Decidi sair de férias para estudar o desenvolvimento do Vive no Unity3D. Pesquisei alguns exemplos no Google e comecei a tentar, mas por algum motivo não funcionou. Tendo começado a entender com mais detalhes e descoberto que a Valve lançou recentemente uma atualização de plug - in para o Unity3D - uma nova versão fortemente refeita. Surgiram algumas inovações fundamentais que tornaram os tutoriais antigos não relevantes. Eu decidi escrever um novo

Vamos precisar do Unity> = 5.4.0 e do novo plugin SteamVR Plugin ( GitHub )
No próprio plugin, existem três PDFs úteis para familiarização
\ Assets \ SteamVR \ SteamVR Unity Plugin.pdf
\ Assets \ SteamVR \ SteamVR Unity Plugin - Sistema de entrada.pdf
\ Assets \ SteamVR \ InteractionSystem \ InteractionSystem.pdf
E dois exemplos:
\ Assets \ SteamVR \ Simple Sample.unity
\ Assets \ SteamVR \ InteractionSystem \ Samples \ Interactions_Example.unity
O plug-in suporta o modo de simulação - ele liga se o capacete não estiver ligado
Bem, agora passo a passo;
Crie um novo projeto de modelo 3D com o plug-in SteamVR Plugin
Nós concordamos com as configurações

Agora, o ponto principal é que você precisa configurar o gerenciamento. Selecione o item de menu Janela \ SteamVR Imput

O Unity perguntará sobre o actions.json ausente e se oferecerá para copiar o arquivo de exemplo (ele se encontra em \ Assets \ SteamVR \ Input \ ExampleJSON) - eu recomendo que você concorde.

Os arquivos json mostram que o plug-in foi projetado não apenas para o Vive, mas também para o Oculus e Windows MR, além de novos controladores de articulações. Grandes mudanças estão associadas a isso.
Na janela que se abre, basta clicar em "Salvar e gerar"

Agora você precisa adicionar o Player (Player de \ Assets \ SteamVR \ InteractionSystem \ Core \ Prefabs) à cena e remover a câmera principal
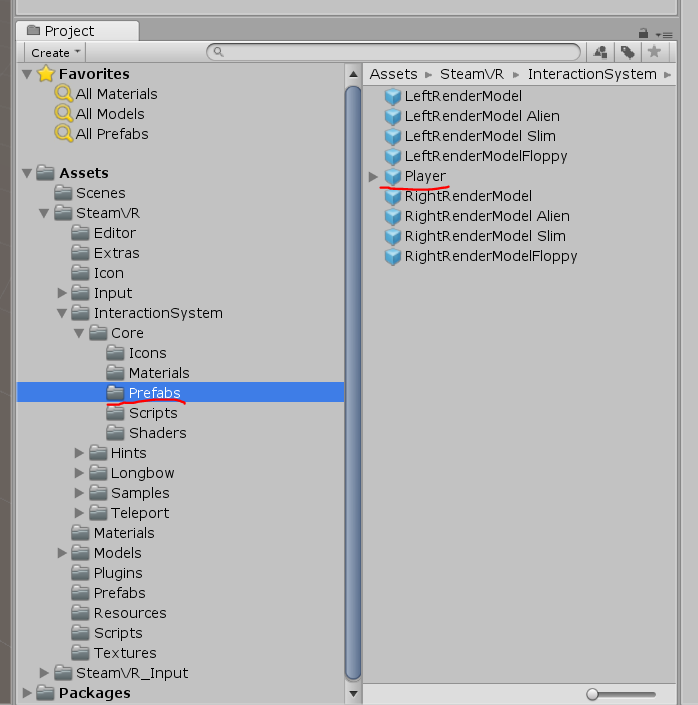
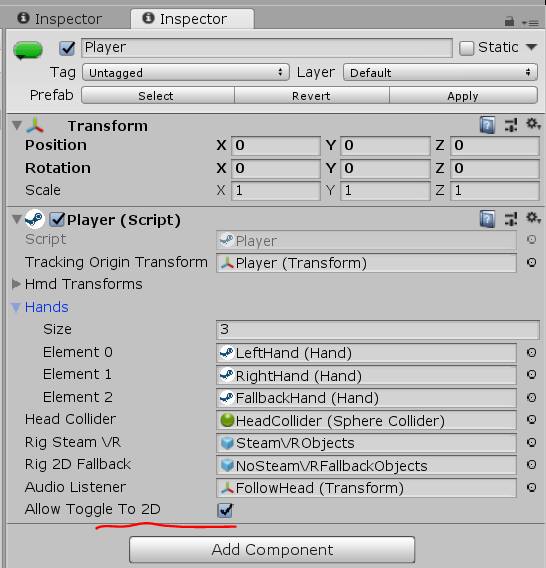
para que o modo de simulação funcione - ele deve estar ativado nas propriedades do Player
Também é útil copiar a pasta \ Assets \ SteamVR \ InteractionSystem \ Core \ Icons para \ Assets e renomeá-la para Gizmos
Você pode clicar em Reproduzir - mas apenas uma mão falsa na simulação não funcionará, é necessário copiar o script daqui e pendurá-lo no Player-> NoSteamVRFallbackObjects-> FallbackHand
