引言
如何发现一个人了解什么是单子? 他本人将在交流的前5分钟内告诉您有关此事,并且一定会尝试解释。 他还将撰写有关此文字的文章,并在可能的情况下将其发布在某处,以便其他所有人也了解什么是monad。
在函数式程序员中,特别是在Haskell上,单子函数已成为本地模因。 从特殊情况开始,并立即给出使用示例,他们经常被尝试解释。 因此,听众可能无法理解该概念的主要本质,而monads仍将保持黑魔法,或者仅仅是一种在纯功能语言中消除副作用的方法。
我将首先讨论类别理论的基本概念,然后从实践的角度出发,我们将对monad进行定义,并发现实际上,许多程序员在其表现形式之一中使用了这种强大的抽象。
我的演讲主要基于Bartosz Milewski的著作《程序员的分类论》,该书是一系列博客文章 ,以PDF格式提供 ,最近已发表在纸上。
这些示例在Haskell中提供,假定读者熟悉该语言的语法和基本概念。 在提到的书中,有一些使用C ++编写的示例,您可以比较代码的纯净度和可理解性。

分类目录
定义
类别本身是非常简单的结构。 类别是对象和对象之间的态素的集合。 形态可以看作是连接对象的单向箭头。 在一般情况下,对对象本身的本质一无所知。 范畴论不适用于对象,而是适用于态射,或更确切地说,适用于其构成 。
使用以下表示法:
- Ob C - C类对象;
- Hom C (A,B)-从A到B的态射;
- g∘f是态射f和g的成分。
在定义类别时,态射还受到其他限制:
- 对于一对态f和g,如果f是从A到B的态(f∈Hom(A,B)),g是从B到C的态(g∈Hom(B,C)),则存在一个成分g∘ f是从A到C的态(g∘f∈Hom(A,C))。
- 对于每个对象,给出了一个同构态id A∈Hom(A,A)。
任何类别都必须满足两个重要的属性(类别理论的核心):
- 组合物的缔合性:h∘(g∘f)=(h∘g)∘f;
- 具有等态同构的组合:如果f∈Hom(A,B),则f∘id A = id B∘f = f。
类别非常容易且自然地可视化为有向图。 原则上,如有必要,可以通过添加态素和相同态素的成分将任何有向图扩展到一个类别。
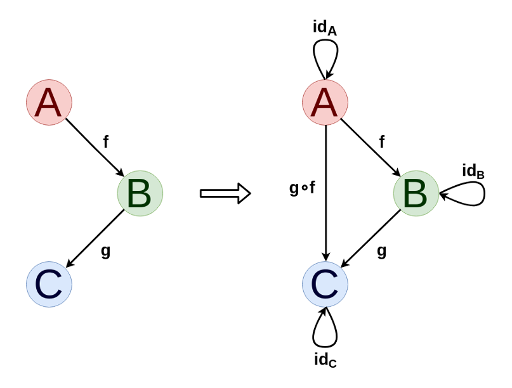
对于任何类别,您都可以定义一个对偶类别 (用C op表示),其中通过旋转原始类别的箭头获得同态,并且对象相同。这使我们能够制定对偶陈述和定理,当箭头倒置时,其对数不变。
对象和词素不一定形成集合(在经典意义上,从集合论出发),因此,在通常情况下,使用短语“对象类”。 仍然包含对象和态射类的类别的类别称为小类别 。 此外,我们将仅与他们合作。
类型和功能
, Haskell, — . , Int Bool — , Int -> Bool — .
id, :
id :: a -> a
id x = x
— , Haskell :
f :: a -> b
g :: b -> c
g . f :: a -> c
(g . f) x = g (f x)
, , — , Set. , — , : . bottom, _|_. , , , bottom. Haskell, , Hask. , Set. , , : HomC(A, B) ∈ C. , a -> b — Haskell.
.
Void, ( ). absurd, , , Void, :
absurd :: Void -> a
Unit, — , (). unit , :
unit :: a -> Unit
unit _ = ()
— Bool:
data Bool = True | False
, Void, Unit Bool.
Void , absurd, Bool, Unit. , Void, , .
Bool -> Unit , unit, . Unit -> Bool . (), True, False. , Unit Bool:
true, false :: a -> Bool
true _ = True
false _ = False
Bool Bool — , 4 ( n — 22n): id, true false, , not:
not :: Bool -> Bool
not True = False
not False = True
, :
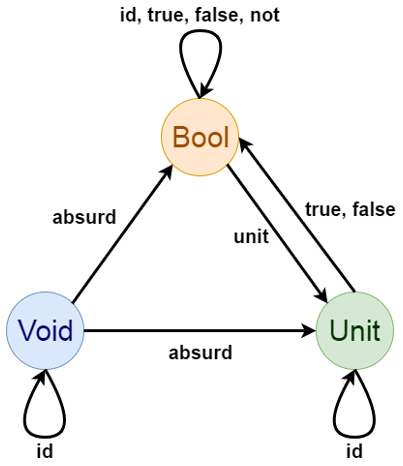
Haskell- .
— . , C D, F . -, C D. a — C, F a — D, . -, : f :: a -> b C F f :: F a -> F b D.
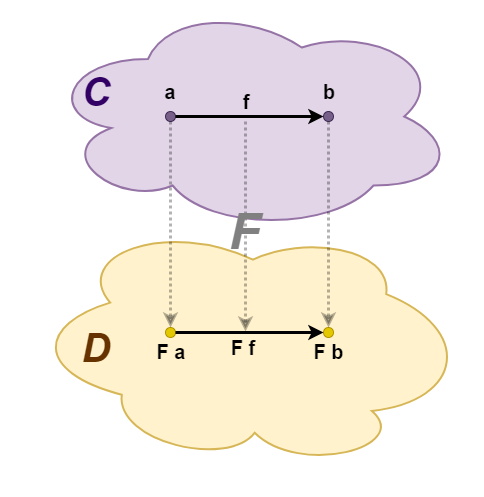
, " " :
- h = g ∘ f, F h = F g ∘ F f.
- ida — a, F ida = idF a — F a.
, "" : , , . , , () . , .
. , F :: C -> D G :: D -> E G . F :: C -> E. , , , , . IdC, IdD IdE. , , .
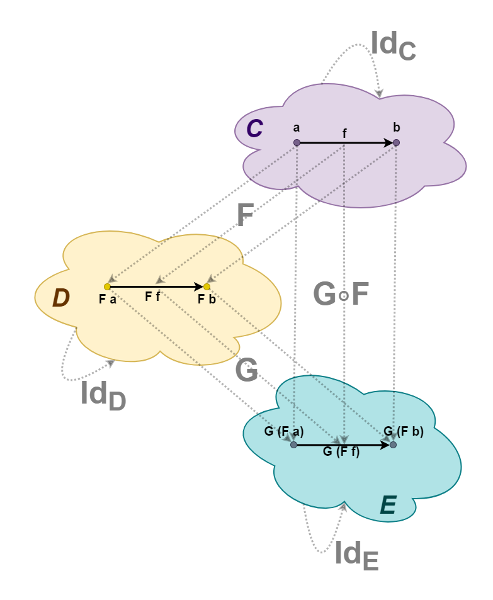
, , -, — (). , Cat ( ).
Haskell . , , - , .
Maybe , a Maybe a ( Maybe !):
data Maybe a = Nothing | Just a
, f :: a -> b F f :: Maybe a -> Maybe b. fmap. , ( ):
-- f F f
-- /------\ /------------------\
fmap :: (a -> b) -> (Maybe a -> Maybe b)
fmap _ Nothing = Nothing
fmap f (Just x) = Just (f x)
, Maybe — . , , Functor. fmap, , ( — ):
class Functor f where
fmap :: (a -> b) -> f a -> f b
— , , fmap . f a -> f b, , .
, , , .. , . : , - .
. , . , , — Haskell.
: upCase, , toWords, . toUpper words:
upCase :: String -> String
upCase = map toUpper
toWords :: String -> [String]
toWords = words
:
processString :: String -> [String]
processString = toWords . upCase
, . , processString "upCase toWords".
— , . -, , , -, , .
, a , .
newtype Writer a = Writer (a, String)
, Writer — , fmap:
instance Functor Writer where
fmap f (Writer (x, s)) = Writer (f x, s)
upCase toWords , , "" Writer:
upCase :: String -> Writer String
upCase s = Writer (map toUpper s, "upCase ")
toWords :: String -> Writer [String]
toWords s = Writer (words s, "toWords ")
, , - . , b , , c c , :
compose :: (a -> Writer b) -> (b -> Writer c) -> (a -> Writer c)
compose f g = \x -> let Writer (y, s1) = f x
Writer (z, s2) = g y
in Writer (z, s1 ++ s2)
processString :
processString :: String -> [String]
processString = compose upCase toWords
. () a -> b a -> Writer b , a b. , .. a -> Writer a:
writerId :: a -> Writer a
writerId x = Writer (x, "")
, , Hask. , a b a -> b, a -> m b, .. "" - m. (embellished). m, Writer — .
