Habr,您好,今天我们将处理TypeScript和React-hooks。 本教程将帮助您了解“脚本”的基础知识,并帮助您进行前端的测试任务 。
在“无水”项目上测试任务是获得代码审查的机会。 本作业的截止日期为2019年4月11日。

影片版本
如果您懒得阅读,请参加3月20日莫斯科时间21:00的网络研讨会。 注册 (不包括电子邮件和短信)。 举行网络研讨会, 录制网络研讨会。
准备工作
首先,您可以使用Create-react-app TypeScript版本,也可以使用我的入门工具 (已经包含到达路由器)
我将使用我的启动器 (有关更多信息,请参见“实践”部分)。
打字稿理论
当您的变量可以采用不同的值时,TS解决了JavaScript中的“动态类型化”问题。 现在是一条线,然后是一个数字,甚至是一个对象。 在“ 19世纪”中编写代码非常方便,但是,现在每个人都同意,如果您具有预定义的类型(考虑规则),则代码库更易于维护。 而且在开发阶段的错误更少。
例如,如果您有一个显示一个新闻项的组件,我们可以为新闻项指定以下类型:
因此,我们为“新闻”对象的属性指定了严格的“静态”类型。 如果我们尝试获取不存在的属性,TypeScript将显示错误。
import * as React from 'react' import { INewsItem } from '../models/news'
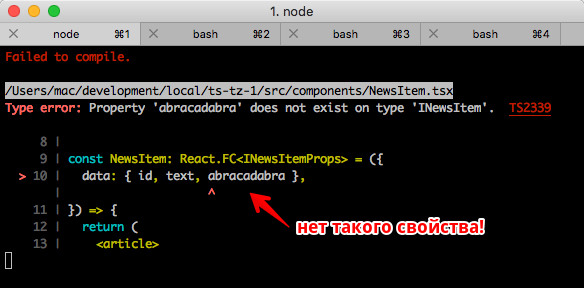
此外,Visual Studio Code和其他高级编辑器还会向您显示错误:

视觉上方便。 以我为例,VS Code一次显示两个错误:未设置变量的类型(即,它在我们的“界面”新闻中不存在)和“未使用该变量”。 此外,默认情况下,在VS Code中使用TypeScript时未使用的变量会以浅色突出显示。
这里值得一提的是指出TypeScript和VS Code如此紧密集成的原因:这两种产品都是Microsoft的开发。
TypeScript还能立即告诉我们什么? 就变量的上下文而言,就是这样。 TS非常强大,他了解什么。
const NewsItem: React.FC<INewsItemProps> = ({ data: { id, title, text } }) => { return ( <article> <div>{id.toUpperCase()}</div> {/* , , 'number' toUpperCase() */} <div>{title.toUpperCase()}</div> {/* ! */} <div>{text}</div> </article> ) }
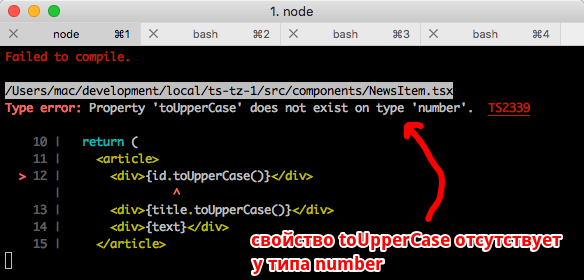
在这里,TypeScript立即宣誓使用不存在的属性-类型number toUpperCase 。 而且我们知道,确实只有字符串类型具有toUpperCase()方法。
现在想象,您开始编写某个函数的名称,打开括号,编辑器将立即为您显示一个弹出帮助窗口,该窗口指示可以向该函数传递哪些参数和哪种类型。
或想像-您严格遵循了建议,并且在项目中键入内容是防弹的。 除了自动替换之外,您还可以解决项目中隐式( undefined )值的问题。
练习
我们用react-hooks + TypeScript重写了第一个测试任务 。 现在,我们省略Redux ,否则,您无需复制“ 重新启动的TK#1 ”,而只需复制所有内容即可。
工具包
(对于那些使用VS Code的人 )
为了方便起见,建议您安装TSLint扩展名 。
要在保存时启用TSLint错误自动修复,请添加编辑器设置:
您可以通过菜单进入这些设置,或查看它们在操作系统中的实际位置。
TSLint设置是标准设置,另外我禁用了一条规则。
{ "extends": ["tslint:recommended", "tslint-react", "tslint-config-prettier"], "linterOptions": { "exclude": [ "node_modules/**/*.ts", "src/serviceWorker.js" ] }, "rules": { "object-literal-sort-keys": false
整合结束!
我们正在编写一个应用程序
在演出过程中,我们会为我们熟悉新事物。 首先,请克隆您的1-start分支或与您代码中的我的代码同步。
所有反应类型脚本文件的扩展名为.tsx 。
起始模板中有什么有趣的东西?
让我们从src / App.tsx开始:
import * as React from 'react' import './App.css' const App = () => { return ( <div className="container"> <h1>TZ #1 with hooks & TypeScript</h1> <nav> <p></p> </nav> <p> </p> </div> ) } const RoutedApp = () => { return <App /> } export { RoutedApp }

好的,标准启动。 让我们尝试向<App />添加一些属性
src / App.tsx
const App = props => { return ( <div className="container"> <h1>TZ #1 with hooks & TypeScript</h1> <nav> <p></p> </nav> <p> </p> {/* name props */} <p>, {props.name}</p> </div> ) } // name const RoutedApp = () => { return <App name="Max Frontend" /> }
我们得到错误:
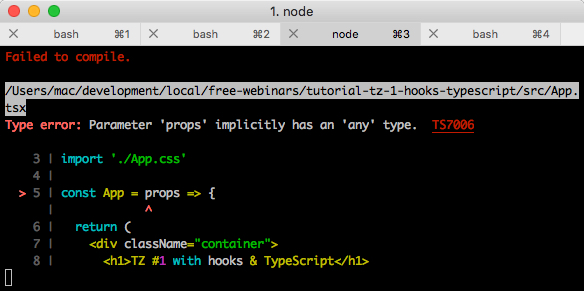
(如果没有收到错误,请检查tsconfig.json设置的严格性,应该有一个noImplicitAny规则)
您已经从错误文本的翻译中猜测到,我们的属性不应为any类型。 此类型可以翻译为“任何内容”。 我们的项目有一条规则,禁止这种类型的隐式输出。
-隐式类型推断?
没错! 默认情况下,TypeScript能够推断出变量的类型,并且可以很好地解决这一问题。 这称为类型推断。
一个例子:
let x = 3
对于props -TS无法100%确定变量的类型,因此说-使其为any )。 这是隐式完成的,并且在项目设置(tsconfig.json)中的noImplicitAny规则禁止这样做
我们可以明确指定任何类型,错误将消失。 变量的类型由冒号表示。
完成,没有错误,该项目可以正常工作,但是当props可以是任何东西时,这种打字有什么用? 我们肯定知道我们的名字是一个
尽量避免输入任何
有时需要采取any措施,这是正常现象,但是通过严格打字,这立即是对腰部以下的打击。
为了描述props类型,我们将使用interface关键字:
尝试将name类型更改为number ,将立即发生错误。
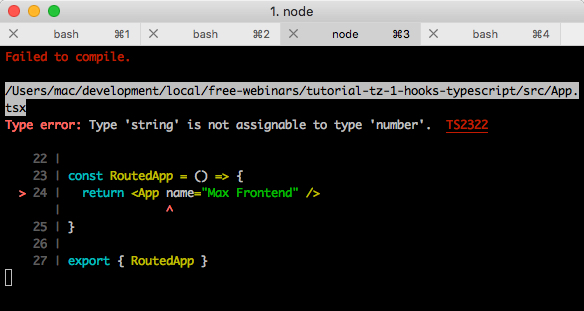
此外,该错误还将在VS Code(和许多其他编辑器)中强调。 该错误表明我们没有匹配项:我们传递了一个字符串,但是我们期望一个数字。
我们props然后在<App />添加其他props -网站
src / App.tsx
interface IAppProps { name: string; } const App = (props: IAppProps) => { return ( <div className="container"> <h1>TZ #1 with hooks & TypeScript</h1> <nav> <p></p> </nav> <p> </p> <p>, {props.name}</p> {/* site */} <p>: {props.site}</p> </div> ) } // site const RoutedApp = () => { return <App name="Max Frontend" site="maxpfrontend.ru" /> }
出现错误:
Type error: Property 'site' does not exist on type 'IAppProps'. TS2339
site属性在IAppProps类型中不存在。 在这里,我立即要说的是,通过类型名称,我们可以立即理解在哪里查找。 因此,正确命名类型。
在修复它之前,我们先做以下操作:删除props.site的段落。
我们得到另一个错误文本:
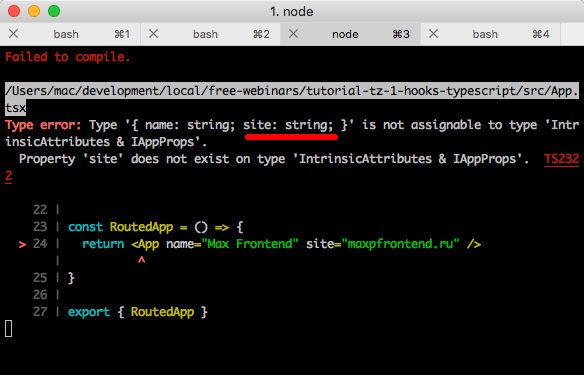
在这里,我只想说明TS的推论: site是一种string类型(在屏幕截图中带有下划线)。
修正:
interface IAppProps { name: string; site: string;
没有错误,没有问题。
要使用路由,我们需要子级渲染。 让我们超越自己,尝试绘制“子组件”。
const App = (props: IAppProps) => { return ( <div className="container"> <h1>TZ #1 with hooks & TypeScript</h1> ... // <p>: {props.site}</p> {props.children} </div> ) } const Baby = () => { return <p> </p> } const RoutedApp = () => { return ( <App name="Max Frontend" site="maxpfrontend.ru"> <Baby /> </App> ) }
他们这么说,TS发誓IAppProps children没有描述children 。
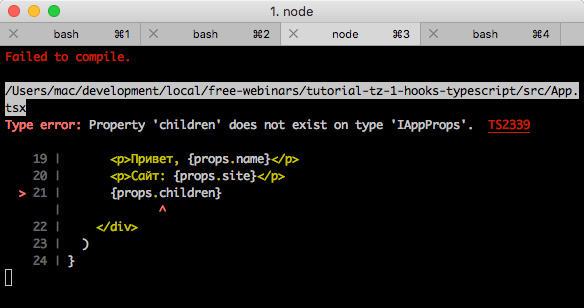
当然,我们不想“典型化”一些标准的东西,在这里,社区开始了救援,这已经在我们面前敲了很多。 例如, @ types / react包包含react的所有类型。
通过安装此软件包(在我的示例中,它已经安装),我们可以使用以下条目:
React.FunctionComponent<P> React.FC<P>
其中<P>是我们props的类型,即记录将采用以下形式。
React.FC<IAppProps>
对于那些喜欢阅读大量文本的人,在练习之前,我可以提供有关“ 泛型 ”(那些<and>)的文章。 对于剩下的内容,就目前而言,这样翻译这个短语就足够了:一个接受<such and such properties>的功能组件。
App组件的条目将略有变化。 完整版。
src / App.tsx
// , // React React.XXX, // XXX - import * as React from 'react' // , , // @types/react // interface IAppProps { name: string; site: string; } // const App: React.FC<IAppProps> = props => { return ( <div className="container"> <h1>TZ #1 with hooks & TypeScript</h1> <nav> <p></p> </nav> <p> </p> <p>, {props.name}</p> <p>: {props.site}</p> {props.children} </div> ) } const Baby = () => { return <p> </p> } const RoutedApp = () => { return ( <App name="Max Frontend" site="maxpfrontend.ru"> <Baby /> </App> ) }
让我们将以下行解析为字符:
const App: React.FC<IAppProps> = props => {
-为什么类型在props后消失了?
