机器学习正变得越来越容易获得,有更多的机会使用“现成的组件”来应用该技术。 例如,转移学习使您可以利用在解决一个问题中获得的经验来解决另一个类似的问题。 首先在大量数据上训练神经网络,然后在目标集上训练神经网络。

在本文中,我将以带食物的图像识别示例为例,介绍如何使用转移学习方法。 我将在
面向开发人员的机器学习和神经网络研讨会上讨论其他机器学习工具。
如果我们面临图像识别的任务,则可以使用现成的服务。 但是,如果需要在自己的数据集上训练模型,则必须自己完成。
对于图像分类等典型任务,您可以使用现成的体系结构(AlexNet,VGG,Inception,ResNet等),并在数据上训练神经网络。 已经使用各种框架实现了此类网络,因此在此阶段,您可以将其中一个用作黑匣子,而无需深入研究其操作原理。
但是,深度神经网络需要大量数据才能使学习趋于一致。 通常在我们的特定任务中,没有足够的数据来正确训练神经网络的所有层。 转移学习解决了这个问题。
转移学习进行图像分类
用于分类的神经网络通常在最后一层包含
N输出神经元,其中
N是类别数。 这样的输出矢量被视为属于一个类别的一组概率。 在我们识别食物图像的任务中,类别的数量可能与原始数据集中的类别数量不同。 在这种情况下,我们将必须完全淘汰最后一层,并放入新一层,并使用正确数量的输出神经元
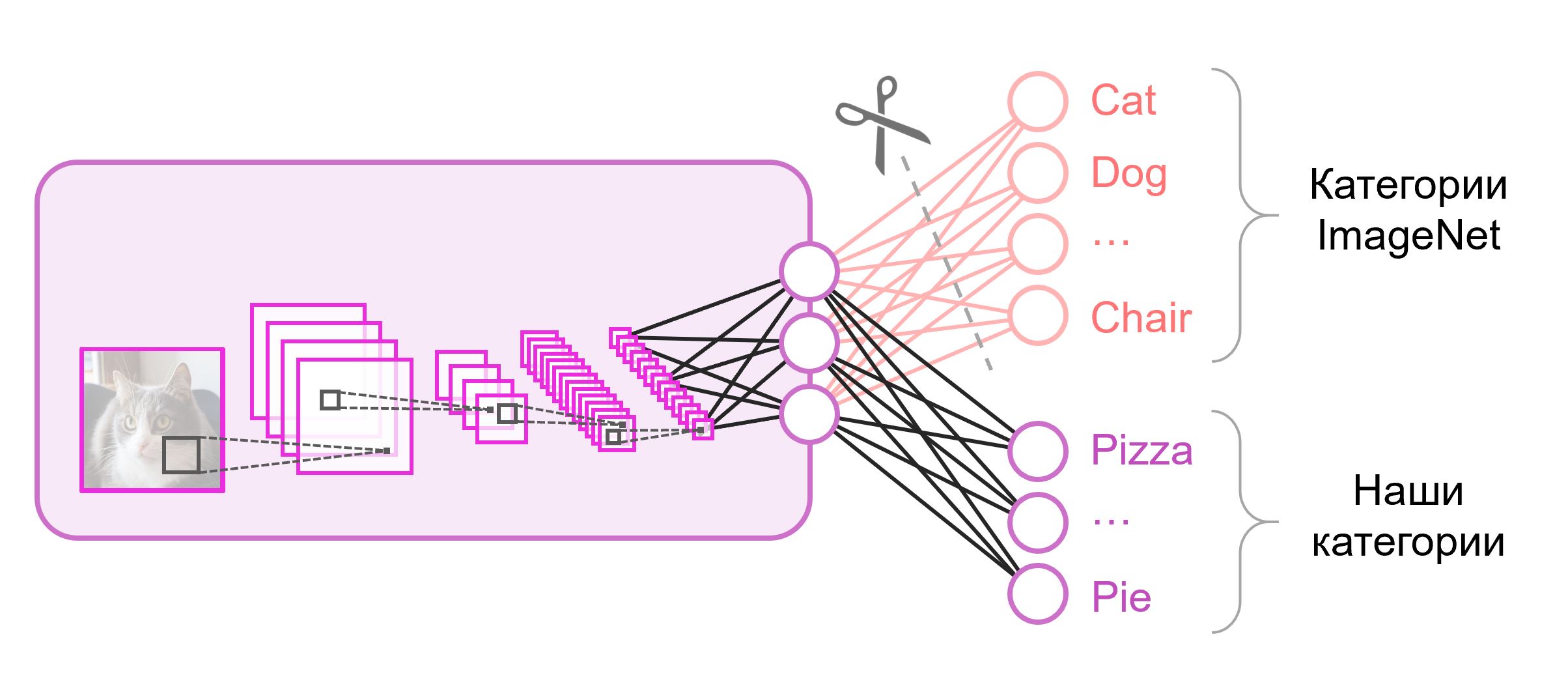
通常在分类网络的末尾使用完全连接的层。 由于我们替换了该层,因此对其使用预训练权重将不起作用。 您将不得不从头开始训练他,并使用随机值初始化他的权重。 我们从预先训练的快照中为所有其他层加载权重。
有多种策略可以进一步训练模型。 我们将使用以下内容:我们将端到端(
end-to-end )训练整个网络,并且我们将不固定预先训练的权重,以允许他们稍微调整并调整我们的数据。 此过程称为
微调 。
结构组件
要解决此问题,我们需要以下组件:
- 神经网络模型的描述
- 学习管道
- 干扰管道
- 该模型的预训练权重
- 培训和验证数据
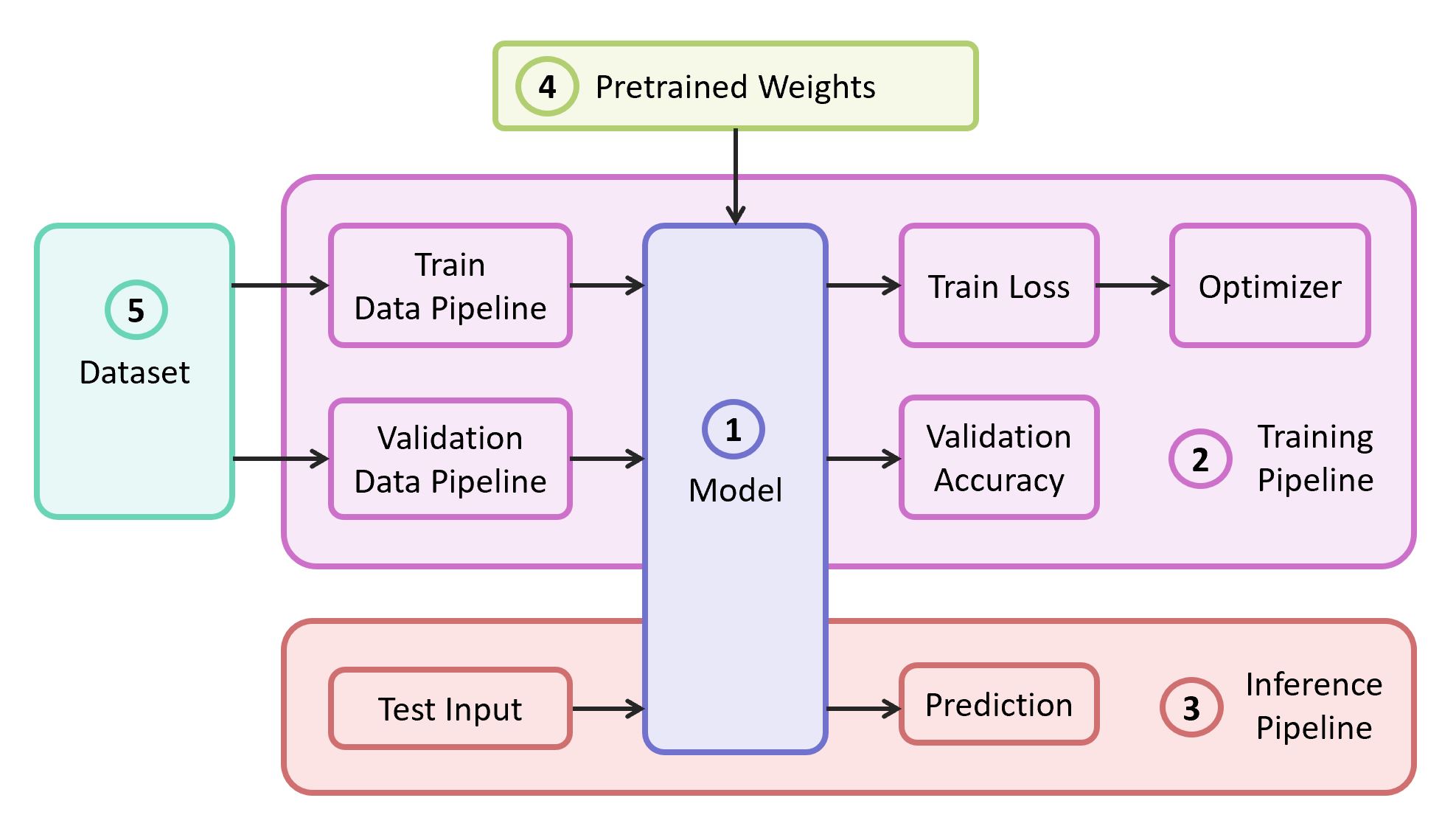
在我们的示例中,我将从
自己的存储库中获取组件(1),(2)和(3),该
存储库包含最轻量的代码-如果需要,您可以轻松地找出来。 我们的示例将在流行的
TensorFlow框架上实现。 如果适合于所选框架的预训练权重(4)与经典架构之一相对应,则可以找到它们。 作为演示的数据集(5),我将选择
Food-101 。
型号
作为模型,我们使用经典的
VGG神经网络(更确切地说是
VGG19 )。 尽管有一些缺点,该模型仍显示出相当高的质量。 另外,它很容易分析。 在TensorFlow Slim上,模型描述看起来非常紧凑:
import tensorflow as tf import tensorflow.contrib.slim as slim def vgg_19(inputs, num_classes, is_training, scope='vgg_19', weight_decay=0.0005): with slim.arg_scope([slim.conv2d], activation_fn=tf.nn.relu, weights_regularizer=slim.l2_regularizer(weight_decay), biases_initializer=tf.zeros_initializer(), padding='SAME'): with tf.variable_scope(scope, 'vgg_19', [inputs]): net = slim.repeat(inputs, 2, slim.conv2d, 64, [3, 3], scope='conv1') net = slim.max_pool2d(net, [2, 2], scope='pool1') net = slim.repeat(net, 2, slim.conv2d, 128, [3, 3], scope='conv2') net = slim.max_pool2d(net, [2, 2], scope='pool2') net = slim.repeat(net, 4, slim.conv2d, 256, [3, 3], scope='conv3') net = slim.max_pool2d(net, [2, 2], scope='pool3') net = slim.repeat(net, 4, slim.conv2d, 512, [3, 3], scope='conv4') net = slim.max_pool2d(net, [2, 2], scope='pool4') net = slim.repeat(net, 4, slim.conv2d, 512, [3, 3], scope='conv5') net = slim.max_pool2d(net, [2, 2], scope='pool5')
从ImageNet上训练并与TensorFlow兼容的VGG19权重是从GitHub上的存储库中的``
预训练模型''部分下载的。
mkdir data && cd data wget http://download.tensorflow.org/models/vgg_19_2016_08_28.tar.gz tar -xzf vgg_19_2016_08_28.tar.gz
数据中心
作为培训和验证样本,我们将使用公开的
Food-101数据集,其中包含超过10万个食物图像,分为101类。

下载并解压缩数据集:
cd data wget http://data.vision.ee.ethz.ch/cvl/food-101.tar.gz tar -xzf food-101.tar.gz
我们在培训中设计了数据管道,因此需要从数据集中解析以下内容:
- 班级清单(类别)
- 教程:图片的路径列表和正确答案的列表
- 验证集:图片的路径列表和正确答案的列表
如果是数据集,则为了
训练和
验证,您需要自己破坏集合。 Food-101已经具有这样的分区,并且此信息存储在
meta目录中。
DATASET_ROOT = 'data/food-101/' train_data, val_data, classes = data.food101(DATASET_ROOT) num_classes = len(classes)
所有负责数据处理的辅助功能都移至单独的
data.py文件中:
data.py from os.path import join as opj import tensorflow as tf def parse_ds_subset(img_root, list_fpath, classes): ''' Parse a meta file with image paths and labels -> img_root: path to the root of image folders -> list_fpath: path to the file with the list (eg train.txt) -> classes: list of class names <- (list_of_img_paths, integer_labels) ''' fpaths = [] labels = [] with open(list_fpath, 'r') as f: for line in f: class_name, image_id = line.strip().split('/') fpaths.append(opj(img_root, class_name, image_id+'.jpg')) labels.append(classes.index(class_name)) return fpaths, labels def