文章摘要。
- 使用GtkApplication。 线框应用程序。 生成文件。
- 由librsvg库渲染。
- 将图像导出到GtkImage并缩放比例。
- 具有自定义功能的SVG缩放。
- 获取应用程序中的完整路径。
- 性能测试GtkDrawingArea与GtkImage。
先前在GTK +集线器中有一些文章(不是我的文章)在示例中使用void gtk_main(void)函数; GtkApplication类允许您显式突出显示application_activate和application_shutdown回调函数。 使用gtk_main,您需要显式挂钩gtk_main_quit,以便在单击十字架时,应用程序终止。 GtkApplication通过单击十字架终止应用程序,这更加合乎逻辑。 应用程序框架本身由main.h,Makefile,string.gresource.xml,main.c组成。
主文件#ifndef MAIN_H #define MAIN_H #include <gtk/gtk.h> typedef struct{ GtkApplication *restrict app; GtkWidget *restrict win; GtkBuilder *restrict builder; }appdata; appdata data; appdata *data_ptr; #endif
生成文件在这里通用,它允许您编译所有源文件而无需指定特定的文件名,但是如果文件夹中有其他文件,则编译器会发誓。
您还可以使用CC = g ++ -std = c ++ 11,但要放入回调函数
外部“ C”。
CC = gcc -std=c99 PKGCONFIG = $(shell which pkg-config) CFLAGS = $(shell $(PKGCONFIG) --cflags gio-2.0 gtk+-3.0 librsvg-2.0) -rdynamic -O3 LIBS = $(shell $(PKGCONFIG) --libs gio-2.0 gtk+-3.0 gmodule-2.0 librsvg-2.0 epoxy) -lm GLIB_COMPILE_RESOURCES = $(shell $(PKGCONFIG) --variable=glib_compile_resources gio-2.0) SRC = $(wildcard *.c) GEN = gresources.c BIN = main ALL = $(GEN) $(SRC) OBJS = $(ALL:.c=.o) all: $(BIN) gresources.c: string.gresource.xml $(shell $(GLIB_COMPILE_RESOURCES) --sourcedir=. --generate-dependencies string.gresource.xml) $(GLIB_COMPILE_RESOURCES) string.gresource.xml --target=$@ --sourcedir=. --generate-source %.o: %.c $(CC) $(CFLAGS) -c -o $(@F) $< $(BIN): $(OBJS) $(CC) -o $(@F) $(OBJS) $(LIBS) clean: @rm -f $(GEN) $(OBJS) $(BIN)
string.gresource.xml用于在可执行文件中包含资源,在这种情况下,它是window.glade接口描述文件
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <gresources> <gresource prefix="/com/example/YourApp"> <file preprocess="xml-stripblanks" compressed="true">window.glade</file> </gresource> </gresources>
main.c #include "main.h" GtkBuilder* builder_init(void) { GError *error = NULL; data.builder = gtk_builder_new(); if (!gtk_builder_add_from_resource (data.builder, "/com/example/YourApp/window.glade", &error)) {
在gtk_application_new函数的第一个参数中,您可以放置任何文本,但是如果没有点号,该文本将不起作用。 此示例还省略了可以在Glade UI编辑器中创建的window.glade文件。
我们将带有GtkBox容器的窗口分为两部分,其中之一是将GtkDrawingArea放在另一部分:
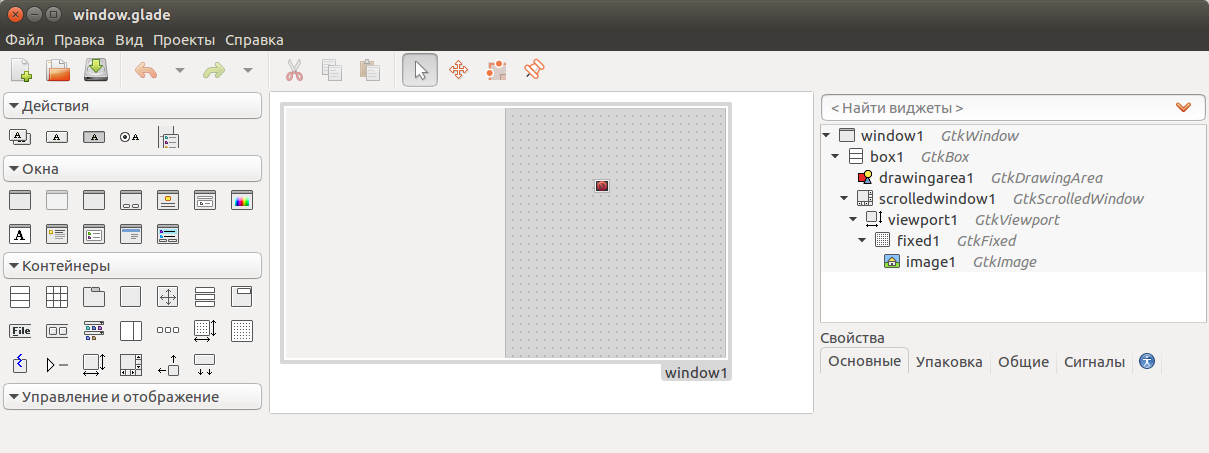
结果,appdata将发生变化
typedef struct{ GtkApplication *restrict app; GtkWidget *restrict win; GtkBuilder *restrict builder; GtkDrawingArea *restrict draw; GtkImage *restrict image; GtkEventBox *restrict eventbox1; RsvgHandle *restrict svg_handle_image; RsvgHandle *restrict svg_handle_svg; GdkPixbuf *pixbuf; cairo_t *restrict cr; cairo_surface_t *restrict surf; }appdata;
并据此初始化。
void application_activate(GtkApplication *application, gpointer user_data) { GtkBuilder *builder=builder_init(); data_ptr=&data; data.win=GTK_WIDGET(gtk_builder_get_object(builder, "window1")); data.draw=GTK_DRAWING_AREA(gtk_builder_get_object(builder, "drawingarea1")); data.image=GTK_IMAGE(gtk_builder_get_object(builder, "image1")); gtk_widget_set_size_request(data.win,640,480); gtk_application_add_window(data.app,GTK_WINDOW(data.win)); gtk_widget_show_all(data.win); }
添加路径#include <librsvg-2.0 / librsvg / rsvg.h>。 (必须安装librsvg和librsvg-dev软件包)。
回调函数的名称取自.glade文件,该函数负责此操作。
gtk_builder_connect_signals(data.builder,NULL);
gboolean drawingarea1_draw_cb (GtkWidget *widget, cairo_t *cr, gpointer user_data) { if(!data.svg_handle_svg) {data.svg_handle_svg=rsvg_handle_new_from_file("compassmarkings.svg",NULL);} gboolean result=rsvg_handle_render_cairo(data.svg_handle_svg,cr); if(result&&cr) {cairo_stroke(cr);} else printf(" \n"); return FALSE; }
在某些情况下(例如HMI),您可能需要调整SVG的大小。 可以
更改SVG文件中的width和height参数。 或转移到GtkPixbuf并在那里进行缩放。 由于GtkImage不是从GtkBin继承的,因此它不能具有自己的ButtonClick类型事件(与光标相关的事件)。 为此有一个空容器-GtkEventBox。 并且图形本身可以直接挂在GtkImage上。
gboolean image1_draw_cb (GtkWidget *widget, cairo_t *cr, gpointer user_data) { if(!data.svg_handle_image) { data.svg_handle_image=rsvg_handle_new_from_file("compassmarkings.svg",NULL); data.surf=cairo_image_surface_create_from_png("2.png"); data.pixbuf=rsvg_handle_get_pixbuf(data.svg_handle_image); } if(data.pixbuf) { cairo_set_source_surface(cr,data.surf,0,0); GdkPixbuf *dest=gdk_pixbuf_scale_simple (data.pixbuf,250,250,GDK_INTERP_BILINEAR); gtk_image_set_from_pixbuf (data.image,dest); g_object_unref(dest); cairo_paint(cr); } }
此函数加载背景图片(2.png),该图片通常表示
具有透明像素的1x1绘图。 然后将绘图(pixbuf)渲染到此表面上,然后进行缩放并导出到图像(图像)。
我们一定不要忘记清除内存。
void application_shutdown(GtkApplication *application, gpointer user_data) { cairo_surface_destroy(data.surf); g_object_unref(data.svg_handle_image); g_object_unref(data.svg_handle_svg); g_object_unref(data.pixbuf); g_object_unref(data.builder); }
结果是:

如果在SVG参数中设置了宽度和高度值,则在导出为png时图片可能会变得模糊。
您还可以以编程方式更改宽度和高度。 为此,我创建了单独的文件
svg_to_pixbuf_class.c和svg_to_pixbuf_class.h。 也就是说,文件将以更改的宽度,高度打开。
它保存在/ dev / shm /中。 将信息导出到svg_handle之后,您需要删除文件本身和文件的行路径。 还支持小数宽度/长度值。
svg_to_pixbuf_class.c #include <string.h> #include <stdlib.h> #include <stdio.h> #include <gtk/gtk.h> #include <sys/types.h> #include <sys/stat.h> #include <fcntl.h> #include <math.h> #include <stdbool.h> int char_to_digit(char num) { switch(num) { case '0': return 0; case '1': return 1; case '2': return 2; case '3': return 3; case '4': return 4; case '5': return 5; case '6': return 6; case '7': return 7; case '8': return 8; case '9': return 9; case '.': return -1; default: return -2; } } // text double read_num_in_text(char* text) { double result=0; int i=0; bool fractional_flag=FALSE; char whole_part[16]={0}; char whole_digits=0; char fractional_part[16]={0}; char fractional_digits=0; while(char_to_digit(text[i])!=-2) { if(char_to_digit(text[i])!=-1&&!fractional_flag) { whole_part[whole_digits]=char_to_digit(text[i]); printf("text_num=%d|%c\n",char_to_digit(text[i]),text[i]); ++whole_digits; ++i; } else { if(char_to_digit(text[i])==-1) { printf("fractional flag is true\n"); fractional_flag=TRUE; ++i; } else { fractional_part[fractional_digits]=char_to_digit(text[i]); ++fractional_digits; printf("frac_digit=%d|%c\n",char_to_digit(text[i]),text[i]); ++i; } } } /// i=whole_digits; result=whole_part[whole_digits]; while(i>0) { --i; printf("whole=%d\n",whole_part[i]); result=result+pow(10,whole_digits-i-1)*whole_part[i]; } i=0; while(i<=fractional_digits) { result=result+pow(0.1,i+1)*fractional_part[i]; ++i; } printf("result_read_num=%lf\n",result); return result; } // , // int count_of_digits_for_delete(char* text) { int i=0; bool fractional_flag=FALSE; char whole_part[16]={0}; int whole_digits=0; char fractional_part[16]={0}; int fractional_digits=0; while(char_to_digit(text[i])!=-2) { if(char_to_digit(text[i])!=-1&&!fractional_flag) { whole_part[whole_digits]=char_to_digit(text[i]); printf("text_num=%d|%c\n",char_to_digit(text[i]),text[i]); ++whole_digits; ++i; } else { if(char_to_digit(text[i])==-1) { printf("fractional flag is true\n"); fractional_flag=TRUE; ++i; } else { fractional_part[fractional_digits]=char_to_digit(text[i]); ++fractional_digits; printf("frac_digit=%d|%c\n",char_to_digit(text[i]),text[i]); ++i; } } } if(fractional_flag) return whole_digits+1+fractional_digits; else return whole_digits; } // /dev/shm // char* create_dump_file(char *file_with_path) { char *file=NULL; int i=0; while(file_with_path[i]!='\0') {++i;} while(file_with_path[i]!='/'&&i>0) {--i;} file=file_with_path+i; GString *string=g_string_new("test -f /dev/shm"); g_string_append(string,file); g_string_append(string,"|| touch /dev/shm/"); g_string_append(string,file); system(string->str); /// - GString *full_path=g_string_new("/dev/shm"); g_string_append(full_path,file); char *result=g_string_free(full_path,FALSE); return result; } //result must be freed with g_string_free GString* read_file_in_buffer(char *file_with_path) { FILE *input = NULL; struct stat buf; int fh, result; char *body=NULL; // GString *resultat=g_string_new(""); fh=open(file_with_path, O_RDONLY); result=fstat(fh, &buf); if (result !=0) printf(" \n"); else { printf("%s",file_with_path); printf(" : %ld\n", buf.st_size); printf(" : %lu\n", buf.st_dev); printf(" : %s", ctime(&buf.st_atime)); input = fopen(file_with_path, "r"); if (input == NULL) { printf("Error opening file"); } body=(char*)calloc(buf.st_size+64,sizeof(char)); // // if(body==NULL) { printf(" body\n"); } int size_count=fread(body,sizeof(char),buf.st_size, input); if(size_count!=buf.st_size) printf(" "); resultat=g_string_append(resultat,body); free(body); } fclose(input); return resultat; } void* write_string_to_file(char* writed_file, char* str_for_write, int lenght) { FILE * ptrFile = fopen (writed_file ,"wb"); size_t writed_byte_count=fwrite(str_for_write,1,lenght,ptrFile); //if(writed_byte_count>4) return TRUE; //else return FALSE; fclose(ptrFile); } // g_free char* get_resized_svg(char *file_with_path, int width, int height) { char *writed_file=create_dump_file(file_with_path); // GString *body=read_file_in_buffer(file_with_path); char *start_search=NULL; char *end_search=NULL; char *width_start=NULL; char *width_end=NULL; char *height_start=NULL; char *height_end=NULL; start_search=strstr(body->str,"<svg"); int j=0; // if(start_search) { end_search=strstr(start_search,">"); if(end_search) { /// width width_start=strstr(start_search,"width"); width_end=width_start+strlen("width"); /// width while(width_end[j]==0x0A||width_end[j]==0x20) ++j; if(width_end[j]=='=') ++j; while(width_end[j]==0x0A||width_end[j]==0x20) ++j; if(width_end[j]!