本文以描述基于Feistel网络上的GOST 28147-89的加密算法实现的示例为例,展示了BE-T1000双核处理器(又名Baikal-T1)的功能,并使用带有和不带有SIMD协处理器的矢量计算对算法实现进行了比较测试。 在这里,我们将演示如何按照GOST 28147-89,ECB模式将SIMD块用于加密任务。
这篇文章是去年由贝加尔电子公司的首席程序员Alexei Kolotnikov为《 电子元器件 》杂志撰写的。 而且由于该杂志的读者并不多,而且该文章对那些从事密码学的专业人士很有用,因此,我在作者和他的少量添加物的允许下,将其发表在这里。
贝加尔湖T1处理器及其内部的SIMD块
Baikal-T1处理器包括MIPS32 P5600系列的多处理器双核系统,以及一组用于交换数据的低速接口和用于控制外围设备的低速。 这是该处理器的结构图:
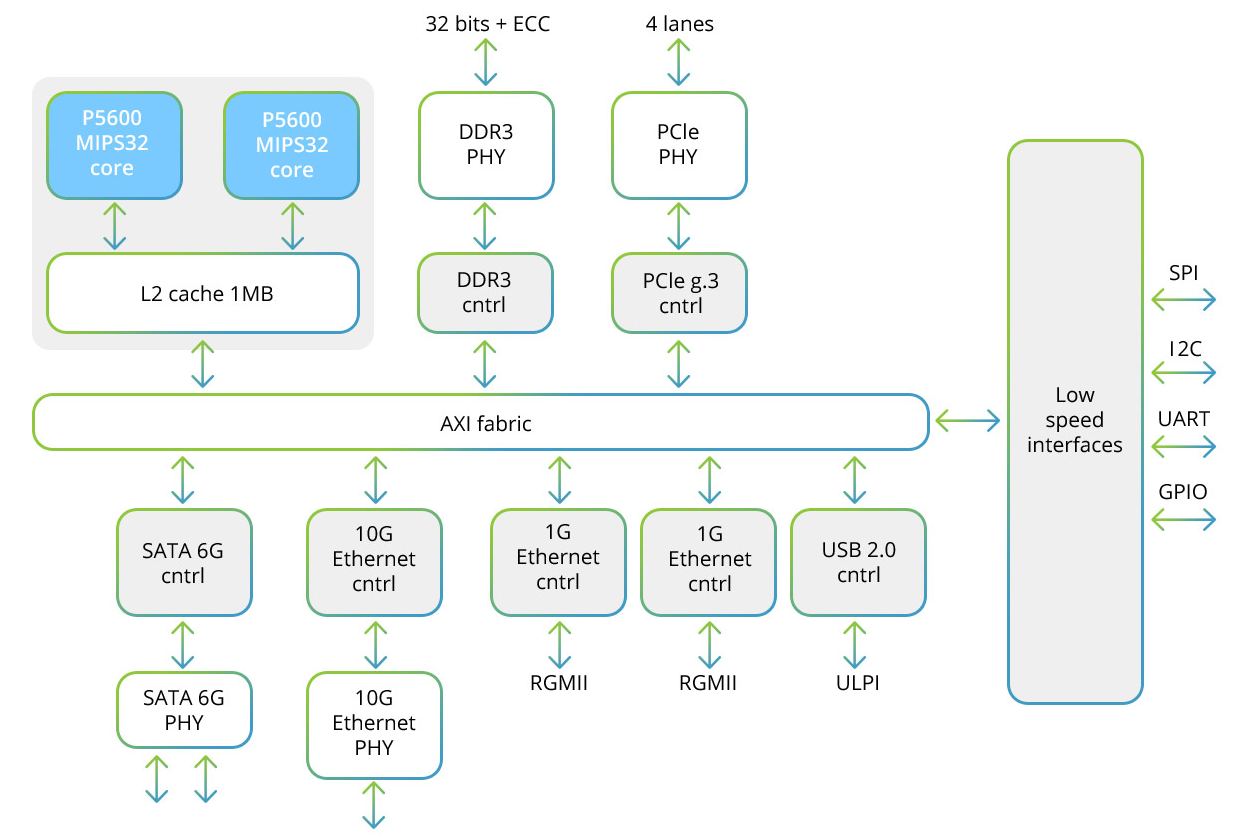
两个内核中的每个内核都包含一个SIMD块,可让您使用128位向量。 使用SIMD方法时,将处理多个样本,
整个向量可能包含多个样本,也就是说,一个命令立即应用于数据的整个向量(数组)。 因此,在一个命令周期中,将处理几个样本。 该处理器使用MIPS32 SIMD模块,该模块允许您使用32个128位寄存器。
每个寄存器可以包含以下尺寸的向量:8×16; 8×16。 16×8; 4×32或
2×64位。 可以使用150多个指令来处理数据:整数,浮点数和定点数,包括按位运算,比较运算和转换运算。
SparF在文章“ MIPS SIMD技术和Baikal-T1处理器”中描述了非常详细的MIPS SIMD技术。
矢量计算有效性的评估
Baikal-T1处理器内核的算术协处理器结合了传统的浮点处理器和并行SIMD处理器,专注于矢量和数字信号的高效处理。 SparF于2017年对向量SIMD协处理器进行了独立的性能评估,同时撰写了文章“ MIPS SIMD技术和Baikal-T1处理器” 。 如果需要,可以通过连接到带有处理器的远程支架来独立执行这些测量。
然后,测试任务是解码使用免费的x264库(H.264演示剪辑)和x265(HEVC视频文件)编码的视频,并定期捕获屏幕截图。 如预期的那样,注意到通过使用SIMD硬件功能,FFmpeg任务的处理器核心性能有了显着提高:

GOST 28147-89算法的简要说明
在这里,我们仅说明了解代码和优化的主要特征:
- 该算法建立在Feistel网络上。

- 该算法包括32个回合。
- 一回合包括混合密钥和将表中4位的8部分替换为11位的移位。
在苏联国家标准中给出了根据GOST 28147-89的信息转换算法的详细说明。
在不使用SIMD块的情况下实现GOST 28147-89算法
为了进行比较,算法最初是使用标准的“非矢量化”命令实现的。
此处提出的MIPS汇编代码允许您以1200 MHz的标称处理器频率在450 ns(或〜150 Mb / s)内加密一个64位块。 计算仅涉及一个核心。
准备替换表意味着将其扩展为32位的表示形式以加快回合的工作:而不是预先通过屏蔽和移位来替换四位
准备好的表将替换每个八位。
uint8_t sbox_test[8][16] = { {0x9, 0x6, 0x3, 0x2, 0x8, 0xb, 0x1, 0x7, 0xa, 0x4, 0xe, 0xf, 0xc, 0x0, 0xd, 0x5}, {0x3, 0x7, 0xe, 0x9, 0x8, 0xa, 0xf, 0x0, 0x5, 0x2, 0x6, 0xc, 0xb, 0x4, 0xd, 0x1}, {0xe, 0x4, 0x6, 0x2, 0xb, 0x3, 0xd, 0x8, 0xc, 0xf, 0x5, 0xa, 0x0, 0x7, 0x1, 0x9}, {0xe, 0x7, 0xa, 0xc, 0xd, 0x1, 0x3, 0x9, 0x0, 0x2, 0xb, 