, y) ... def start(self): self.fruit = Cell(0, 0, self.config.APPLE_SIZE, self.config.MARGIN) self.worm = Worm(self.config) self.fruit_dislocate() self.add_widget(self.worm) self.add_widget(self.fruit) self.cur_dir = (1, 0) Clock.schedule_interval(self.update, self.config.INTERVAL)
Hasil saat ini:

Sekarang kita harus mendeklarasikan beberapa metode Worm:
class Worm(Widget): ...
Bonus lain dari fungsi collect_positionsNgomong-ngomong, setelah kami menyatakan collect_positions, kami dapat meningkatkan fruit_dislocate:
class Form(Widget): def fruit_dislocate(self): x, y = self.random_location(2) while (x, y) in self.worm.gather_positions(): x, y = self.random_location(2) self.fruit.move_to(x, y)
Pada titik ini, posisi apel tidak sesuai dengan posisi ekor
... dan tambahkan tanda centang untuk memperbarui ()
class Form(Widget): ... def update(self, _): self.worm.move(self.cur_dir) if self.worm.head_intersect(self.fruit): directions = [(0, 1), (0, -1), (1, 0), (-1, 0)] self.worm.lengthen(direction=random.choice(directions)) self.fruit_dislocate()
Penentuan persimpangan kepala dan ekor
Kami ingin mengetahui apakah posisi kepala sama dengan beberapa sel ekor.
class Form(Widget): ... def __init__(self, config): super().__init__() self.config = config self.worm = None self.cur_dir = (0, 0) self.fruit = None self.game_on = True def update(self, _): if not self.game_on: return self.worm.move(self.cur_dir) if self.worm.head_intersect(self.fruit): directions = [(0, 1), (0, -1), (1, 0), (-1, 0)] self.worm.lengthen(direction=random.choice(directions)) self.fruit_dislocate() if self.worm_bite_self(): self.game_on = False def worm_bite_self(self): for cell in self.worm.cells[1:]: if self.worm.head_intersect(cell): return cell return False
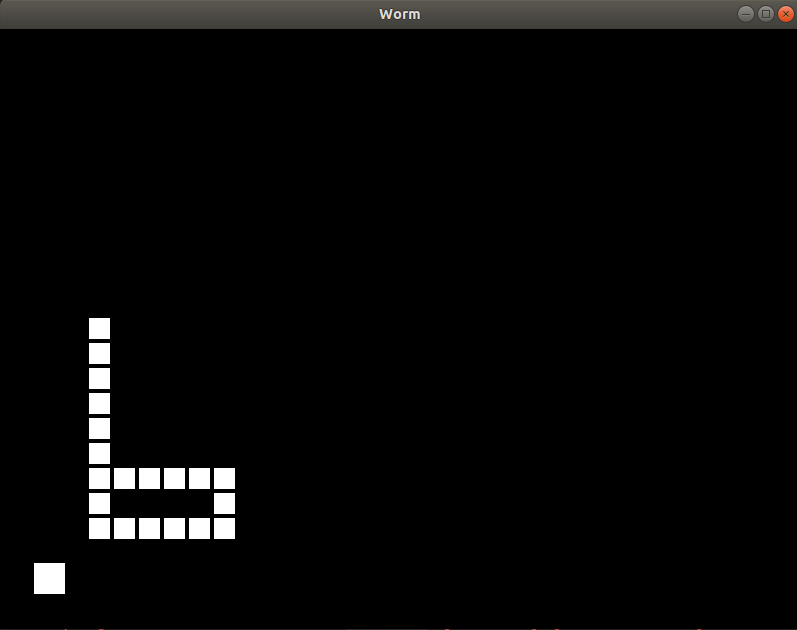
Pewarnaan, dekorasi, refactoring kode
Mari kita mulai dengan refactoring.
Tulis ulang dan tambahkan
class Form(Widget): ... def start(self): self.worm = Worm(self.config) self.add_widget(self.worm) if self.fruit is not None: self.remove_widget(self.fruit) self.fruit = Cell(0, 0, self.config.APPLE_SIZE) self.fruit_dislocate() self.add_widget(self.fruit) Clock.schedule_interval(self.update, self.config.INTERVAL) self.game_on = True self.cur_dir = (0, -1) def stop(self): self.game_on = False Clock.unschedule(self.update) def game_over(self): self.stop() ... def on_touch_down(self, touch): if not self.game_on: self.worm.destroy() self.start() return ...
Sekarang jika wormnya mati (beku), jika Anda mengklik layar, permainan akan dimulai kembali.
Sekarang mari kita beralih ke dekorasi dan pewarnaan.
worm.kv
<Form>: popup_label: popup_label score_label: score_label canvas: Color: rgba: (.5, .5, .5, 1.0) Line: width: 1.5 points: (0, 0), self.size Line: width: 1.5 points: (self.size[0], 0), (0, self.size[1]) Label: id: score_label text: "Score: " + str(self.parent.worm_len) width: self.width Label: id: popup_label width: self.width <Worm>: <Cell>: canvas: Color: rgba: self.color Rectangle: size: self.graphical_size pos: self.graphical_pos
Kami menulis ulang WormApp:
class WormApp(App): def build(self): self.config = Config() self.form = Form(self.config) return self.form def on_start(self): self.form.start()

Mewarnai Tulis ulang Sel di .kv:
<Cell>: canvas: Color: rgba: self.color Rectangle: size: self.graphical_size pos: self.graphical_pos
Tambahkan ini ke Sel .__ init__:
self.color = (0.2, 1.0, 0.2, 1.0)
dan ini untuk Form.start
self.fruit.color = (1.0, 0.2, 0.2, 1.0)
Luar biasa, nikmati ular

Akhirnya, kita akan membuat tulisan "game over"
class Form(Widget): ... def __init__(self, config): ... self.popup_label.text = "" ... def stop(self, text=""): self.game_on = False self.popup_label.text = text Clock.unschedule(self.update) def game_over(self): self.stop("GAME OVER" + " " * 5 + "\ntap to reset")
Dan mengatur sel "terluka" menjadi merah:
bukannya
def update(self, _): ... if self.worm_bite_self(): self.game_over() ...
tulis
def update(self, _): cell = self.worm_bite_self() if cell: cell.color = (1.0, 0.2, 0.2, 1.0) self.game_over()
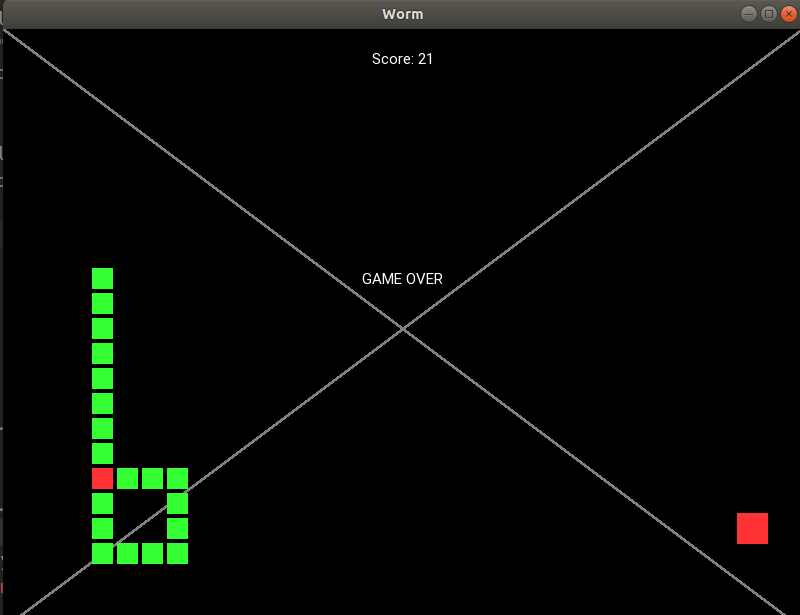
Apakah kamu masih di sini Bagian yang paling menarik ada di depan!
Bonus - gerakan halus
Karena langkah worm sama dengan cell_size, itu tidak terlihat sangat mulus. Tapi kami ingin melangkah sesering mungkin tanpa sepenuhnya menulis ulang logika permainan. Jadi, kita membutuhkan mekanisme yang menggerakkan posisi grafis kita (graphical_pos) tetapi tidak mempengaruhi yang asli (actual_pos). Saya menulis kode berikut:
smooth.py
from kivy.clock import Clock import time class Timing: @staticmethod def linear(x): return x class Smooth: def __init__(self, interval=1.0/60.0): self.objs = [] self.running = False self.interval = interval def run(self): if self.running: return self.running = True Clock.schedule_interval(self.update, self.interval) def stop(self): if not self.running: return self.running = False Clock.unschedule(self.update) def setattr(self, obj, attr, value): exec("obj." + attr + " = " + str(value)) def getattr(self, obj, attr): return float(eval("obj." + attr)) def update(self, _): cur_time = time.time() for line in self.objs: obj, prop_name_x, prop_name_y, from_x, from_y, to_x, to_y, start_time, period, timing = line time_gone = cur_time - start_time if time_gone >= period: self.setattr(obj, prop_name_x, to_x) self.setattr(obj, prop_name_y, to_y) self.objs.remove(line) else: share = time_gone / period acs = timing(share) self.setattr(obj, prop_name_x, from_x * (1 - acs) + to_x * acs) self.setattr(obj, prop_name_y, from_y * (1 - acs) + to_y * acs) if len(self.objs) == 0: self.stop() def move_to(self, obj, prop_name_x, prop_name_y, to_x, to_y, t, timing=Timing.linear): self.objs.append((obj, prop_name_x, prop_name_y, self.getattr(obj, prop_name_x), self.getattr(obj, prop_name_y), to_x, to_y, time.time(), t, timing)) self.run() class XSmooth(Smooth): def __init__(self, props, timing=Timing.linear, *args, **kwargs): super().__init__(*args, **kwargs) self.props = props self.timing = timing def move_to(self, obj, to_x, to_y, t): super().move_to(obj, *self.props, to_x, to_y, t, timing=self.timing)
Mereka yang tidak suka kode iniModul ini bukan bagian atas keanggunan. Saya mengakui keputusan ini sebagai hal yang buruk. Tapi ini hanya solusi halo-dunia.
Jadi, Anda cukup membuat smooth.py dan menyalin kode ke file.
Akhirnya, buat IT berfungsi!
class Form(Widget): ... def __init__(self, config): ... self.smooth = smooth.XSmooth(["graphical_pos[0]", "graphical_pos[1]"])
Ganti self.worm.move () dengan
class Form(Widget): ... def update(self, _): ... self.worm.move(self.cur_dir, smooth_motion=(self.smooth, self.config.INTERVAL))
Dan ini adalah bagaimana seharusnya metode Cell
class Cell(Widget): ... def graphical_pos_attach(self, smooth_motion=None): to_x, to_y = self.actual_pos[0] - self.graphical_size[0] / 2, self.actual_pos[1] - self.graphical_size[1] / 2 if smooth_motion is None: self.graphical_pos = to_x, to_y else: smoother, t = smooth_motion smoother.move_to(self, to_x, to_y, t) def move_to(self, x, y, **kwargs): self.actual_pos = (x, y) self.graphical_pos_attach(**kwargs) def move_by(self, x, y, **kwargs): self.move_to(self.actual_pos[0] + x, self.actual_pos[1] + y, **kwargs)
Baiklah, itu saja, terima kasih atas perhatian Anda! Kode di bawah.
Demo video cara kerjanya:
Kode akhirmain.py from kivy.app import App from kivy.uix.widget import Widget from kivy.clock import Clock from kivy.properties import * import random import smooth class Cell(Widget): graphical_size = ListProperty([1, 1]) graphical_pos = ListProperty([1, 1]) color = ListProperty([1, 1, 1, 1]) def __init__(self, x, y, size, margin=4): super().__init__() self.actual_size = (size, size) self.graphical_size = (size - margin, size - margin) self.margin = margin self.actual_pos = (x, y) self.graphical_pos_attach() self.color = (0.2, 1.0, 0.2, 1.0) def graphical_pos_attach(self, smooth_motion=None): to_x, to_y = self.actual_pos[0] - self.graphical_size[0] / 2, self.actual_pos[1] - self.graphical_size[1] / 2 if smooth_motion is None: self.graphical_pos = to_x, to_y else: smoother, t = smooth_motion smoother.move_to(self, to_x, to_y, t) def move_to(self, x, y, **kwargs): self.actual_pos = (x, y) self.graphical_pos_attach(**kwargs) def move_by(self, x, y, **kwargs): self.move_to(self.actual_pos[0] + x, self.actual_pos[1] + y, **kwargs) def get_pos(self): return self.actual_pos def step_by(self, direction, **kwargs): self.move_by(self.actual_size[0] * direction[0], self.actual_size[1] * direction[1], **kwargs) class Worm(Widget): def __init__(self, config): super().__init__() self.cells = [] self.config = config self.cell_size = config.CELL_SIZE self.head_init((100, 100)) for i in range(config.DEFAULT_LENGTH): self.lengthen() def destroy(self): for i in range(len(self.cells)): self.remove_widget(self.cells[i]) self.cells = [] def lengthen(self, pos=None, direction=(0, 1)): if pos is None: px = self.cells[-1].get_pos()[0] + direction[0] * self.cell_size py = self.cells[-1].get_pos()[1] + direction[1] * self.cell_size pos = (px, py) self.cells.append(Cell(*pos, self.cell_size, margin=self.config.MARGIN)) self.add_widget(self.cells[-1]) def head_init(self, pos): self.lengthen(pos=pos) def move(self, direction, **kwargs): for i in range(len(self.cells) - 1, 0, -1): self.cells[i].move_to(*self.cells[i - 1].get_pos(), **kwargs) self.cells[0].step_by(direction, **kwargs) def gather_positions(self): return [cell.get_pos() for cell in self.cells] def head_intersect(self, cell): return self.cells[0].get_pos() == cell.get_pos() class Form(Widget): worm_len = NumericProperty(0) def __init__(self, config): super().__init__() self.config = config self.worm = None self.cur_dir = (0, 0) self.fruit = None self.game_on = True self.smooth = smooth.XSmooth(["graphical_pos[0]", "graphical_pos[1]"]) def random_cell_location(self, offset): x_row = self.size[0] // self.config.CELL_SIZE x_col = self.size[1] // self.config.CELL_SIZE return random.randint(offset, x_row - offset), random.randint(offset, x_col - offset) def random_location(self, offset): x_row, x_col = self.random_cell_location(offset) return self.config.CELL_SIZE * x_row, self.config.CELL_SIZE * x_col def fruit_dislocate(self): x, y = self.random_location(2) while (x, y) in self.worm.gather_positions(): x, y = self.random_location(2) self.fruit.move_to(x, y) def start(self): self.worm = Worm(self.config) self.add_widget(self.worm) if self.fruit is not None: self.remove_widget(self.fruit) self.fruit = Cell(0, 0, self.config.APPLE_SIZE) self.fruit.color = (1.0, 0.2, 0.2, 1.0) self.fruit_dislocate() self.add_widget(self.fruit) self.game_on = True self.cur_dir = (0, -1) Clock.schedule_interval(self.update, self.config.INTERVAL) self.popup_label.text = "" def stop(self, text=""): self.game_on = False self.popup_label.text = text Clock.unschedule(self.update) def game_over(self): self.stop("GAME OVER" + " " * 5 + "\ntap to reset") def align_labels(self): try: self.popup_label.pos = ((self.size[0] - self.popup_label.width) / 2, self.size[1] / 2) self.score_label.pos = ((self.size[0] - self.score_label.width) / 2, self.size[1] - 80) except: print(self.