现代网络的问题之一是它们的脆弱性。 许多过滤规则,路由信息交换策略,动态路由协议使网络混乱并受人为因素的影响。 更改路由映射或ACL(
一个 ,
两个 )时,可能会无意中发生网络崩溃。 我们绝对缺少在更改生产之前使用新配置评估网络行为的工具。 我想确定是否可以过滤掉从提供商B收到的一些BGP公告,网络A是否对我可用? 如果在其中一个传输链路上将IGP度量加倍,数据包将从网络C到达服务器D的路由是什么? Batfish将帮助我们回答这些以及许多其他问题!
蝙蝠鱼的评论
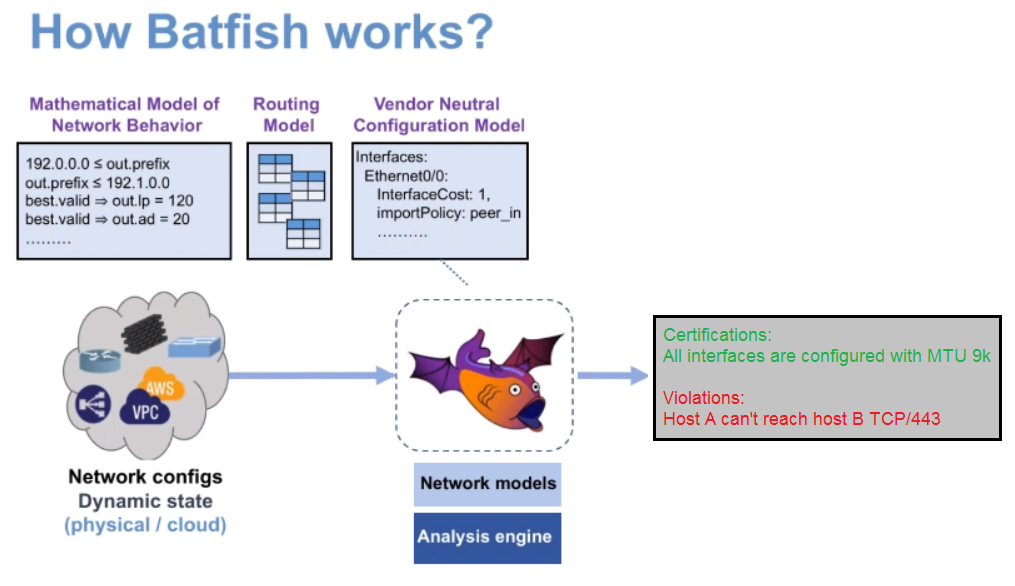
Batfish是网络建模工具。 其主要目的是在将配置更改引入生产网络之前对其进行测试。 Batfish还可以用于分析和检查网络的当前状态。 网络世界中现有的CI / CD流程显然缺少测试新配置的工具。 Batfish解决了这个问题。
Batfish不需要直接直接访问现有的网络设备,Batfish根据设备配置文件中包含的数据对网络行为进行建模。
Batfish可以:
- 确定网络中动态路由协议(BGP,IS-IS,OSPF)的邻居状态
- 计算每个网元的RIB
- 检查NTP,AAA,MTU设置
- 允许确定ACL是否阻止网络流量通过(Cisco ASA上的Packet-tracer模拟)
- 检查网络内主机之间的端到端连接
- 显示通过网络的流量路径(虚拟跟踪)
支持平台:
- 阿里斯塔
- 阿鲁巴岛
- AWS(VPC,网络ACL,VPN GW,NAT GW,Internet GW,安全组)
- 思科(NX-OS,IOS,IOS-XE,IOS-XR和ASA)
- 戴尔force10
- 铸造厂
- iptables
- 瞻博网络(MX,EX,QFX,SRX,T系列,PTX)
- v
- 帕洛阿尔托网络
- Quagga / FRR
- 广达
- 维约斯
Batfish是Java应用程序。 为了方便使用,编写了Pybatfish-python SDK。
让我们继续练习。 我将通过示例向您展示蝙蝠鱼的可能性。
例子
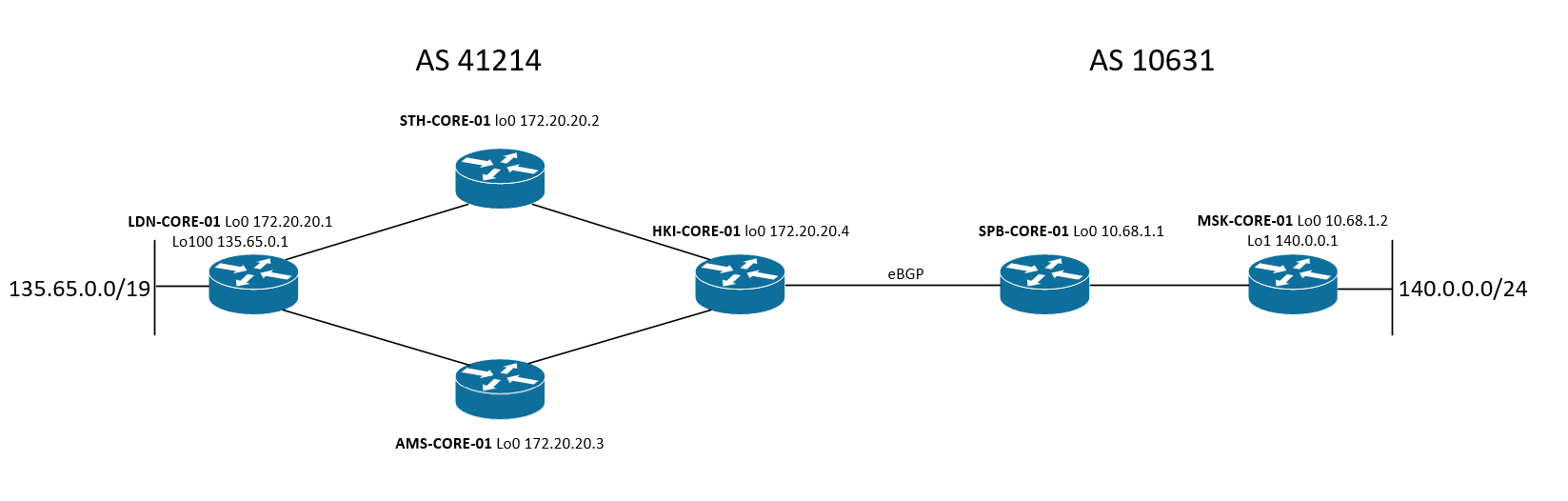
