UPD
Link para o github.
Recentemente, uma ideia me veio à mente - escrever um jogo simples com um número mínimo de linhas. Minha escolha recaiu sobre Tetris. Neste artigo, descreverei meu código.
Para começar, vale a pena notar que na minha implementação incluí apenas os recursos básicos:
- movimento de figuras esquerda / direita;
- figuras em queda;
- rotação de figuras;
- excluir figuras preenchidas;
- o fim do jogo.
Portanto, primeiro adicione uma PictureBox ao formulário e crie um cronômetro.
Também para o jogo você precisará:
public const int width = 15, height = 25, k = 15;
Preencha o campo nas bordas:
for (int i = 0; i < width; i++) field[i, height - 1] = 1; for (int i = 0; i < height; i++) { field[0, i] = 1; field[width - 1, i] = 1; }
Preencha a figura:
public void SetShape(){ Random x = new Random(DateTime.Now.Millisecond); switch (x.Next(7)){
O procedimento que desenha o "copo" na PictureBox:
public void FillField(){ gr.Clear(Color.Black);
Primeiro movo as figuras e depois verifico se essa opção é possível ou não. Se, em algum lugar, houver um erro (a figura está fora do campo ou sobreposta à figura que já está no campo), a figura retorna ao seu local original. Para fazer isso, escrevi uma função que retorna true se um erro foi encontrado no campo ou false se não houver erro:
public bool FindMistake(){ for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) if (shape[1, i] >= width || shape[0, i] >= height || shape[1, i] <= 0 || shape[0, i] <= 0 || field[shape[1, i], shape[0, i]] == 1) return true; return false; }
Agora vamos às figuras. Crie um evento KeyDown no construtor.
Mover para a esquerda:
switch (e.KeyCode){ case Keys.A: for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) shape[1, i]--;
Da mesma forma, o movimento para a direita:
case Keys.D: for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) shape[1, i]++; if (FindMistake()) for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) shape[1, i]--; break;
A inversão da figura é um pouco mais complicada:
case Keys.W: var shapeT = new int[2, 4]; Array.Copy(shape, shapeT, shape.Length);
Agora resta apenas adicionar uma gota de figuras e remover linhas. Tudo isso acontecerá no evento TimerTick:
private void TickTimer_Tick(object sender, System.EventArgs e){ if (field[8, 3] == 1) Environment.Exit(0);
E, finalmente, ao criar o formulário, você precisa chamar:
SetShape();
Código final:
using System; using System.Linq; using System.Drawing; using System.Windows.Forms; namespace LittleTetris{ public partial class Form1 : Form{ public const int width = 15, height = 25, k = 15; public int[,] shape = new int[2, 4]; public int[,] field = new int[width, height]; public Bitmap bitfield = new Bitmap(k * (width + 1) + 1, k * (height + 3) + 1); public Graphics gr; public Form1(){ InitializeComponent(); gr = Graphics.FromImage(bitfield); for (int i = 0; i < width; i++) field[i, height - 1] = 1; for (int i = 0; i < height; i++) { field[0, i] = 1; field[width - 1, i] = 1; } SetShape(); } public void FillField(){ gr.Clear(Color.Black); for (int i = 0; i < width; i++) for (int j = 0; j < height; j++) if (field[i, j] == 1){ gr.FillRectangle(Brushes.Green, i * k, j * k, k, k); gr.DrawRectangle(Pens.Black, i * k, j * k, k, k); } for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++){ gr.FillRectangle(Brushes.Red, shape[1, i] * k, shape[0, i] * k, k, k); gr.DrawRectangle(Pens.Black, shape[1, i] * k, shape[0, i] * k, k, k); } FieldPictureBox.Image = bitfield; } private void TickTimer_Tick(object sender, System.EventArgs e){ if (field[8, 3] == 1) Environment.Exit(0); for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) shape[0, i]++; for (int i = height - 2; i > 2; i--){ var cross = (from t in Enumerable.Range(0, field.GetLength(0)).Select(j => field[j, i]).ToArray() where t == 1 select t).Count(); if (cross == width) for (int k = i; k > 1; k--) for (int l = 1; l < width - 1; l++) field[l, k] = field[l, k - 1];} if (FindMistake()){ for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) field[shape[1, i], --shape[0, i]]++; SetShape();} FillField(); } private void Form1_KeyDown(object sender, KeyEventArgs e){ switch (e.KeyCode){ case Keys.A: for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) shape[1, i]--; if (FindMistake()) for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) shape[1, i]++; break; case Keys.D: for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) shape[1, i]++; if (FindMistake()) for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) shape[1, i]--; break; case Keys.W: var shapeT = new int[2, 4]; Array.Copy(shape, shapeT, shape.Length); int maxx = 0, maxy = 0; for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++){ if (shape[0, i] > maxy) maxy = shape[0, i]; if (shape[1, i] > maxx) maxx = shape[1, i]; } for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) { int temp = shape[0, i]; shape[0, i] = maxy - (maxx - shape[1, i]) - 1; shape[1, i] = maxx - (3 - (maxy - temp)) + 1; } if (FindMistake()) Array.Copy(shapeT, shape, shape.Length); break; } } public void SetShape(){ Random x = new Random(DateTime.Now.Millisecond); switch (x.Next(7)){ case 0: shape = new int[,] { { 2, 3, 4, 5 }, { 8, 8, 8, 8 } }; break; case 1: shape = new int[,] { { 2, 3, 2, 3 }, { 8, 8, 9, 9 } }; break; case 2: shape = new int[,] { { 2, 3, 4, 4 }, { 8, 8, 8, 9 } }; break; case 3: shape = new int[,] { { 2, 3, 4, 4 }, { 8, 8, 8, 7 } }; break; case 4: shape = new int[,] { { 3, 3, 4, 4 }, { 7, 8, 8, 9 } }; break; case 5: shape = new int[,] { { 3, 3, 4, 4 }, { 9, 8, 8, 7 } }; break; case 6: shape = new int[,] { { 3, 4, 4, 4 }, { 8, 7, 8, 9 } }; break; } } public bool FindMistake(){ for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) if (shape[1, i] >= width || shape[0, i] >= height || shape[1, i] <= 0 || shape[0, i] <= 0 || field[shape[1, i], shape[0, i]] == 1) return true; return false; } } }
Como resultado, se você não contar linhas com um colchete de fechamento e uma condição pintada no FindMistake, obterá 95 linhas.
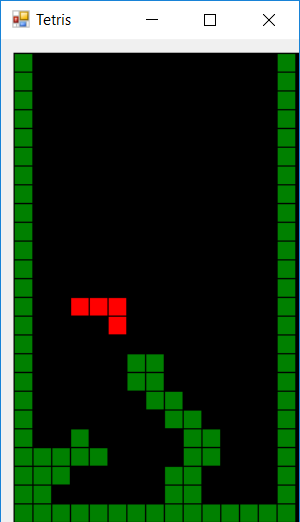
Aqui está uma captura de tela de um programa em execução: