在本地网络中,您通常需要找出设备的特定MAC地址位于交换机的哪个端口上。 如果网络中有多个交换机,则可以轻松解决该问题,但是当交换机数量超过30时,一切都会变得更加复杂。 我想共享一个小的Python脚本,该脚本在网络上寻找所需的MAC地址,并返回此MAC在其上注册的交换机的名称和端口。
欢迎进行建设性的批评。 细节剪下。
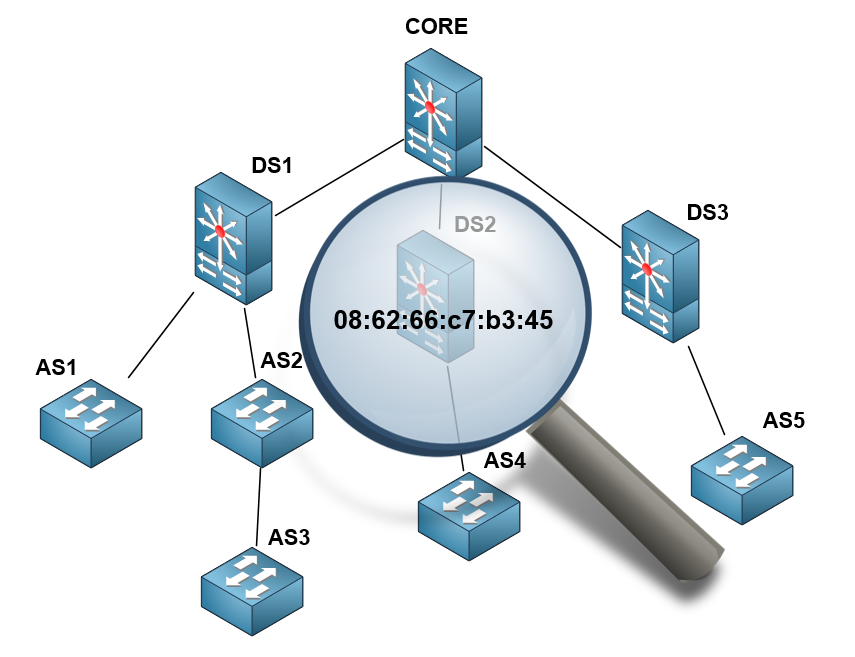
如果网络设计正确完成,即
DS (分发交换机)分发交换机所连接的
CORE根交换机,然后是访问级别
AS (访问交换机)交换机。 此规则并不总是正确的;访问开关可以串联连接。 无论如何,上游交换机端口都包含连接到下游交换机的设备的所有MAC地址。
例如,如果我们感兴趣的设备连接到
AS3交换机,
则从CORE开始搜索,我们将在通向
DS1的端口上找到此地址。 转到
DS1 ,我们将在通向
AS2的端口上找到此MAC,再转到
AS2 ,将看到它将我们引至
AS3 ,只有在
AS3上,我们才能找到目标设备所连接的特定端口。
我不想手动完成所有任务,将所有交换机循环排序,并确定上行链路在哪里,何处不是,所以我想分享下一个解决方案。
有点理论。
要在Juniper交换机上找到MAC
08:62:66:c7:b3:45 ,请运行以下命令:
show ethernet-switching table | match 08:62:66:c7:b3:45
如果有这样的MAC,答案将如下所示:
vlan151 08:62:66:c7:b3:45 D - xe-0/0/23.0
最后一栏将是注册MAC的交换机的接口名称。 但是,如何了解该界面的方向呢? 此处的
接口说明可助您一臂之力。 这些是交换机配置文件中的行,允许您为接口分配文本标签。
团队
show interfaces xe-0/0/23 descriptions
将显示以下内容:
Interface Admin Link Description xe-0/0/23 up up SW>DS1
在配置中,我们指示此接口通向下游交换机:
set interfaces xe-0/0/23 description SW>DS1
实作
建议的脚本将执行以下操作:
- 通过SSH连接到根交换机
- 检查参数中传递的MAC地址位于哪个接口上;
- 检查此接口的描述;
- 如果接口通向交换机,请递归访问链中的下一个交换机。
因此,脚本将从内核开始遍历所有网络交换机,并尝试查找所需的MAC。 为了使操作成功,足以使接口的描述保持最新,并且拓扑几乎可以具有任何复杂性。
脚本示例:
python findmac.py 00:17:fc:21:e8:f9 {"host": "CORE", "iface": "xe-0/0/23.0", "description": "SW>DS1"} {"host": "DS1", "iface": "xe-0/0/11.0", "description": "SW>AS2"} {"host": "AS2", "iface": "xe-1/0/1.0", "description": "SW>AS3"} {"host": "AS3", "iface": "ge-0/0/26.0", "description": "none"}
如果没有MAC,我们得到
{"host": "CORE", "iface": "none"}
最后一行是我们感兴趣的交换机和端口,但同时我们可以跟踪整个搜索路径。
完整的代码位于破坏者的下面,感谢您的关注。
findmac.py import paramiko import time import sys import json import threading import logging login = 'user1' password = 'pass1234' searchpass = [] port = 22 class LogPipe(threading.Thread): def __init__(self, level): threading.Thread.__init__(self) self.daemon = False self.level = level self.fdRead, self.fdWrite = os.pipe() self.pipeReader = os.fdopen(self.fdRead) self.start() def fileno(self): return self.fdWrite def run(self): for line in iter(self.pipeReader.readline, ''): logging.log(self.level, line.strip('\n')) self.pipeReader.close() def close(self): os.close(self.fdWrite) def execute_ssh_command(host, port, username, password, command): try: