参赛作品
在本文中,我将讨论著名的霍夫曼算法及其在数据压缩中的应用。
结果,我们将编写一个简单的存档器。
在Habré上已经有
关于它的
文章 ,但是没有实际实施。 当前职位的理论材料来自学校的计算机科学课程以及Robert Lafore的书“ Java中的数据结构和算法”。 因此,一切都在削减之中!
有点想
在纯文本文件中,一个字符用8位(ASCII编码)或16位(Unicode编码)编码。 此外,我们将考虑ASCII编码。 例如,以s1 =“ SUSIE SAYS IT IS EASY \ n”行。 总的来说,该行中总共有22个字符,包括空格和换行符-'\ n'。 包含此行的文件将重22 * 8 = 176位。 问题立即出现:使用所有8位编码1个字符是否合理? 我们不会使用所有ASCII字符。 即使使用,最频繁的字母S给出尽可能短的代码,而最稀有的字母T T给出更真实的代码更为合理。 这是霍夫曼算法:您需要找到最佳的编码选项,使文件的重量最小。 不同的字符具有不同的代码长度是很正常的-这是算法的基础。
编码方式
为什么不给字符'S'一个代码,例如1位长:0或1。让它为1。那么我们将给第二个最常遇到的字符-”(空格)-0。想象一下,您开始解码消息-编码的字符串s1-您会看到代码以1开头。那么该怎么做:它是字符S,还是其他字符,例如A? 因此,出现了一条重要规则:
任何代码都不应该是另一个的前缀此规则是算法中的关键。 因此,代码的创建从频率表开始,该频率表指示每个字符的频率(出现次数):
出现次数最多的字符应使用
尽可能少的位数进行编码。 我将给出一个可能的代码表示例:
因此,编码后的消息将如下所示:
10 01111 10 110 1111 00 10 010 1110 10 00 110 0110 00 110 10 00 1111 010 10 1110 01110
我用空格分隔了每个字符的代码。 这实际上不会在压缩文件中发生!
问题出现了:
此salaga是如何提出
代码的 ?如何创建代码表? 这将在下面讨论。
建立霍夫曼树
在这里,二叉搜索树可以解救。 不用担心,这里不需要搜索,插入和删除方法。 这是java中的树结构:
public class Node { private int frequence; private char letter; private Node leftChild; private Node rightChild; ... }
class BinaryTree { private Node root; public BinaryTree() { root = new Node(); } public BinaryTree(Node root) { this.root = root; } ... }
这不是完整的代码,完整的代码将在下面。
这是树构建算法本身:
- 为消息中的每个字符创建一个Node对象(第s1行)。 在我们的例子中,将有9个节点(Node对象)。 每个节点都包含两个数据字段:符号和频率
- 为每个Node节点创建一个Tree对象(BinaryTree)。 该节点成为树的根。
- 将这些树粘贴到优先级队列中。 频率越低,优先级越高。 因此,提取时,总是以最低的频率选择dervo。
接下来,您需要循环执行以下操作:
- 从优先级队列中提取两棵树,并使它们成为新节点(不带字母的新创建节点)的后代。 新节点的频率是两个后代树的频率之和。
- 对于此节点,创建一个在此节点中具有根的树。 将此树粘贴回优先级队列。 (由于树具有新的频率,因此很可能会到达队列中的新位置)
- 继续步骤1和2,直到队列中只剩下一棵树-Huffman树
考虑在线s1上的此算法:

在此,符号“ lf”(换行符)表示到新行的过渡,“ sp”(空格)是空格。
接下来是什么?
我们有一棵霍夫曼树。 好吧,好 以及如何处理呢?
他们不会免费获取它,然后,您需要跟踪从树的根到叶的所有可能路径。 让我们同意指定边缘0(如果它导致左后代)和1(如果它导致右后代)。 严格来说,在这些符号中,符号代码是从树的根到包含相同符号的工作表的路径。
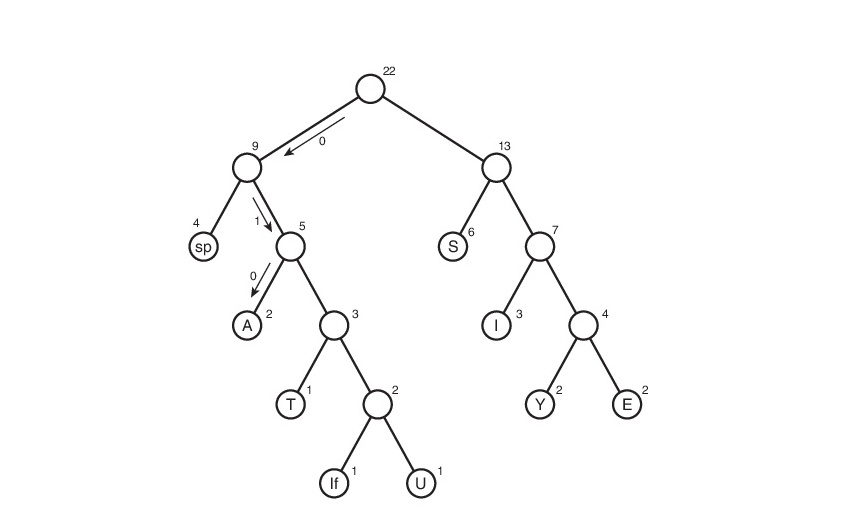
因此,代码表出现了。 请注意,如果考虑此表,我们可以得出每个字符的“权重”的结论-这是其代码的长度。 然后压缩文件的权重为:2 * 3 + 2 * 4 + 3 * 3 + 6 * 2 +1 * 4 +1 * 5 + 2 * 4 + 4 * 2 +1 * 5 = 65位。 最初,它的重量为176位。 因此,我们将其降低了176/65 = 2.7倍! 但这是乌托邦。 这样的系数不太可能获得。 怎么了 这将在稍后讨论。
解码方式
好吧,也许剩下的最简单的事情就是解码。 我想很多人都猜想不可能简单地创建压缩文件而没有任何编码方式的提示-我们将无法对其进行解码! 是的,我很难意识到这一点,但是我必须创建一个带有压缩表的文本文件table.txt:
01110 00 A010 E1111 I110 S10 T0110 U01111 Y1110
以“字符”“字符代码”的形式记录表。 为什么01110没有字符? 实际上,它带有一个符号,只是我输出到文件时使用的java工具,换行符-'\ n'-会转换为换行符(无论听起来多么愚蠢)。 因此,顶部的空行是代码01110的字符。对于代码00,该字符是该行开头的空格。 我必须马上说,
我们存储该表的方法可能是最不合理的。 但是很容易理解和实施。 我很高兴听到您在有关优化的评论中提出的建议。
拥有此表非常容易解码。 回忆一下创建编码时遵循的规则:
任何代码都不应在其前缀这是它发挥促进作用的地方。 我们逐位顺序读取,并且一旦接收到的由读取的位组成的字符串d与对应于字符的编码匹配,我们便立即知道字符已被编码(并且只有它!)。 接下来,我们在解码行(包含解码消息的行)中写入字符,将d行清零,然后读取编码文件。
实作
现在该
通过编写存档器来
羞辱我的代码了 。 我们称之为Compressor。
让我们从头开始。 首先,我们编写Node类:
public class Node { private int frequence;
现在这棵树:
class BinaryTree { private Node root; public BinaryTree() { root = new Node(); } public BinaryTree(Node root) { this.root = root; } public int getFrequence() { return root.getFrequence(); } public Node getRoot() { return root; } }
优先队列:
import java.util.ArrayList;
创建霍夫曼树的类:
public class HuffmanTree { private final byte ENCODING_TABLE_SIZE = 127;
包含编码/解码的类:
public class HuffmanOperator { private final byte ENCODING_TABLE_SIZE = 127;
有助于写入文件的类:
import java.io.File; import java.io.PrintWriter; import java.io.FileNotFoundException; import java.io.FileOutputStream; import java.io.IOException; import java.io.Closeable; public class FileOutputHelper implements Closeable { private File outputFile; private FileOutputStream fileOutputStream; public FileOutputHelper(File file) throws FileNotFoundException { outputFile = file; fileOutputStream = new FileOutputStream(outputFile); } public void writeByte(byte msg) throws IOException { fileOutputStream.write(msg); } public void writeBytes(byte[] msg) throws IOException { fileOutputStream.write(msg); } public void writeString(String msg) { try (PrintWriter pw = new PrintWriter(outputFile)) { pw.write(msg); } catch (FileNotFoundException e) { System.out.println(" , !"); } } @Override public void close() throws IOException { fileOutputStream.close(); } public void finalize() throws IOException { close(); } }
有助于读取文件的类:
import java.io.FileInputStream; import java.io.EOFException; import java.io.BufferedReader; import java.io.InputStreamReader; import java.io.Closeable; import java.io.File; import java.io.IOException; public class FileInputHelper implements Closeable { private FileInputStream fileInputStream; private BufferedReader fileBufferedReader; public FileInputHelper(File file) throws IOException { fileInputStream = new FileInputStream(file); fileBufferedReader = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(fileInputStream)); } public byte readByte() throws IOException { int cur = fileInputStream.read(); if (cur == -1)
好吧,和主要的类:
import java.io.File; import java.nio.charset.MalformedInputException; import java.io.FileNotFoundException; import java.io.IOException; import java.nio.file.Files; import java.nio.file.NoSuchFileException; import java.nio.file.Paths; import java.util.List; import java.io.EOFException; public class Main { private static final byte ENCODING_TABLE_SIZE = 127; public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { try {
readme.txt指令文件由您自己决定:-)
结论
这可能就是我想说的。 如果您对
我在代码,算法和总体上的优化方面的改进
无能为力 ,请随时撰写。 如果我误解了一些东西,也要写。 我很高兴收到您的评论!
聚苯乙烯
是的,是的,我仍然在这里,因为我没有忘记系数。 对于字符串s1,编码表的重量为48个字节-比原始文件大得多,并且他们没有忘记其他零(添加的零的数量为7)=>压缩率将小于1:176 /(65 + 48 * 8 + 7)= 0.38。 如果您也注意到了这一点,那么您
就不会做得很好。 是的,对于小文件,此实现效率极低。 但是大文件会怎样? 文件大小远远超过了编码表的大小。 在这里,算法可以正常工作! 例如,对于《
浮士德》独白,存档者给出的真实(未理想化)系数等于1.46,几乎是原来的一半! 是的,该文件应该是英文的。