Código de script de mão falsausing System.Collections.Generic; using UnityEngine; using Valve.VR; public class VrSimulatorHandFixer156 : SteamVR_Behaviour_Pose { Valve.VR.InteractionSystem.Hand _hand; protected override void Start() { base.Start(); _hand = this.gameObject.GetComponent<Valve.VR.InteractionSystem.Hand>(); _hand.handType = SteamVR_Input_Sources.RightHand; GameObject broHand = GameObject.Instantiate(_hand.gameObject); Destroy(broHand.GetComponent<VrSimulatorHandFixer156>()); broHand.SetActive(false); _hand.otherHand = broHand.GetComponent<Valve.VR.InteractionSystem.Hand>(); _hand.otherHand.handType = SteamVR_Input_Sources.LeftHand; var spoofMouse = new SpoofMouseAction(); _hand.grabGripAction = spoofMouse; spoofMouse.InitializeDictionariesExposed(_hand.handType); this.poseAction = new Poser_SteamVR_Action_Pose(); } protected override void OnEnable() { } protected override void Update() { _hand.grabGripAction.UpdateValue(SteamVR_Input_Sources.RightHand); } protected override void OnDisable() { } protected override void CheckDeviceIndex() { }
No modo VR com os controladores ligados - eles estarão visíveis
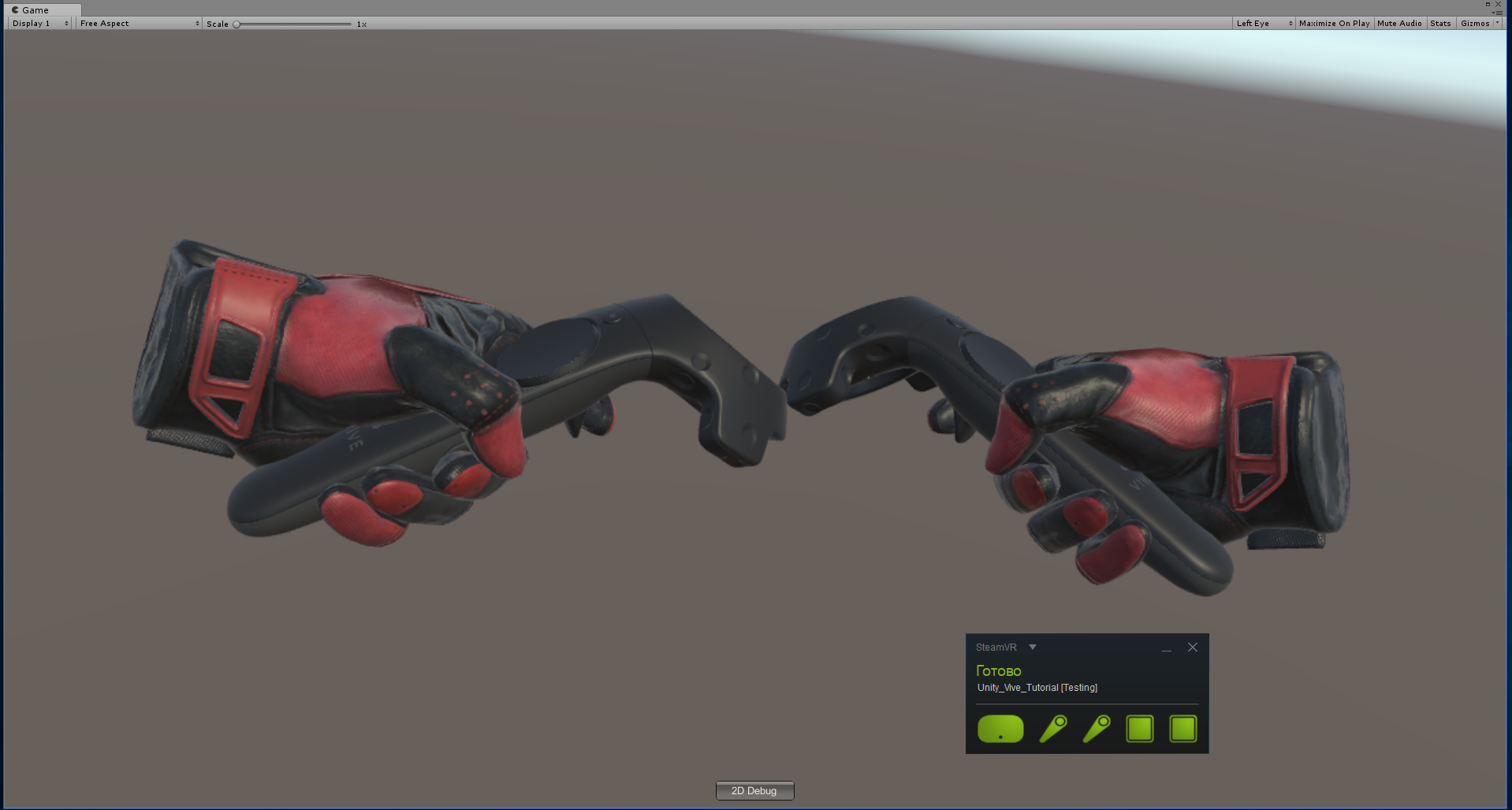
Adicionamos VR, mas não podemos nem nos mover. O plugin possui uma implementação de teletransporte
para habilitá-lo, você precisa adicionar à cena Teleporting de \ Assets \ SteamVR \ InteractionSystem \ Teleport \ Prefabs
e também organizar o TeleportPoint a partir daí

Você também pode se teletransportar por imitação usando a tecla T.
Você pode criar uma superfície de teletransporte - Crie um avião e pendure o script TeleportArea.cs em \ Assets \ SteamVR \ InteractionSystem \ Teleport \ Scripts nele

Vamos tentar interagir com objetos - crie um cubo e pendure o script Interactable.cs em \ Assets \ SteamVR \ InteractionSystem \ Core \ Scripts nele
agora está destacado, mas nada acontece

Precisamos registrar a interação - criaremos um novo script para o Cube
Código para interação using System.Collections; using System.Collections.Generic; using UnityEngine; using Valve.VR.InteractionSystem; public class NewBehaviourScript : MonoBehaviour { private Hand.AttachmentFlags attachmentFlags = Hand.defaultAttachmentFlags & (~Hand.AttachmentFlags.SnapOnAttach) & (~Hand.AttachmentFlags.DetachOthers) & (~Hand.AttachmentFlags.VelocityMovement); private Interactable interactable; // Use