0x4, 0xf, 0x8, 0x5, 0x6}, {0xb, 0x5, 0x1, 0x9, 0x8, 0xd, 0xf, 0x0, 0xe, 0x4, 0x2, 0x3, 0xc, 0x7, 0xa, 0x6}, {0x3, 0xa, 0xd, 0xc, 0x1, 0x2, 0x0, 0xb, 0x7, 0x5, 0x9, 0x4, 0x8, 0xf, 0xe, 0x6}, {0x1, 0xd, 0x2, 0x9, 0x7, 0xa, 0x6, 0x0, 0x8, 0xc, 0x4, 0x5, 0xf, 0x3, 0xb, 0xe}, {0xb, 0xa, 0xf, 0x5, 0x0, 0xc, 0xe, 0x8, 0x6, 0x2, 0x3, 0x9, 0x1, 0x7, 0xd, 0x4} }; uint32_t sbox_cvt[4*256]; for (i = 0; i < 256; ++i) { uint32_t p; p = sbox[7][i >> 4] << 4 | sbox[6][i & 15]; p = p << 24; p = p << 11 | p >> 21; sbox_cvt[i] = p; // S87 p = sbox[5][i >> 4] << 4 | sbox[4][i & 15]; p = p << 16; p = p << 11 | p >> 21; sbox_cvt[256 + i] = p; // S65 p = sbox[3][i >> 4] << 4 | sbox[2][i & 15]; p = p << 8; p = p << 11 | p >> 21; sbox_cvt[256 * 2 + i] = p; // S43 p = sbox[1][i >> 4] << 4 | sbox[0][i & 15]; p = p << 11 | p >> 21; sbox_cvt[256 * 3 + i] = p; // S21 }
块加密是使用密钥进行的这一轮重复的32倍。
// input: a0 - &in, a1 - &out, a2 - &key, a3 - &sbox_cvt LEAF(gost_encrypt_block_asm) .set reorder lw n1, (a0) // n1, IN lw n2, 4(a0) // n2, IN + 4 lw t0, (a2) // key[0] -> t0 gostround n1, n2, 1 gostround n2, n1, 2 gostround n1, n2, 3 gostround n2, n1, 4 gostround n1, n2, 5 gostround n2, n1, 6 gostround n1, n2, 7 gostround n2, n1, 0 gostround n1, n2, 1 gostround n2, n1, 2 gostround n1, n2, 3 gostround n2, n1, 4 gostround n1, n2, 5 gostround n2, n1, 6 gostround n1, n2, 7 gostround n2, n1, 0 gostround n1, n2, 1 gostround n2, n1, 2 gostround n1, n2, 3 gostround n2, n1, 4 gostround n1, n2, 5 gostround n2, n1, 6 gostround n1, n2, 7 gostround n2, n1, 7 gostround n1, n2, 6 gostround n2, n1, 5 gostround n1, n2, 4 gostround n2, n1, 3 gostround n1, n2, 2 gostround n2, n1, 1 gostround n1, n2, 0 gostround n2, n1, 0 1: sw n2, (a1) sw n1, 4(a1) jr ra nop END(gost_encrypt_block_asm)
分布表回合只是表交换。
.macro gostround x_in, x_out, rkey addu t8, t0, \x_in /* key[0] + n1 = x */ lw t0, \rkey * 4 (a2) /* next key to t0 */ ext t2, t8, 24, 8 /* get bits [24,31] */ ext t3, t8, 16, 8 /* get bits [16,23] */ ext t4, t8, 8, 8 /* get bits [8,15] */ ext t5, t8, 0, 8 /* get bits [0, 7] */ sll t2, t2, 2 /* convert to dw offset */ sll t3, t3, 2 /* convert to dw offset */ sll t4, t4, 2 /* convert to dw offset */ sll t5, t5, 2 /* convert to dw offset */ addu t2, t2, a3 /* add sbox_cvt */ addu t3, t3, a3 /* add sbox_cvt */ addu t4, t4, a3 /* add sbox_cvt */ addu t5, t5, a3 /* add sbox_cvt */ lw t6, (t2) /* sbox[x[3]] -> t2 */ lw t7, 256*4(t3) /* sbox[256 + x[2]] -> t3 */ lw t9, 256*2*4(t4) /* sbox[256 *2 + x[1]] -> t4 */ lw t1, 256*3*4(t5) /* sbox[256 *3 + x[0]] -> t5 */ or t2, t7, t6 /* | */ or t3, t1, t9 /* | */ or t2, t2, t3 /* | */ xor \x_out, \x_out, t2 /* n2 ^= f(...) */ .endm
使用SIMD块实现GOST 28147-89算法
下面提出的代码使您可以在相同条件下同时对每720 ns(约350 Mbit / s)的64位四个块进行加密:处理器频率1200 MHz,一个内核。
用shuffle指令和随后的有效四位数掩盖,将其替换成两个四倍体,然后立即分成4个块。
扩展替代表
for(i = 0; i < 16; ++i) { sbox_cvt_simd[i] = (sbox[7][i] << 4) | sbox[0][i]; // $w8 [7 0] sbox_cvt_simd[16 + i] = (sbox[1][i] << 4) | sbox[6][i]; // $w9 [6 1] sbox_cvt_simd[32 + i] = (sbox[5][i] << 4) | sbox[2][i]; // $w10[5 2] sbox_cvt_simd[48 + i] = (sbox[3][i] << 4) | sbox[4][i]; // $w11[3 4] }
初始化掩码。
l0123: .int 0x0f0f0f0f .int 0xf000000f /* substitute from $w8 [7 0] mask in w12*/ .int 0x0f0000f0 /* substitute from $w9 [6 1] mask in w13*/ .int 0x00f00f00 /* substitute from $w10 [5 2] mask in w14*/ .int 0x000ff000 /* substitute from $w11 [4 3] mask in w15*/ .int 0x000f000f /* mask $w16 x N x N */ .int 0x0f000f00 /* mask $w17 N x N x */ LEAF(gost_prepare_asm) .set reorder .set msa la t1, l0123 /* masks */ lw t2, (t1) lw t3, 4(t1) lw t4, 8(t1) lw t5, 12(t1) lw t6, 16(t1) lw t7, 20(t1) lw t8, 24(t1) fill.w $w2, t2 /* 0f0f0f0f -> w2 */ fill.w $w12, t3 /* f000000f -> w12*/ fill.w $w13, t4 /* 0f0000f0 -> w13*/ fill.w $w14, t5 /* 00f00f00 -> w14*/ fill.w $w15, t6 /* 000ff000 -> w15*/ fill.w $w16, t7 /* 000f000f -> w16*/ fill.w $w17, t8 /* 0f000f00 -> w17*/ ld.b $w8, (a0) /* load sbox */ ld.b $w9, 16(a0) ld.b $w10, 32(a0) ld.b $w11, 48(a0) jr ra nop END(gost_prepare_asm)
4块加密
LEAF(gost_encrypt_4block_asm) .set reorder .set msa lw t1, (a0) // n1, IN lw t2, 4(a0) // n2, IN + 4 lw t3, 8(a0) // n1, IN + 8 lw t4, 12(a0) // n2, IN + 12 lw t5, 16(a0) // n1, IN + 16 lw t6, 20(a0) // n2, IN + 20 lw t7, 24(a0) // n1, IN + 24 lw t8, 28(a0) // n2, IN + 28 lw t0, (a2) // key[0] -> t0 insert.w ns1[0],t1 insert.w ns2[0],t2 insert.w ns1[1],t3 insert.w ns2[1],t4 insert.w ns1[2],t5 insert.w ns2[2],t6 insert.w ns1[3],t7 insert.w ns2[3],t8 gostround4 ns1, ns2, 1 gostround4 ns2, ns1, 2 gostround4 ns1, ns2, 3 gostround4 ns2, ns1, 4 gostround4 ns1, ns2, 5 gostround4 ns2, ns1, 6 gostround4 ns1, ns2, 7 gostround4 ns2, ns1, 0 gostround4 ns1, ns2, 1 gostround4 ns2, ns1, 2 gostround4 ns1, ns2, 3 gostround4 ns2, ns1, 4 gostround4 ns1, ns2, 5 gostround4 ns2, ns1, 6 gostround4 ns1, ns2, 7 gostround4 ns2, ns1, 0 gostround4 ns1, ns2, 1 gostround4 ns2, ns1, 2 gostround4 ns1, ns2, 3 gostround4 ns2, ns1, 4 gostround4 ns1, ns2, 5 gostround4 ns2, ns1, 6 gostround4 ns1, ns2, 7 gostround4 ns2, ns1, 7 gostround4 ns1, ns2, 6 gostround4 ns2, ns1, 5 gostround4 ns1, ns2, 4 gostround4 ns2, ns1, 3 gostround4 ns1, ns2, 2 gostround4 ns2, ns1, 1 gostround4 ns1, ns2, 0 gostround4 ns2, ns1, 0 1: copy_s.w t1,ns2[0] copy_s.w t2,ns1[0] copy_s.w t3,ns2[1] copy_s.w t4,ns1[1] copy_s.w t5,ns2[2] copy_s.w t6,ns1[2] copy_s.w t7,ns2[3] copy_s.w t8,ns1[3] sw t1, (a1) // n2, OUT sw t2, 4(a1) // n1, OUT + 4 sw t3, 8(a1) // n2, OUT + 8 sw t4, 12(a1) // n1, OUT + 12 sw t5, 16(a1) // n2, OUT + 16 sw t6, 20(a1) // n1, OUT + 20 sw t7, 24(a1) // n2, OUT + 24 sw t8, 28(a1) // n1, OUT + 28 jr ra nop END(gost_encrypt_4block_asm)
使用SIMD块命令同时计算4个块
.macro gostround4 x_in, x_out, rkey fill.w $w0, t0 /* key -> Vi */ addv.w $w1, $w0, \x_in /* key[0] + n1 = x */ srli.b $w3, $w1, 4 /* $w1 >> 4 */ and.v $w4, $w1, $w16 /* x 4 x 0*/ and.v $w5, $w1, $w17 /* 6 x 2 x*/ and.v $w6, $w3, $w17 /* 7 x 3 x */ and.v $w7, $w3, $w16 /* x 5 x 1 */ lw t0, \rkey * 4(a2) /* next key -> t0 */ or.v $w4, $w6, $w4 /* 7 4 3 0 */ or.v $w5, $w5, $w7 /* 6 5 2 1 */ move.v $w6, $w5 /* 6 5 2 1 */ move.v $w7, $w4 /* 7 4 3 0 */ /* 7 xx 0 */ /* 6 xx 1 */ /* x 5 2 x */ /* x 4 3 x */ vshf.b $w4, $w8, $w8 /* substitute $w8 [7 0] */ and.v $w4, $w4, $w12 vshf.b $w5, $w9, $w9 /* substitute $w9 [6 1] */ and.v $w5, $w5, $w13 vshf.b $w6, $w10, $w10 /* substitute $w10 [5 2] */ and.v $w6, $w6, $w14 vshf.b $w7, $w11, $w11 /* substitute $w11 [4 3] */ and.v $w7, $w7, $w15 or.v $w4, $w4, $w5 or.v $w6, $w6, $w7 or.v $w4, $w4, $w6 srli.w $w1, $w4, 21 /* $w4 >> 21 */ slli.w $w3, $w4, 11 /* $w4 << 11 */ or.v $w1, $w1, $w3 xor.v \x_out, \x_out, $w1 .endm
简要结论
根据GOST 28147-89算法,使用贝加尔湖T1处理器的SIMD块可实现约350 Mbit / s的数据转换速率,这比标准命令的实现高出两倍半 (!)倍。 由于该处理器具有两个内核,因此理论上可以以〜700 Mbps的速度加密流。 至少IPsec的测试实现(根据GOST 28147-89进行了加密)显示,双工上的信道吞吐量约为400 Mbps。