='"') printf(" svg. width=%c\n",width_end[j]); else ++j; /// /// , gssize size=count_of_digits_for_delete(width_end+j); /// (1 - 1 ) gssize pos=width_end+j-body->str; /// g_string_erase(body,pos,size); char width_new[8]; g_snprintf(width_new,8,"%d",width); g_string_insert(body, pos, width_new); /// height height_start=strstr(start_search,"height"); height_end=height_start+strlen("height"); /// height j=0; while(height_end[j]==0x0A||height_end[j]==0x20) ++j; if(height_end[j]=='=') ++j; while(height_end[j]==0x0A||height_end[j]==0x20) ++j; if(height_end[j]!='"') printf(" svg. \ height=%c%c%c\n",height_end[j-1],height_end[j],height_end[j+1]); else ++j; /// /// , size=count_of_digits_for_delete(height_end+j); /// (1 - 1 ) pos=height_end+j-body->str; /// g_string_erase(body,pos,size); char height_new[8]; g_snprintf(height_new,8,"%d",height); g_string_insert(body, pos, height_new); /// dev/shm/ /// write_string_to_file(writed_file,body->str,strlen(body->str)); return writed_file; //g_free(writed_file); g_string_free(body,TRUE); } else printf(" : svg"); } } void resized_svg_free(char *path) { if (remove (path)==-1 ) { printf(" %s\n",path); } }
svg_to_pixbuf_class.h #ifndef SVG_TO_PIXBUF_CLASS_H #define SVG_TO_PIXBUF_CLASS_H void resized_svg_free(char *path); char* get_resized_svg(char *file_with_path, int width, int height);
现在调整左侧的大小(即GtkDrawingArea)
gboolean drawingarea1_draw_cb (GtkWidget *widget, cairo_t *cr, gpointer user_data) { if(!data.svg_handle_svg) { char* path=get_resized_svg("/home/alex/svg_habr/compassmarkings.svg", 220, 220); data.svg_handle_svg=rsvg_handle_new_from_file(path,NULL); resized_svg_free(path); g_free(path); } gboolean result=rsvg_handle_render_cairo(data.svg_handle_svg,cr); if(result&&cr) {cairo_stroke(cr);} else printf(" \n"); return FALSE; }
如您所见,这里有一个令人不快的功能-完整路径。 也就是说,值得移动文件夹,因为左侧部分(GtkDrawingArea)不再显示。 这同样适用于可执行文件中未包括的所有资源。 为此,我编写了一个函数,该函数计算可执行文件的完整路径,而不管其运行方式如何。
代码中有两个示例,介绍了如何运行manager.elf文件。 您还需要将main()放在函数的开头
char cwd[1024]; getcwd(cwd, sizeof(cwd)); get_real_path(argv[0]);
绘图功能将采用以下形式
gboolean drawingarea1_draw_cb (GtkWidget *widget, cairo_t *cr, gpointer user_data) { if(!data.svg_handle_svg) { char image_path[1024]; strcat(image_path,data.path); strcat(image_path,"compassmarkings.svg"); printf("image_path=%s\n",image_path); char* path=get_resized_svg(image_path, 220, 220); data.svg_handle_svg=rsvg_handle_new_from_file(path,NULL); resized_svg_free(path); g_free(path); } gboolean result=rsvg_handle_render_cairo(data.svg_handle_svg,cr); if(result&&cr) {cairo_stroke(cr);} else printf(" \n"); return FALSE; }
快速行动测试。我们有2个绘制函数(GtkDrawingArea和GtkImage)。
我们将它们放置在一种类型的设计中(不要忘记连接<time.h>)
clock_t tic = clock(); clock_t toc = clock(); printf("image1_draw_cb elapsed : %f seconds\n", (double)(toc - tic) / CLOCKS_PER_SEC);
在htop应用程序中,您可以看到程序如何吞噬每个核心Athlon 2 X3 2.5 GHz的20-30%。
错误很快被发现。
gboolean image1_draw_cb (GtkWidget *widget, cairo_t *cr, gpointer user_data) { clock_t tic = clock(); if(!data.svg_handle_image) { data.svg_handle_image=rsvg_handle_new_from_file("compassmarkings.svg",NULL); data.surf=cairo_image_surface_create_from_png("2.png"); data.pixbuf=rsvg_handle_get_pixbuf(data.svg_handle_image);
事实证明,GtkImage具有自己的渲染系统,并且image1_draw_cb的内容只能初始化一次。 评论行是多余的。

如您所见,第一次使用GtkImage渲染要比使用GtkDrawingArea花费更长的时间,但是从理论上讲,更新图像应该更快。 每重绘220像素* 220像素的图像需要400万个处理器周期,因此您只能通过pixbuf进行缓存(至少,我不知道其他方法)。
谢谢您的关注。