我们管理两个自治系统:AS 41214和AS10631。作为IGP,AS-41214使用IS-IS,而AS-10631-OSPF。 在每个AS内,都使用IBGP-fullmesh。 LDN-CORE-01宣布其BGP邻居前缀135.65.0.0/19,MSK-CORE-01-140.0.0.0/24。 自治系统之间的路由信息交换发生在HKI-CORE-01-SPB-CORE-01的交界处。
HKI-CORE-01,STH-CORE-01 -Junos路由器
LDN-CORE-01,AMS-CORE-01,SPB-CORE-01,MSK-CORE-01 -Cisco IOS路由器
使用Batfish和python SDK安装容器:
docker pull batfish/allinone docker run batfish/allinone docker container exec -it <container> bash
通过python交互模式了解该库:
root@ea9a1559d88e:/
bf_init_snapshot('tmp / habr') -该函数将配置文件加载到Batfish中并准备进行分析。
/ tmp / habr-包含路由器配置文件的目录。
root@ea9a1559d88e:/tmp/habr
现在,让我们确定LDN-CORE-01路由器上BGP会话的状态:
>>> bgp_peers = bfq.bgpSessionStatus(nodes='LDN-CORE-01').answer().frame() >>> bgp_peers Node VRF Local_AS Local_IP Remote_AS Remote_Node Remote_IP Session_Type Est_Status 0 ldn-core-01 default 41214 172.20.20.1 41214 sth-core-01 172.20.20.2 IBGP EST 1 ldn-core-01 default 41214 172.20.20.1 41214 ams-core-01 172.20.20.3 IBGP EST 2 ldn-core-01 default 41214 172.20.20.1 41214 hki-core-01 172.20.20.4 IBGP EST
好吧? 听起来像事实吗?