food101(dataset_root): ''' Get lists of train and validation examples for Food-101 dataset -> dataset_root: root of the Food-101 dataset <- ((train_fpaths, train_labels), (val_fpaths, val_labels), classes) ''' img_root = opj(dataset_root, 'images') train_list_fpath = opj(dataset_root, 'meta', 'train.txt') test_list_fpath = opj(dataset_root, 'meta', 'test.txt') classes_list_fpath = opj(dataset_root, 'meta', 'classes.txt') with open(classes_list_fpath, 'r') as f: classes = [line.strip() for line in f] train_data = parse_ds_subset(img_root, train_list_fpath, classes) val_data = parse_ds_subset(img_root, test_list_fpath, classes) return train_data, val_data, classes def imread_and_crop(fpath, inp_size, margin=0, random_crop=False): ''' Construct TF graph for image preparation: Read the file, crop and resize -> fpath: path to the JPEG image file (TF node) -> inp_size: size of the network input (eg 224) -> margin: cropping margin -> random_crop: perform random crop or central crop <- prepared image (TF node) ''' data = tf.read_file(fpath) img = tf.image.decode_jpeg(data, channels=3) img = tf.image.convert_image_dtype(img, dtype=tf.float32) shape = tf.shape(img) crop_size = tf.minimum(shape[0], shape[1]) - 2 * margin if random_crop: img = tf.random_crop(img, (crop_size, crop_size, 3)) else:
模型训练
模型训练代码包括以下步骤:
- 建立火车/验证数据管道
- 构建训练/验证图(网络)
- 损失( 交叉熵损失 )分类函数在火车图上的附着。
- 在训练期间计算验证样本上预测的准确性所需的代码
- 从快照加载预训练的比例尺的逻辑
- 建立各种培训结构
- 学习周期本身(迭代优化)
图的最后一层是使用所需数量的神经元构造的,并从预先训练的快照加载的参数列表中排除。
示范培训守则 import numpy as np import tensorflow as tf import tensorflow.contrib.slim as slim tf.logging.set_verbosity(tf.logging.INFO) import model import data
开始训练后,您可以使用TensorBoard实用程序查看其进度,该实用程序与TensorFlow捆绑在一起,用于可视化各种指标和其他参数。
tensorboard --logdir checkpoints/
在TensorBoard的培训结束时,我们看到了几乎完美的画面:
火车损失减少,
验证准确性增加

结果,我们将保存的快照保存在
checkpoints/vgg19_food ,我们将在模型测试期间使用该快照(
推理 )。
模型测试
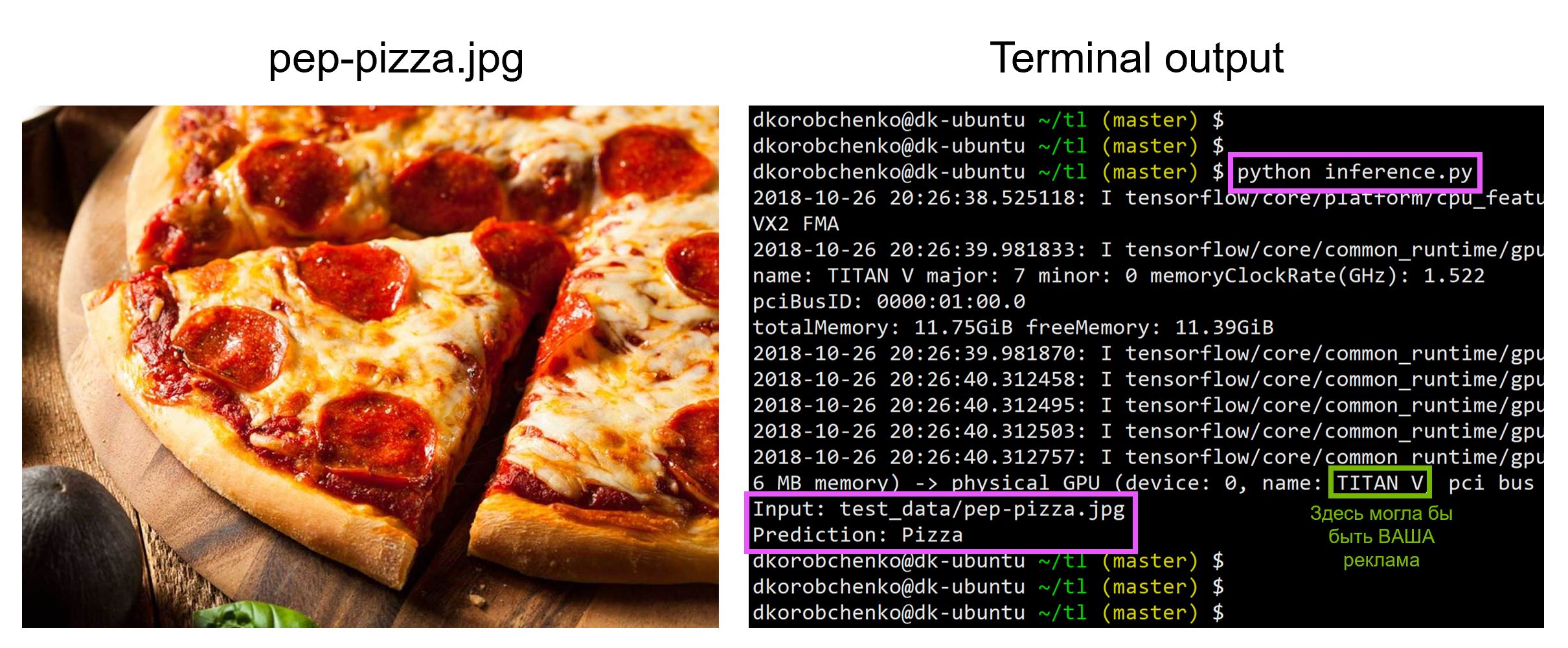
现在测试我们的模型。 为此:
- 我们构造了一个专门为推理而设计的新图(
is_training=False ) - 从快照加载经过训练的权重
- 下载并预处理输入的测试图像。
- 让我们通过神经网络驱动图像并获得预测
推断 import sys import numpy as np import imageio from skimage.transform import resize import tensorflow as tf import model
所有代码,包括用于构建和运行带有所有必需版本库的Docker容器的资源,都在
此存储库中 -在阅读本文时,存储库中的代码可能已更新。
在
“面向开发人员的机器学习和神经网络”研讨会上
,我将分析机器学习的其他任务,并且学生们将在密集课程结束时介绍他们的项目。