this for initialization void Start () { interactable = this.GetComponent<Interactable>(); } private void HandHoverUpdate(Hand hand) { GrabTypes startingGrabType = hand.GetGrabStarting(); bool isGrabEnding = hand.IsGrabEnding(this.gameObject); if (startingGrabType != GrabTypes.None) { // Call this to continue receiving HandHoverUpdate messages, // and prevent the hand from hovering over anything else hand.HoverLock(interactable); // Attach this object to the hand hand.AttachObject(gameObject, startingGrabType, attachmentFlags); } else if (isGrabEnding) { // Detach this object from the hand hand.DetachObject(gameObject); // Call this to undo HoverLock hand.HoverUnlock(interactable); } } }
Mais detalhes sobre a interação podem ser encontrados nos exemplos do plug-in, em particular em \ Assets \ SteamVR \ InteractionSystem \ Samples \ Scripts \ InteractableExample.cs
E então tentaremos fazer o que não está nos exemplos - adicione novas ações
Abra o script Player.cs e adicione os campos
[SteamVR_DefaultAction("PlayerMove", "default")] public SteamVR_Action_Vector2 a_move; [SteamVR_DefaultAction("PlayerRotate", "default")] public SteamVR_Action_Vector2 a_rotate; [SteamVR_DefaultAction("MenuClick", "default")] public SteamVR_Action_Boolean a_menu;
Tipos de retorno válidos podem ser encontrados em \ Assets \ SteamVR \ Input
E o método Update:
private void Update() { bool st = a_menu.GetStateDown(SteamVR_Input_Sources.Any); if (st) { this.transform.position = new Vector3(0, 0, 0); } else { Camera camera = this.GetComponentInChildren<Camera>(); Quaternion cr = Quaternion.Euler(0, 0, 0); if (camera != null) { Vector2 r = a_rotate.GetAxis(SteamVR_Input_Sources.RightHand); Quaternion qp = this.transform.rotation; qp.eulerAngles += new Vector3(0, rx, 0); this.transform.rotation = qp; cr = camera.transform.rotation; } Vector2 m = a_move.GetAxis(SteamVR_Input_Sources.LeftHand); m = Quaternion.Euler(0, 0, -cr.eulerAngles.y) * m; this.transform.position += new Vector3(mx / 10, 0, my / 10); } }