LDN-CORE-01
现在,根据蝙蝠鱼,我们来看一下HKI-CORE-01路由器上RIB中的IS-IS路由:
>>> isis_routes = bfq.routes(nodes='HKI-CORE-01', protocols='isis').answer().frame() >>> isis_routes Node VRF Network Next_Hop Next_Hop_IP Protocol Admin_Distance Metric Tag 0 hki-core-01 default 172.20.20.3/32 ams-core-01 10.0.0.6 isisL2 18 20 None 1 hki-core-01 default 172.20.20.1/32 ams-core-01 10.0.0.6 isisL2 18 30 None 2 hki-core-01 default 172.20.20.2/32 sth-core-01 10.0.0.4 isisL2 18 10 None 3 hki-core-01 default 172.20.20.1/32 sth-core-01 10.0.0.4 isisL2 18 30 None 4 hki-core-01 default 10.0.0.0/31 sth-core-01 10.0.0.4 isisL2 18 20 None 5 hki-core-01 default 10.0.0.2/31 ams-core-01 10.0.0.6 isisL2 18 20 None
在命令行中:
showroute@HKI-CORE-01
太好了! 我想您已经清楚有蝙蝠鱼了。
在本文的开头,我写道,Batfish可用于在使配置进入“战斗”网络之前检查配置更改。 现在,我建议考虑基于
RobotFramework的网络测试过程。 为此,我编写了一个基于PyBatfish的小模块,该模块可让您执行以下检查:
- 确定网络上BGP会话的状态
- 确定IS-IS邻居状态
- 通过跟踪演示检查网络上节点之间的端到端连接性
- 确定路由器上特定动态路由协议的RIB大小
LibraryBatfish.py import logging from pybatfish.client.commands import bf_logger, bf_init_snapshot from pybatfish.question.question import load_questions, list_questions from pybatfish.question import bfq from pybatfish.datamodel.flow import HeaderConstraints, PathConstraints from robot.api import logger class LibraryBatfish(object): def __init__(self, snapshot): bf_logger.setLevel(logging.ERROR) load_questions() bf_init_snapshot(snapshot) def check_bgp_peers(self): not_established_peers = list() bgp_peers = bfq.bgpSessionStatus().answer() for peer in bgp_peers.rows: if peer.get('Established_Status') != 'ESTABLISHED': not_established_peers.append(dict.fromkeys(peer.get('Local_IP').split(), peer.get('Remote_IP').get('value'))) if len(not_established_peers) == 0: return 1 else: logger.warn('BGP neighbors are not in an established state:') for neighborship in not_established_peers: for peer in neighborship: logger.warn('{} - {}'.format(peer, neighborship.get(peer))) return 