C m. K, , C, .. ObK = ObC. a -> b K a -> m b C: HomK(a, b) = HomC(a, m b). , , K — C.
, , , . , m — . Haskell ( Hask):
class Monad m where
--
(>=>) :: (a -> m b) -> (b -> m c) -> (a -> m c)
--
return :: a -> m a
>=>, "fish", : . , , — , , , . Writer — , compose — >=>, writerId — return.
>=> . , -. a, f, , , bind:
f >=> g = \a -> let mb = f a
in (bind mb g)
where
bind :: m b -> (b -> m c) -> m c
bind b " " m , b m c. >=>. : m b -> (b -> m c) -> m c. , . "" Haskell >>=, bind, return:
class Monad m where
(>>=) :: m a -> (a -> m b) -> m b
return :: a -> m a
, - b -> m c b, m b. , m, fmap, (a -> m b) -> m a -> m (m b). >>= m (m b) m b, "" , . join:
ma >>= g = join (fmap g ma)
where
join :: m (m a) -> m a
, Writer :
join :: Writer (Writer a) -> Writer a
join (Writer ((Writer (x, s2)), s1)) = Writer (x, s1 ++ s2)
Monad:
class Functor m => Monad m where
join :: m (m a) -> m a
return :: a -> m a
, m . , fmap >>=:
fmap :: (a -> b) -> m a -> m b
fmap f ma = ma >>= (\a -> return (f a))
, "" .
(.. , ) .
(a -> [b]) -> (b -> [c]) -> (a -> [c]). :
(>=>) :: (a -> [b]) -> (b -> [c]) -> (a -> [c])
f >=> g = \x -> concat (map g (f x))
. a, , — f [b]. , b — g : map g (f x) :: [[c]]. , .
>>= :
(>>=) :: [a] -> (a -> [b]) -> [b]
xs >>= f = concat (map f xs)
return :: a -> [a]. :
return :: a -> [a]
return x = [x]
Monad:
instance Monad [] where
xs >>= f = concat (map f xs)
return x = [x]
, . , , . , — , ..
, , - .
, , Maybe. Just, — Nothing. , , :
(>=>) :: (a -> Maybe b) -> (b -> Maybe c) -> (a -> Maybe c)
f >=> g = \x -> case f x of
Just y -> g y
Nothing -> Nothing
Monad Maybe:
instance Monad Maybe where
(Just x) >>= f = f x
Nothing >>= f = Nothing
return x = Just x
, . , - , , - . Either String a, : , . :
data Either a b = Left a | Right b
, . . :
type WithException a = Either String a
Maybe:
(>=>) :: (a -> WithException b) -> (b -> WithException c) -> (a -> WithException c)
f >=> g = \x -> case f x of
Right y -> g y
err -> err
Monad :
instance Monad WithException where
(Right x) >>= f = f x
err >>= f = err
return x = Right x
, , write-only , . a -> b , , . , , ( , ):
a -> s -> (b, s)
:
newtype State s a = State (s -> (a, s))
s , State s . runState:
runState :: State s a -> s -> (a, s)
runState (State f) s = f s
Functor:
instance Functor (State s) where
fmap f state = State st'
where
st' prevState = let (a, newState) = runState state prevState
in (f a, newState)
, a b, , a -> State s b, State s — . , :
(>=>) :: (a -> State s b) -> (b -> State s c) -> (a -> State s c)
f >=> g = \x -> State (\s -> let (y, s') = runState (f x) s
in runState (g y) s')
Monad. , return, , -:
instance Monad (State s) where
stateA >>= f = State (\s -> let (a, s') = runState stateA s
in runState (f a) s')
return a = State (\s -> (a, s))
, . , Unit s , Unit -> State s s:
get :: Unit -> State s s
get _ = State (\s -> (s, s))
, Unit . , .
, , . , , , s Unit, s -> State s Unit:
put :: s -> State s Unit
put s = State (\_ -> ((), s))
, , /. , " " RealWorld, . RealWorld - , (, ). :
type IO a = State RealWorld a
IO — , Haskell, "". , . , , , -, .