-因为在App -添加了。
我们记录了App变量的类型: React.FC<IAppProps> 。
React.FC是“函数”的一种,在<>内,我们指示了它采用的参数类型,即指示我们的props将是IAppProps类型。
(我可能会对您撒谎,但是为了简化示例,我认为可以)
总计:我们学会了为传输的props指定属性的类型,同时又不丢失React-components的“其”属性。
目前的源代码 。
添加路由
我们将使用到达路由器来拓宽视野。 该软件包与react-router非常相似。
添加页面-新闻(新闻),清理<App /> 。
src /页面/ News.tsx
import * as React from 'react' const News = () => { return ( <div className="news"> <p></p> </div> ) } export { News }
src / App.tsx
import * as React from 'react'
应用程序已损坏,这是一个错误(错误之一,因为终端显示了第一个错误):

我们已经习惯了该记录,并且从中了解到<App />的类型描述中不存在path 。
同样,一切都摆在我们面前。 我们将使用@ types / reach__router包和RouteComponentProps类型。 为了不丢失我们的属性,我们将使用extends 。
import * as React from 'react'
出于好奇, RouteComponentProps中描述了哪些类型。
<App />的错误消失了,但仍保留在<News /> ,因为我们没有为该组件指定类型。
迷你拼图:指定<News /> 。 目前,仅路由器的属性被传输到那里。
答案是:
src /页面/ News.tsx
import * as React from 'react' import { RouteComponentProps } from '@reach/router'
我们继续并添加带有参数的路线。 到达路由器中的参数直接存在于道具中。 您记得,在react-router中,它们位于props.match 。
src / App.tsx
import * as React from 'react' import { Link, RouteComponentProps, Router } from '@reach/router' import { About } from './pages/About' import { News } from './pages/News'
src /页面/ About.tsx
import * as React from 'react' import { RouteComponentProps } from '@reach/router' const About: React.FC<RouteComponentProps> = props => { return ( <div className="about"> <p> about</p> {/* source */} <p>{props.source}</p> </div> ) } export { About }
我们没想到的错误:
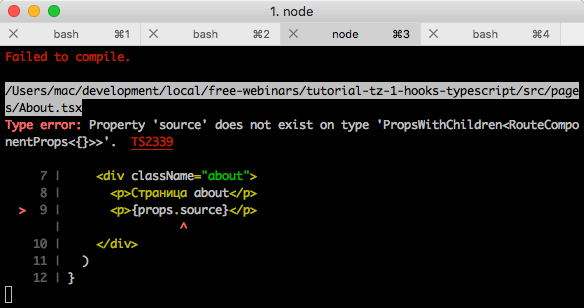
source属性不存在...一方面,困惑:我们将其传递给字符串形式的path,另一方面,喜悦:嗯,好吧,库的作者和键入如何尝试向我们添加此警告。
要修复它,我们将使用以下选项之一 :从RouteComponentProps扩展并指定可选的source属性。 可选,因为它可能不在我们的URL中。
TypeScript使用问号表示可选属性。
src /页面/ About.tsx
import * as React from 'react' import { RouteComponentProps } from '@reach/router' interface IAboutProps extends RouteComponentProps { source?: string;
src / App.tsx (同时我们将Russify导航)
import * as React from 'react' import { Link, RouteComponentProps, Router } from '@reach/router' import { About } from './pages/About' import { News } from './pages/News' import './App.css' interface IAppProps extends RouteComponentProps { name: string; site: string; } const App: React.FC<IAppProps> = props => { return ( <div className="container"> <h1>TZ #1 with hooks & TypeScript</h1> <nav> <Link to="/"></Link> <Link to="news"></Link>{' '} <Link to="/about/habr"> habr</Link>{' '} </nav> <hr /> <p> {' '} : {props.name} | : {props.site} </p> <hr /> {props.children} </div> ) } const RoutedApp = () => { return ( <Router> <App path="/" name="Max Frontend" site="maxpfrontend.ru"> <News path="/news" /> <About path="/about/:source" /> </App> </Router> ) } export { RoutedApp }
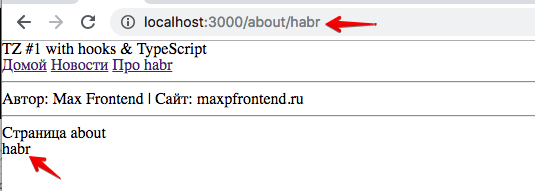