0 def check_routes(self, node, protocol): routes = bfq.routes(nodes=node, protocols=protocol).answer() return len(routes.rows) def check_isis_neighbors(self, description): not_isis_enabled_links = list() for link in self._get_isis_enabled_links(description): if link not in self._get_isis_neighbors(): not_isis_enabled_links.append(link) if len(not_isis_enabled_links) == 0: return 1 else: for link in not_isis_enabled_links: logger.warn('{} {} has no IS-IS neighbor'.format(link.get('hostname'), link.get('interface'))) return 0 def ping(self, source_ip, destination_ip): ip_owners = bfq.ipOwners().answer() traceroute = self._get_traceroute_status(source_ip, destination_ip, ip_owners) reverse_traceroute = self._get_traceroute_status(destination_ip, source_ip, ip_owners) if traceroute == True and reverse_traceroute == True: self._show_trace(source_ip, destination_ip, ip_owners) return 1 else: logger.warn('Ping {} -> {} failed'.format(source_ip, destination_ip)) return 0 def _get_traceroute_status(self, source_ip, destination_ip, addresses): tracert = self._unidirectional_virtual_traceroute(source_ip, destination_ip, addresses) isAccepted = True if tracert != None: for trace in tracert.rows[0].get('Traces'): if trace.get('disposition') != 'ACCEPTED': isAccepted = False if isAccepted == True: return True else: return False def _get_paths(self, source_ip, destination_ip, addresses): tracert = self._unidirectional_virtual_traceroute(source_ip, destination_ip, addresses) traces = tracert.rows[0].get('Traces') paths = dict() path_number = 1 for trace in traces: if trace.get('disposition') == 'ACCEPTED': path = list() for hop in trace.get('hops'): path.append(hop.get('node').get('name')) paths[path_number] = path path_number += 1 return paths def _unidirectional_virtual_traceroute(self, source_ip, destination_ip, addresses): for address in