__dict__) assert False def update(self, _): if not self.game_on: return self.worm.move(self.cur_dir, smooth_motion=(self.smooth, self.config.INTERVAL)) if self.worm.head_intersect(self.fruit): directions = [(0, 1), (0, -1), (1, 0), (-1, 0)] self.worm.lengthen(direction=random.choice(directions)) self.fruit_dislocate() cell = self.worm_bite_self() if cell: cell.color = (1.0, 0.2, 0.2, 1.0) self.game_over() self.worm_len = len(self.worm.cells) self.align_labels() def on_touch_down(self, touch): if not self.game_on: self.worm.destroy() self.start() return ws = touch.x / self.size[0] hs = touch.y / self.size[1] aws = 1 - ws if ws > hs and aws > hs: cur_dir = (0, -1) elif ws > hs >= aws: cur_dir = (1, 0) elif ws <= hs < aws: cur_dir = (-1, 0) else: cur_dir = (0, 1) self.cur_dir = cur_dir def worm_bite_self(self): for cell in self.worm.cells[1:]: if self.worm.head_intersect(cell): return cell return False class Config: DEFAULT_LENGTH = 20 CELL_SIZE = 25 APPLE_SIZE = 35 MARGIN = 4 INTERVAL = 0.3 DEAD_CELL = (1, 0, 0, 1) APPLE_COLOR = (1, 1, 0, 1) class WormApp(App): def build(self): self.config = Config() self.form = Form(self.config) return self.form def on_start(self): self.form.start() if __name__ == '__main__': WormApp().run()
smooth.py from kivy.clock import Clock import time class Timing: @staticmethod def linear(x): return x class Smooth: def __init__(self, interval=1.0/60.0): self.objs = [] self.running = False self.interval = interval def run(self): if self.running: return self.running = True Clock.schedule_interval(self.update, self.interval) def stop(self): if not self.running: return self.running = False Clock.unschedule(self.update) def setattr(self, obj, attr, value): exec("obj." + attr + " = " + str(value)) def getattr(self, obj, attr): return float(eval("obj." + attr)) def update(self, _): cur_time = time.time() for line in self.objs: obj, prop_name_x, prop_name_y, from_x, from_y, to_x, to_y, start_time, period, timing = line time_gone = cur_time - start_time if time_gone >= period: self.setattr(obj, prop_name_x, to_x) self.setattr(obj, prop_name_y, to_y) self.objs.remove(line) else: share = time_gone / period acs = timing(share) self.setattr(obj, prop_name_x, from_x * (1 - acs) + to_x * acs) self.setattr(obj, prop_name_y, from_y * (1 - acs) + to_y * acs) if len(self.objs) == 0: self.stop() def move_to(self, obj, prop_name_x, prop_name_y, to_x, to_y, t, timing=Timing.linear): self.objs.append((obj, prop_name_x, prop_name_y, self.getattr(obj, prop_name_x), self.getattr(obj, prop_name_y), to_x, to_y, time.time(), t, timing)) self.run() class XSmooth(Smooth): def __init__(self, props, timing=Timing.linear, *args, **kwargs): super().__init__(*args, **kwargs) self.props = props self.timing = timing def move_to(self, obj, to_x, to_y, t): super().move_to(obj, *self.props, to_x, to_y, t, timing=self.timing)
worm.kv <Form>: popup_label: popup_label score_label: score_label canvas: Color: rgba: (.5, .5, .5, 1.0) Line: width: 1.5 points: (0, 0), self.size Line: width: 1.5 points: (self.size[0], 0), (0, self.size[1]) Label: id: score_label text: "Score: " + str(self.parent.worm_len) width: self.width Label: id: popup_label width: self.width <Worm>: <Cell>: canvas: Color: rgba: self.color Rectangle: size: self.graphical_size pos: self.graphical_pos