总计 :我们学会了区分轮换所涉及的组件。
目前的源代码 。
让我们使用钩子并继续输入
提醒您,我们的任务是实施测试任务 ,但不使用Redux。
我准备了一个分支 ,以通过路由,无效的登录表单和必要的页面开始此步骤。
下载新闻
新闻是一系列对象。
展示我们的新闻:
{ id: 1, title: ' CRUD React-hooks', text: ' CRUD- ', link: 'https://maxpfrontend.ru/perevody/delaem-crud-prilozhenie-s-pomoschyu-react-hooks/', timestamp: new Date('01-15-2019'), },
让我们立即编写一个模型(新闻类型):
src / models / news.ts ( .ts扩展名)
export interface INewsItem { id: number; title: string; text: string; link: string; timestamp: Date; }
从新的一个时间戳指示类型Date 。
想象一下我们的数据通话:
const fakeData = [ { id: 1, title: ' CRUD React-hooks', text: ' CRUD- ', link: 'https://maxpfrontend.ru/perevody/delaem-crud-prilozhenie-s-pomoschyu-react-hooks/', timestamp: new Date('01-15-2019'), }, { id: 2, title: ' React hooks', text: ' useState useEffect ', link: 'https://maxpfrontend.ru/perevody/znakomstvo-s-react-hooks/', timestamp: new Date('01-06-2019'), }, { id: 3, title: ' Google Sign In', text: ' Google Sign In ', link: 'https://maxpfrontend.ru/vebinary/avtorizatsiya-s-pomoschyu-google-sign-in/', timestamp: new Date('11-02-2018'), }, ] export const getNews = () => { const promise = new Promise(resolve => { resolve({ status: 200, data: fakeData,
我们从api getNews调用返回Promise ,并且此“ Promise”具有某种类型,我们还可以描述以下类型:
interface INewsResponse { status: number;
很热吗 由于Promise类型是泛型,所以现在变得更热了,我们将不得不再次处理<和> 。 这是本教程中最困难的部分,因此我们阅读了最终代码:
src / api / News.ts
import { INewsItem } from '../models/news'
抽烟。
显示新闻
src /页面/ News.tsx
import * as React from 'react' import { RouteComponentProps } from '@reach/router' import { getNews } from '../api/news' import { NewsItem } from '../components/NewsItem'
该代码给出了与TypeScript相关的注释。 如果您需要有关React Hook的帮助,则可以在这里阅读: 文档 (EN), 教程 (RU)。
任务:编写一个将显示新闻的<NewsItem />组件。 记住要指定正确的类型。 使用INewsItem模型。
结果可能如下所示:

解决方案如下。
src /组件/ NewsItem.tsx
import * as React from 'react' import { INewsItem } from '../models/news' interface INewsItemProps { data: INewsItem;
问题是为什么我们以这种方式描述接口(代码[1]和[2]中的注释)。 我们可以写:
React.FC<INewsItem>
答案如下。
。
。
。
可以,因为我们要在data属性中传递新闻,也就是说,我们必须编写:
React.FC<{ data: INewsItem }>
我们所做的只是区别在于我们指定了interface ,以防其他属性被添加到组件中。 而且可读性更好。
总计:我们练习了Promise和useEffect的键入。 描述了另一个组件的类型。
如果您仍然不愿意接受TS自动替代和严格性认证,那么您要么不练习,要么不适合严格输入。 在第二种情况下-我无能为力,这只是一个品味问题。 我要引起您的注意的是,市场决定了它的条件,并且越来越多的项目使用打字(如果不是使用TypeScript,则使用flow) 。
目前的源代码 。
身份验证API
编写用于登录的api 。 原理相似-我们返回带有授权/错误答案的promise 。 我们会将有关授权状态的信息存储在localStorage ( 许多人认为这是对安全的公然侵犯,我在争端中有些落后,并且不知道它如何结束 )。
在我们的应用程序中,登录名是一堆用户名和密码(均为字符串),我们将描述模型:
src /模型/ user.ts
export interface IUserIdentity { username: string; password: string; }
src / api / auth.ts
import { navigate } from '@reach/router' import { IUserIdentity } from '../models/user'
, .