addresses.rows: if address.get('IP') == source_ip: node = address.get('Node').get('name') int = address.get('Interface') headers = HeaderConstraints(srcIps=source_ip, dstIps=destination_ip, ipProtocols=['ICMP']) try: tracert = bfq.traceroute(startLocation="{}[{}]".format(node,int), headers=headers).answer() return tracert except: logger.warn('{} address has not been found'.format(source_ip)) def _get_isis_enabled_links(self, description='core-link'): isis_enabled_links = list() interfaces = bfq.interfaceProperties().answer() for int in interfaces.rows: if int.get('Description') != None and description in int.get('Description'): isis_enabled_links.append({'hostname' : int.get('Interface').get('hostname'), 'interface' : int.get('Interface').get('interface')}) return isis_enabled_links def _get_isis_neighbors(self): isis_neighbors = list() isis_adjacencies = bfq.edges(edgeType='isis').answer() for neighbor in isis_adjacencies.rows: isis_neighbors.append(neighbor.get('Interface')) return isis_neighbors def _show_trace(self, source_ip, destination_ip, addresses): logger.console('\nTraceroute to {} from {}'.format(destination_ip, source_ip)) paths = self._get_paths(source_ip, destination_ip, addresses) path_num = 1 for path in paths: n = 1 logger.console('\n Path N{}'.format(path_num)) for hop in paths.get(path): logger.console(' {} {}'.format(n, hop)) n += 1 path_num += 1
场景N1

在我的控制之下,仍然是同一个网络。 假设我需要对
AS 41214和
AS 10631的边界上的过滤器进行
排序 ,并阻塞包含BOGONS范围中的源或目标ip地址的结点数据包。
进行更改之前,请运行测试。
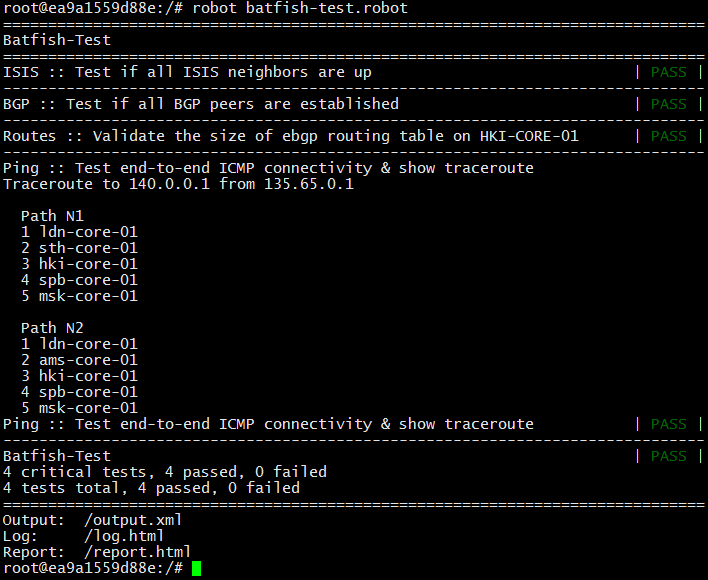
测试通过。
我们将更改
HKI-CORE-01路由器的测试配置-/tmp/habr/configs/
HKI-CORE- 01.cfg:
set firewall family inet filter BOGONS term TERM010 from address 0.0.0.0/8 set firewall family inet filter BOGONS term TERM010 from address 10.0.0.0/8 set firewall family inet filter BOGONS term TERM010 from address 100.64.0.0/10 set firewall family inet filter BOGONS term TERM010 from