Código Player.cs completo //======= Copyright (c) Valve Corporation, All rights reserved. =============== // // Purpose: Player interface used to query HMD transforms and VR hands // //============================================================================= using UnityEngine; using System.Collections; using System.Collections.Generic; namespace Valve.VR.InteractionSystem { //------------------------------------------------------------------------- // Singleton representing the local VR player/user, with methods for getting // the player's hands, head, tracking origin, and guesses for various properties. //------------------------------------------------------------------------- public class Player : MonoBehaviour { [Tooltip( "Virtual transform corresponding to the meatspace tracking origin. Devices are tracked relative to this." )] public Transform trackingOriginTransform; [Tooltip( "List of possible transforms for the head/HMD, including the no-SteamVR fallback camera." )] public Transform[] hmdTransforms; [Tooltip( "List of possible Hands, including no-SteamVR fallback Hands." )] public Hand[] hands; [Tooltip( "Reference to the physics collider that follows the player's HMD position." )] public Collider headCollider; [Tooltip( "These objects are enabled when SteamVR is available" )] public GameObject rigSteamVR; [Tooltip( "These objects are enabled when SteamVR is not available, or when the user toggles out of VR" )] public GameObject rig2DFallback; [Tooltip( "The audio listener for this player" )] public Transform audioListener; public bool allowToggleTo2D = true; [SteamVR_DefaultAction("PlayerMove", "default")] public SteamVR_Action_Vector2 a_move; [SteamVR_DefaultAction("PlayerRotate", "default")] public SteamVR_Action_Vector2 a_rotate; [SteamVR_DefaultAction("MenuClick", "default")] public SteamVR_Action_Boolean a_menu; //------------------------------------------------- // Singleton instance of the Player. Only one can exist at a time. //------------------------------------------------- private static Player _instance; public static Player instance { get { if ( _instance == null ) { _instance = FindObjectOfType<Player>(); } return _instance; } } //------------------------------------------------- // Get the number of active Hands. //------------------------------------------------- public int handCount { get { int count = 0; for ( int i = 0; i < hands.Length; i++ ) { if ( hands[i].gameObject.activeInHierarchy ) { count++; } } return count; } } //------------------------------------------------- // Get the i-th active Hand. // // i - Zero-based index of the active Hand to get //------------------------------------------------- public Hand GetHand( int i ) { for ( int j = 0; j < hands.Length; j++ ) { if ( !hands[j].gameObject.activeInHierarchy ) { continue; } if ( i > 0 ) { i--; continue; } return hands[j]; } return null; } //------------------------------------------------- public Hand leftHand { get { for ( int j = 0; j < hands.Length; j++ ) { if ( !hands[j].gameObject.activeInHierarchy ) { continue; } if ( hands[j].handType != SteamVR_Input_Sources.LeftHand) { continue; } return hands[j]; } return null; } } //------------------------------------------------- public Hand rightHand { get { for ( int j = 0; j < hands.Length; j++ ) { if ( !hands[j].gameObject.activeInHierarchy ) { continue; } if ( hands[j].handType != SteamVR_Input_Sources.RightHand) { continue; } return hands[j]; } return null; } } //------------------------------------------------- // Get Player scale. Assumes it is scaled equally on all axes. //------------------------------------------------- public float scale { get { return transform.lossyScale.x; } } //------------------------------------------------- // Get the HMD transform. This might return the fallback camera transform if SteamVR is unavailable or disabled. //------------------------------------------------- public Transform hmdTransform { get { if (hmdTransforms != null) { for (int i = 0; i < hmdTransforms.Length; i++) { if (hmdTransforms[i].gameObject.activeInHierarchy) return hmdTransforms[i]; } } return null; } } //------------------------------------------------- // Height of the eyes above the ground - useful for estimating player height. //------------------------------------------------- public float eyeHeight { get { Transform hmd = hmdTransform; if ( hmd ) { Vector3 eyeOffset = Vector3.Project( hmd.position - trackingOriginTransform.position, trackingOriginTransform.up ); return eyeOffset.magnitude / trackingOriginTransform.lossyScale.x; } return 0.0f; } } //------------------------------------------------- // Guess for the world-space position of the player's feet, directly beneath the HMD. //------------------------------------------------- public Vector3 feetPositionGuess { get { Transform hmd = hmdTransform; if ( hmd ) { return trackingOriginTransform.position + Vector3.ProjectOnPlane( hmd.position - trackingOriginTransform.position, trackingOriginTransform.up ); } return trackingOriginTransform.position; } } //------------------------------------------------- // Guess for the world-space direction of the player's hips/torso. This is effectively just the gaze direction projected onto the floor plane. //------------------------------------------------- public Vector3 bodyDirectionGuess { get { Transform hmd = hmdTransform; if ( hmd ) { Vector3 direction = Vector3.ProjectOnPlane( hmd.forward, trackingOriginTransform.up ); if ( Vector3.Dot( hmd.up, trackingOriginTransform.up ) < 0.0f ) { // The HMD is upside-down. Either // -The player is bending over backwards // -The player is bent over looking through their legs direction = -direction; } return direction; } return trackingOriginTransform.forward; } } //------------------------------------------------- void Awake() { SteamVR.Initialize(true); //force openvr if ( trackingOriginTransform == null ) { trackingOriginTransform = this.transform; } } //------------------------------------------------- private IEnumerator Start() { _instance = this; while (SteamVR_Behaviour.instance.forcingInitialization) yield return null; if ( SteamVR.instance != null ) { ActivateRig( rigSteamVR ); } else {
Execute Window \ SteamVR Imput, crie nossas ações no conjunto padrão e salve-as, agora selecione "Open binding UI" (o SteamVR deve estar em execução e pelo menos um controlador está ativado)
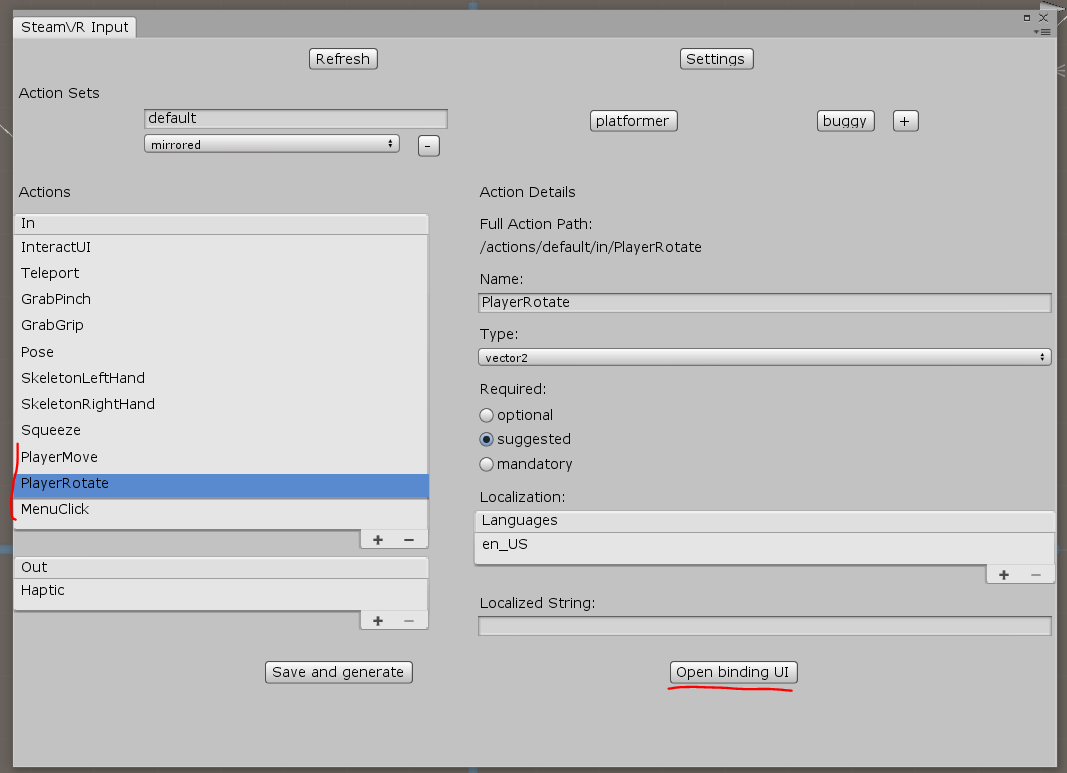
A guia Ligação do controlador é aberta no navegador - nele você precisa configurar a conexão de nossas ações com os controladores: travaremos o PlayerMove no TRACKPAD esquerdo (não esqueça de desativar o modo Espelho), PlayerRotate no TRACKPAD direito e travar o MenuClique nas teclas de menu
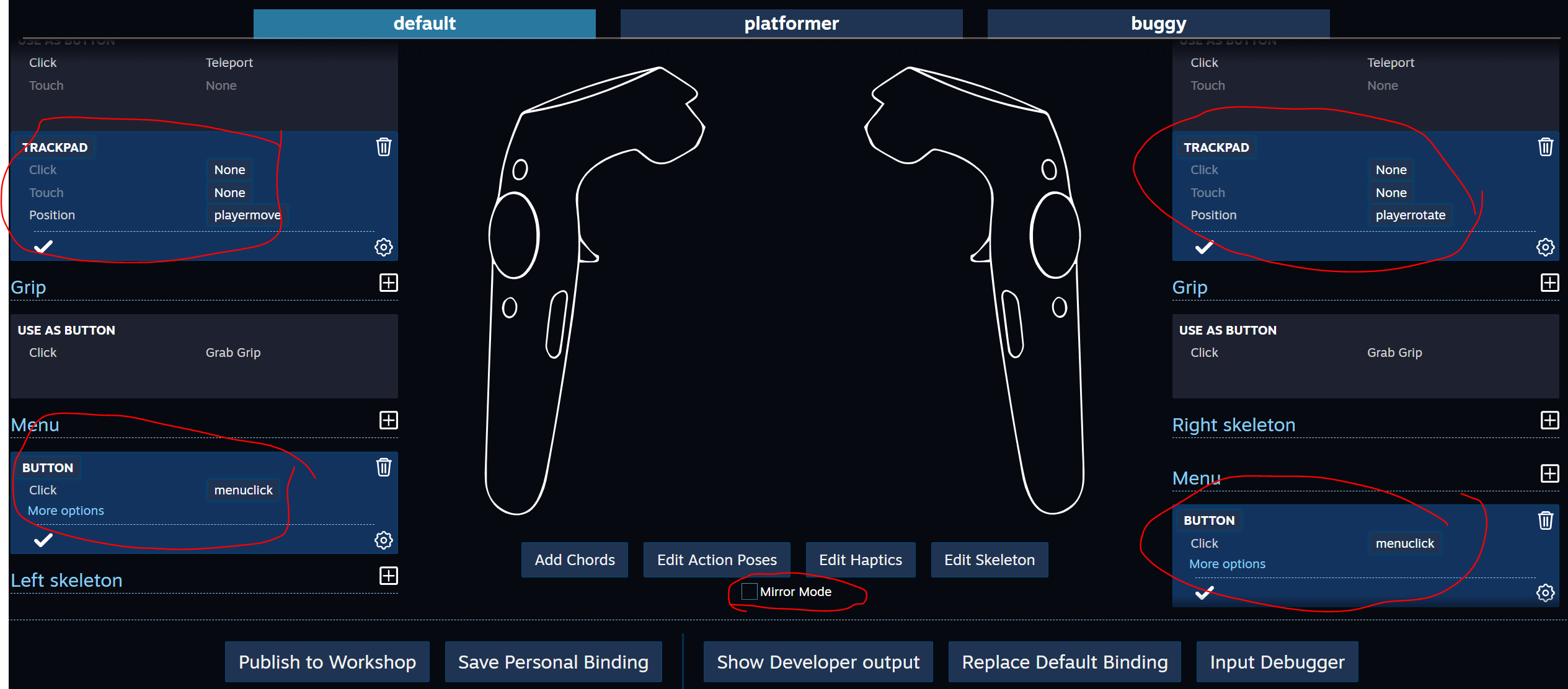
Feche a ligação do controlador e salve as alterações.
Nas propriedades do Player, conectaremos as novas ações

Iniciar o Play
Projeto
Conclusão
Alguns pontos devem ser observados. Algumas ações no SteamVR Imput podem fazer o Unity pensar por um longo tempo; em princípio, você pode fazer essas alterações no código e, em vez de usar o Controller Binding, pode editar diretamente os arquivos json, mas há um grande risco de erros que podem ser difíceis de detectar.
Para um estudo mais aprofundado do plug-in - é útil estudar os exemplos em detalhes e, é claro - leia a documentação.