:
: . useState . event onChange / onSubmit — any . .
React.useState — , ( React.useState<T> )
, , , . , /profile ( navigate )
.
。
。
。
。
src/pages/Login.tsx
import * as React from 'react' import { navigate, RouteComponentProps } from '@reach/router' import { authenticate } from '../api/auth' import { IUserIdentity } from '../models/user'
, TS — . , , JavaScript.
: useState event
→
TypeScript' , .
, reach-router , react-router. , , , .
src/components/common/Authenticated.tsx
import * as React from 'react' import { Redirect, RouteComponentProps } from '@reach/router' import { checkAuthStatus } from '../../api/auth'
src/App.tsx
import * as React from 'react' import { Link, RouteComponentProps, Router } from '@reach/router' import { Authenticated } from './components/ommon/Authenticated' import { Home } from './pages/Home' import { Login } from './pages/Login' import { News } from './pages/News' import { Profile } from './pages/Profile' import { checkAuthStatus, logout } from './api/auth' import './App.css' const App: React.FC<RouteComponentProps> = props => { return ( <div className="container"> <h1>TZ #1 with hooks & TypeScript</h1> <nav> <Link to="/"></Link> <Link to="news"></Link>{' '} <Link to="profile"></Link>{' '} {checkAuthStatus() ? <button onClick={logout}></button> : null} </nav> {props.children} </div> ) } const RoutedApp = () => { return ( <Router> <App path="/"> <Home path="/" /> <Login path="/login" /> <News path="/news" /> <Authenticated path="/profile"> <Profile path="/" /> </Authenticated> </App> </Router> ) } export { RoutedApp }
.
. type="password" .
, . "-", , , react-intl , react-i18next .
, . :
src/localization/formErrors.ts
const formErrors = { ru: { incorrect_login_or_password: ' ', }, en: { incorrect_login_or_password: 'Incorrect login or password', }, } export { formErrors }
<Login />
src/pages/Login.tsx
import * as React from 'react' import { navigate, RouteComponentProps } from '@reach/router' import { authenticate } from '../api/auth'
, .
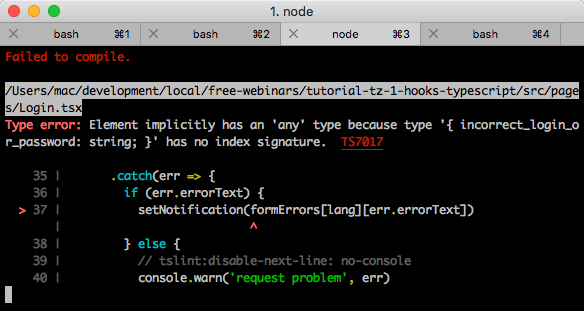
TypeScript , , . , index signature ( , StackOverflow ).
interface IFormErrors { [key: string]: { [key: string]: string, }; } const formErrors: IFormErrors = { ru: { incorrect_login_or_password: ' ', }, en: { incorrect_login_or_password: 'Incorrect login or password', }, } export { formErrors }
, . , "".
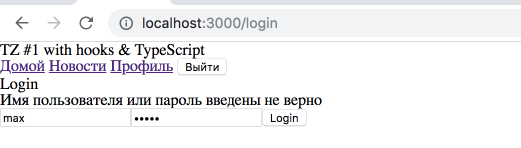
→
结论
TypeScript. , TS . , , "one" "two" ( — union).
, — .
" " telegram youtube ( 11 2019).
感谢您的关注! , :

CRA + TypeScript
TypeScript Playground
— Understanding TypeScript's type notation ( Dr.Axel Rauschmayer)
Microsoft,
TSLint
tslint
tslint
tsconfig.json tslint.json
d.ts .ts
, staging .
react-typescript-samples LemonCode
:
es5 (!)
React v16
typescript-.
Microsoft. UI- Fabric . , github .