address 127.0.0.0/8 set firewall family inet filter BOGONS term TERM010 from address 169.254.0.0/16 set firewall family inet filter BOGONS term TERM010 from address 172.16.0.0/12 set firewall family inet filter BOGONS term TERM010 from address 192.0.2.0/24 set firewall family inet filter BOGONS term TERM010 from address 192.88.99.0/24 set firewall family inet filter BOGONS term TERM010 from address 192.168.0.0/16 set firewall family inet filter BOGONS term TERM010 from address 198.18.0.0/15 set firewall family inet filter BOGONS term TERM010 from address 198.51.100.0/24 set firewall family inet filter BOGONS term TERM010 from address 203.0.113.0/24 set firewall family inet filter BOGONS term TERM010 from address 224.0.0.0/4 set firewall family inet filter BOGONS term TERM010 from address 240.0.0.0/4 set firewall family inet filter BOGONS term TERM010 then discard set firewall family inet filter BOGONS term PERMIT-IP-ANY-ANY then accept set interfaces ge-0/0/2.0 family inet filter input BOGONS set interfaces ge-0/0/2.0 family inet filter output BOGONS
运行测试。
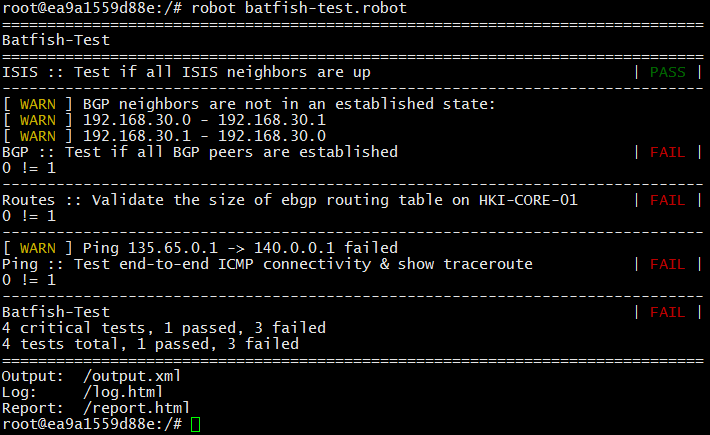
我非常接近,但是如测试输出所示,在进行BGP更改之后,邻居192.168.30.0-192.168.30.1不在“已建立”状态->结果是,点135.65.0.1 <-> 140.0.0.1之间的IP连接丢失了。 怎么了 我们仔细查看了
HKI-CORE-01配置,并看到在专用地址上安装了eBGP对等连接:
showroute@HKI-CORE-01
结论:有必要更改结点的地址或将192.168.30.0/31子网添加到异常中。
我将在例外处的交界处添加一个网络,我将再次更新/tmp/habr/configs/HKI-CORE-01.cfg:
set firewall family inet filter BOGONS term TERM005 from address 192.168.0.0/31 set firewall family inet filter BOGONS term TERM005 then accept
运行测试。

现在,不需要的流量将不再通过ebgp接口AS 41214-AS10631。您可以安全地进行更改,而不必担心后果。
场景N2
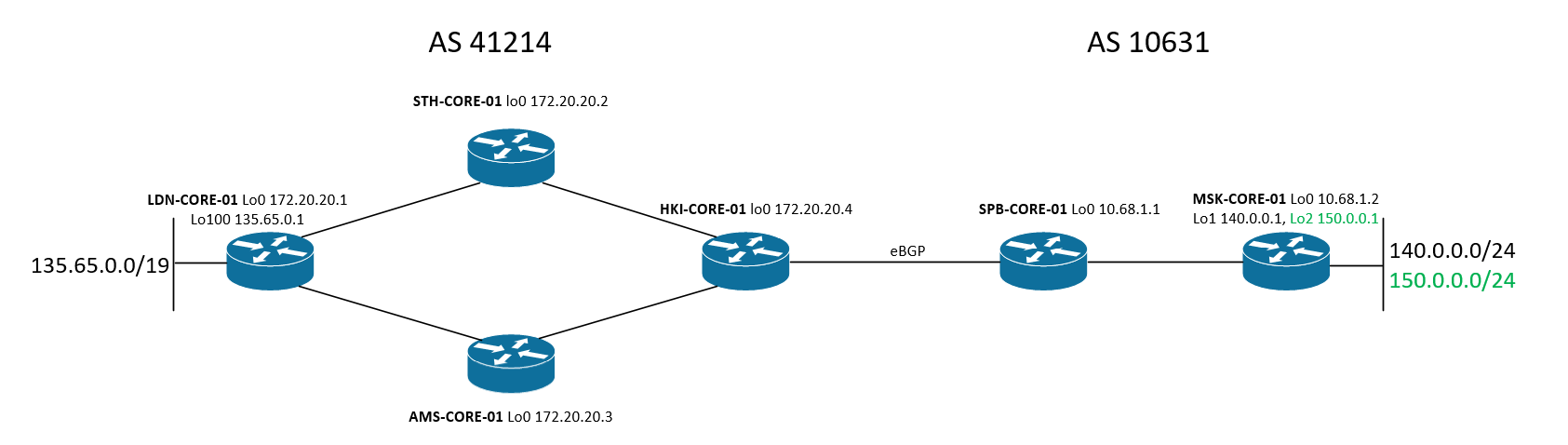
在这里,我需要终止
MSK-CORE-01路由器上的网络150.0.0.0/24,并确保点135.65.0.1和150.0.0.1之间的连接
我在MSK-CORE-01路由器的测试配置中添加了以下几行-tmp / habr / configs / MSK-CORE-01.cfg:
interface Loopback2 ip address 150.0.0.1 255.255.255.255 ! ip route 150.0.0.0 255.255.255.0 Null0 ! router bgp 10631 ! address-family ipv4 network 150.0.0.0 mask 255.255.255.0 !
我更改测试脚本并运行测试:
git diff HEAD~ diff --git a/batfish-robot.robot b/batfish-robot.robot index 8d963c5..ce8cb6a 100644 --- a/batfish-robot.robot +++ b/batfish-robot.robot @@ -5,7 +5,7 @@ Library LibraryBatfish.py tmp/habr ${ISIS-ENABLED-LINK-DESCRIPTION} ISIS-LINK ${NODE} HKI-CORE-01 ${PROTOCOL} ebgp -${RIB-SIZE} 1 +${RIB-SIZE} 2 *** Test Cases *** ISIS @@ -27,3 +27,8 @@ Ping [Documentation] Test end-to-end ICMP connectivity & show traceroute ${result}= Ping 135.65.0.1 140.0.0.1 Should Be Equal As Integers ${result} 1 + +Ping2 + [Documentation] Test end-to-end ICMP connectivity & show traceroute + ${result}= Ping 135.65.0.1 150.0.0.1 + Should Be Equal As Integers ${result} 1
现在,我希望在HKI-CORE-01路由器上看到两条eBGP路由,添加了额外的连接检查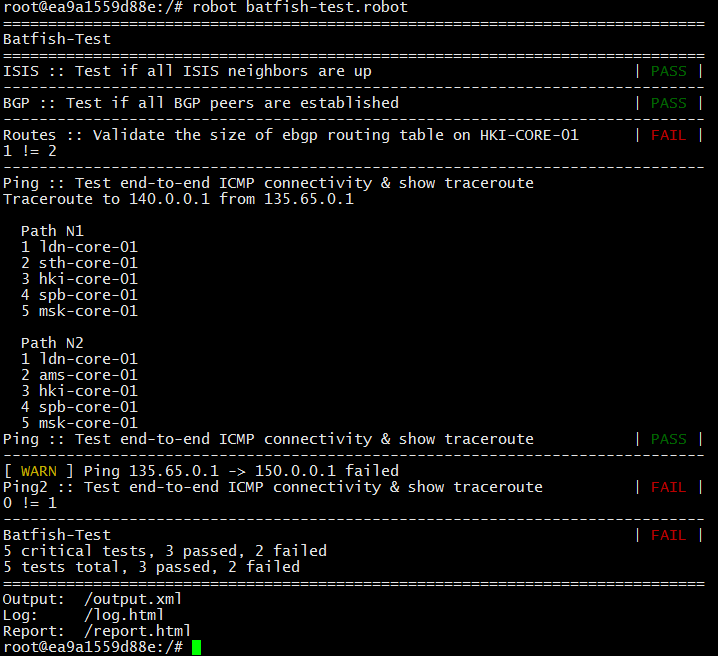
135.65.0.1和150.0.0.1之间没有连接,而且
HKI-CORE-01路由器只有一条eBGP路由,而不是两条。
在向
MSK-CORE-01路由器添加新配置时,请检查
HKI-CORE-01上RIB的内容:
showroute@HKI-CORE-01
请注意从
SPB-CORE-01收到的前缀的导入策略:
set protocols bgp group AS10631 import FROM-AS10631 set protocols bgp group AS10631 neighbor 192.168.30.1 description SPB-CORE-01 set protocols bgp group AS10631 neighbor 192.168.30.1 peer-as 10631 set policy-options policy-statement FROM-AS10631 term TERM010 from route-filter 140.0.0.0/24 exact set policy-options policy-statement FROM-AS10631 term TERM010 then accept set policy-options policy-statement FROM-AS10631 term DENY then reject
缺少150.0.0.0/24的规则。 将其添加到测试配置并运行测试:
showroute@HKI-CORE-01
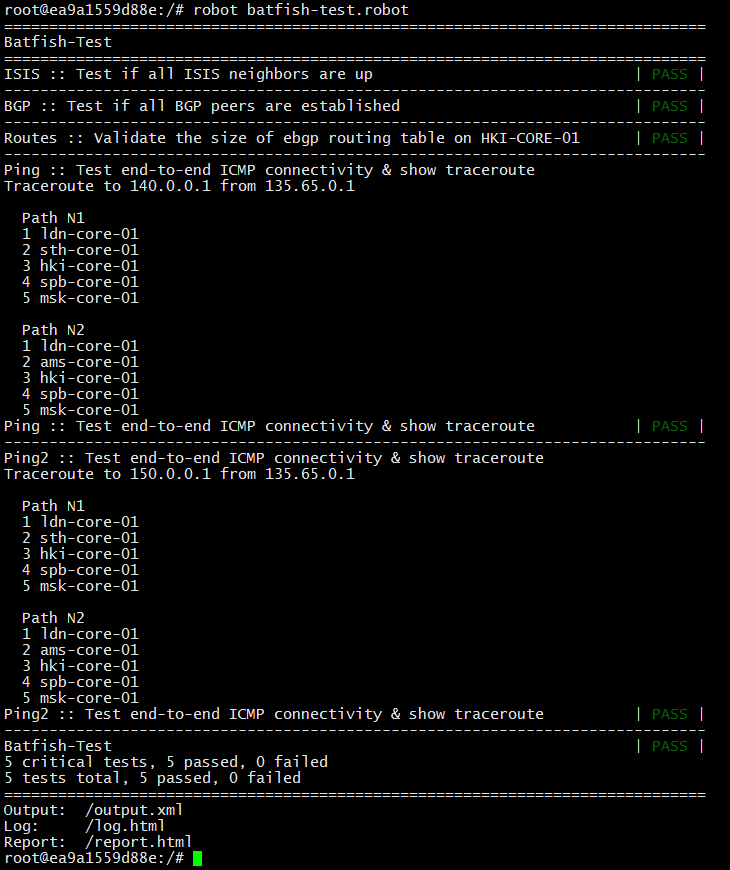
太好了,网络之间存在连通性,所有测试都通过了! 因此,您可以对“战斗”网络的工作进行这些更改。
结论
在我看来,Batfish是具有巨大潜力的强大工具。 试试看,自己看看。
如果您对这个主题感兴趣-加入闲聊,Batfish开发人员将很乐意回答任何问题并快速修复错误。
batfish-org.slack.com谢谢您的关注。
参考文献
www.batfish.orgwww.youtube.com/channel/UCA-OUW_3IOt9U_s60KvmJYAgithub.com/batfish/batfishmedia.readthedocs.org/pdf/pybatfish/latest/pybatfish.pdfgithub.com/showroute/batfish-habr