Kode sedikit dimodifikasi oleh @tshirtmanKode saya diperiksa oleh tshirtman, salah satu kontributor Kivy, yang menyarankan agar saya menggunakan instruksi Point daripada membuat widget untuk setiap sel. Namun, kode ini sepertinya tidak mudah bagi saya untuk memahami daripada milik saya, meskipun jelas lebih baik dalam memahami pengembangan UI dan gamedev. Secara umum, ini kodenya:
main.py from kivy.app import App from kivy.uix.widget import Widget from kivy.clock import Clock from kivy.properties import * import random import smooth class Cell: def __init__(self, x, y): self.actual_pos = (x, y) def move_to(self, x, y): self.actual_pos = (x, y) def move_by(self, x, y): self.move_to(self.actual_pos[0] + x, self.actual_pos[1] + y) def get_pos(self): return self.actual_pos class Fruit(Cell): def __init__(self, x, y): super().__init__(x, y) class Worm(Widget): margin = NumericProperty(4) graphical_poses = ListProperty() inj_pos = ListProperty([-1000, -1000]) graphical_size = NumericProperty(0) def __init__(self, config, **kwargs): super().__init__(**kwargs) self.cells = [] self.config = config self.cell_size = config.CELL_SIZE self.head_init((self.config.CELL_SIZE * random.randint(3, 5), self.config.CELL_SIZE * random.randint(3, 5))) self.margin = config.MARGIN self.graphical_size = self.cell_size - self.margin for i in range(config.DEFAULT_LENGTH): self.lengthen() def destroy(self): self.cells = [] self.graphical_poses = [] self.inj_pos = [-1000, -1000] def cell_append(self, pos): self.cells.append(Cell(*pos)) self.graphical_poses.extend([0, 0]) self.cell_move_to(len(self.cells) - 1, pos) def lengthen(self, pos=None, direction=(0, 1)): if pos is None: px = self.cells[-1].get_pos()[0] + direction[0] * self.cell_size py = self.cells[-1].get_pos()[1] + direction[1] * self.cell_size pos = (px, py) self.cell_append(pos) def head_init(self, pos): self.lengthen(pos=pos) def cell_move_to(self, i, pos, smooth_motion=None): self.cells[i].move_to(*pos) to_x, to_y = pos[0], pos[1] if smooth_motion is None: self.graphical_poses[i * 2], self.graphical_poses[i * 2 + 1] = to_x, to_y else: smoother, t = smooth_motion smoother.move_to(self, "graphical_poses[" + str(i * 2) + "]", "graphical_poses[" + str(i * 2 + 1) + "]", to_x, to_y, t) def move(self, direction, **kwargs): for i in range(len(self.cells) - 1, 0, -1): self.cell_move_to(i, self.cells[i - 1].get_pos(), **kwargs) self.cell_move_to(0, (self.cells[0].get_pos()[0] + self.cell_size * direction[0], self.cells[0].get_pos()[1] + self.cell_size * direction[1]), **kwargs) def gather_positions(self): return [cell.get_pos() for cell in self.cells] def head_intersect(self, cell): return self.cells[0].get_pos() == cell.get_pos() class Form(Widget): worm_len = NumericProperty(0) fruit_pos = ListProperty([0, 0]) fruit_size = NumericProperty(0) def __init__(self, config, **kwargs): super().__init__(**kwargs) self.config = config self.worm = None self.cur_dir = (0, 0) self.fruit = None self.game_on = True self.smooth = smooth.Smooth() def random_cell_location(self, offset): x_row = self.size[0] // self.config.CELL_SIZE x_col = self.size[1] // self.config.CELL_SIZE return random.randint(offset, x_row - offset), random.randint(offset, x_col - offset) def random_location(self, offset): x_row, x_col = self.random_cell_location(offset) return self.config.CELL_SIZE * x_row, self.config.CELL_SIZE * x_col def fruit_dislocate(self, xy=None): if xy is not None: x, y = xy else: x, y = self.random_location(2) while (x, y) in self.worm.gather_positions(): x, y = self.random_location(2) self.fruit.move_to(x, y) self.fruit_pos = (x, y) def start(self): self.worm = Worm(self.config) self.add_widget(self.worm) self.fruit = Fruit(0, 0) self.fruit_size = self.config.APPLE_SIZE self.fruit_dislocate() self.game_on = True self.cur_dir = (0, -1) Clock.schedule_interval(self.update, self.config.INTERVAL) self.popup_label.text = "" def stop(self, text=""): self.game_on = False self.popup_label.text = text Clock.unschedule(self.update) def game_over(self): self.stop("GAME OVER" + " " * 5 + "\ntap to reset") def align_labels(self): self.popup_label.pos = ((self.size[0] - self.popup_label.width) / 2, self.size[1] / 2) self.score_label.pos = ((self.size[0] - self.score_label.width) / 2, self.size[1] - 80) def update(self, _): if not self.game_on: return self.worm.move(self.cur_dir, smooth_motion=(self.smooth, self.config.INTERVAL)) if self.worm.head_intersect(self.fruit): directions = [(0, 1), (0, -1), (1, 0), (-1, 0)] self.worm.lengthen(direction=random.choice(directions)) self.fruit_dislocate() cell = self.worm_bite_self() if cell is not None: self.worm.inj_pos = cell.get_pos() self.game_over() self.worm_len = len(self.worm.cells) self.align_labels() def on_touch_down(self, touch): if not self.game_on: self.worm.destroy() self.start() return ws = touch.x / self.size[0] hs = touch.y / self.size[1] aws = 1 - ws if ws > hs and aws > hs: cur_dir = (0, -1) elif ws > hs >= aws: cur_dir = (1, 0) elif ws <= hs < aws: cur_dir = (-1, 0) else: cur_dir = (0, 1) self.cur_dir = cur_dir def worm_bite_self(self): for cell in self.worm.cells[1:]: if self.worm.head_intersect(cell): return cell return None class Config: DEFAULT_LENGTH = 20 CELL_SIZE = 26
smooth.py from kivy.clock import Clock import time class Timing: @staticmethod def linear(x): return x class Smooth: def __init__(self, interval=1.0/60.0): self.objs = [] self.running = False self.interval = interval def run(self): if self.running: return self.running = True Clock.schedule_interval(self.update, self.interval) def stop(self): if not self.running: return self.running = False Clock.unschedule(self.update) def set_attr(self, obj, attr, value): exec("obj." + attr + " = " + str(value)) def get_attr(self, obj, attr): return float(eval("obj." + attr)) def update(self, _): cur_time = time.time() for line in self.objs: obj, prop_name_x, prop_name_y, from_x, from_y, to_x, to_y, start_time, period, timing = line time_gone = cur_time - start_time if time_gone >= period: self.set_attr(obj, prop_name_x, to_x) self.set_attr(obj, prop_name_y, to_y) self.objs.remove(line) else: share = time_gone / period acs = timing(share) self.set_attr(obj, prop_name_x, from_x * (1 - acs) + to_x * acs) self.set_attr(obj, prop_name_y, from_y * (1 - acs) + to_y * acs) if len(self.objs) == 0: self.stop() def move_to(self, obj, prop_name_x, prop_name_y, to_x, to_y, t, timing=Timing.linear): self.objs.append((obj, prop_name_x, prop_name_y, self.get_attr(obj, prop_name_x), self.get_attr(obj, prop_name_y), to_x, to_y, time.time(), t, timing)) self.run() class XSmooth(Smooth): def __init__(self, props, timing=Timing.linear, *args, **kwargs): super().__init__(*args, **kwargs) self.props = props self.timing = timing def move_to(self, obj, to_x, to_y, t): super().move_to(obj, *self.props, to_x, to_y, t, timing=self.timing)
worm.kv <Form>: popup_label: popup_label score_label: score_label canvas: Color: rgba: (.5, .5, .5, 1.0) Line: width: 1.5 points: (0, 0), self.size Line: width: 1.5 points: (self.size[0], 0), (0, self.size[1]) Color: rgba: (1.0, 0.2, 0.2, 1.0) Point: points: self.fruit_pos pointsize: self.fruit_size / 2 Label: id: score_label text: "Score: " + str(self.parent.worm_len) width: self.width Label: id: popup_label width: self.width <Worm>: canvas: Color: rgba: (0.2, 1.0, 0.2, 1.0) Point: points: self.graphical_poses pointsize: self.graphical_size / 2 Color: rgba: (1.0, 0.2, 0.2, 1.0) Point: points: self.inj_pos pointsize: self.graphical_size / 2
Ajukan pertanyaan.