本文继续
正如我们在第一篇文章中已经写的那样,有很多基于rsync的备份程序。
在最适合我们条件的那些选项中,我将考虑3:rdiff-backup,rsnapshot和burp。
测试文件集
对于所有候选人,包括将来的文章,测试文件集都将相同。第一组 :10 GB的媒体文件,大约50 MB-该站点的源代码(以php为单位),文件大小从源代码的几千字节到媒体文件的几十兆字节。 目的是模拟具有静态的站点。
第二组 :重命名具有5 GB媒体文件的子目录时,从第一
组获得。 目的是研究备份系统重命名目录时的行为。
第三组 :从第一组中删除3GB媒体文件并添加新的3GB媒体文件。 目的是研究典型站点更新操作期间备份系统的行为。
获得结果
任何备份至少执行3次,并伴随测试服务器和备份存储服务器上的
sync和
echo 3 > /proc/sys/vm/drop_caches重置文件系统缓存。
在将作为备份源的服务器上,安装了监视软件-netdata,将在备份期间估计服务器上的负载,这对于通过备份过程评估服务器上的负载是必需的。
我还认为,备份存储服务器比主服务器要慢,但是具有更大的磁盘且随机写入速度相对较低-这是备份时最常见的情况,并且由于备份服务器不应以良好的方式进行操作除了备份之外,我将不会监视负载,也不会使用netdata监视其负载。
另外,我的服务器已更改,我将在该服务器上检查各种系统以进行备份。
现在它们具有以下特征中央处理器 sysbench --threads=2 --time=30 --cpu-max-prime=20000 cpu run sysbench 1.0.17 (using system LuaJIT 2.0.4) Running the test with following options: Number of threads: 2 Initializing random number generator from current time Prime numbers limit: 20000 Initializing worker threads... Threads started! CPU speed: events per second: 1081.62 General statistics: total time: 30.0013s total number of events: 32453 Latency (ms): min: 1.48 avg: 1.85 max: 9.84 95th percentile: 2.07 sum: 59973.40 Threads fairness: events (avg/stddev): 16226.5000/57.50 execution time (avg/stddev): 29.9867/0.00
RAM,读取中... sysbench --threads=4 --time=30 --memory-block-size=1K --memory-scope=global --memory-total-size=100G --memory-oper=read memory run sysbench 1.0.17 (using system LuaJIT 2.0.4) Running the test with following options: Number of threads: 4 Initializing random number generator from current time Running memory speed test with the following options: block size: 1KiB total size: 102400MiB operation: read scope: global Initializing worker threads... Threads started! Total operations: 104857600 (5837637.63 per second) 102400.00 MiB transferred (5700.82 MiB/sec) General statistics: total time: 17.9540s total number of events: 104857600 Latency (ms): min: 0.00 avg: 0.00 max: 66.08 95th percentile: 0.00 sum: 18544.64 Threads fairness: events (avg/stddev): 26214400.0000/0.00 execution time (avg/stddev): 4.6362/0.12
...和录音 sysbench --threads=4 --time=30 --memory-block-size=1K --memory-scope=global --memory-total-size=100G --memory-oper=write memory run sysbench 1.0.17 (using system LuaJIT 2.0.4) Running the test with following options: Number of threads: 4 Initializing random number generator from current time Running memory speed test with the following options: block size: 1KiB total size: 102400MiB operation: write scope: global Initializing worker threads... Threads started! Total operations: 91414596 (3046752.56 per second) 89272.07 MiB transferred (2975.34 MiB/sec) General statistics: total time: 30.0019s total number of events: 91414596 Latency (ms): min: 0.00 avg: 0.00 max: 1022.90 95th percentile: 0.00 sum: 66430.91 Threads fairness: events (avg/stddev): 22853649.0000/945488.53 execution time (avg/stddev): 16.6077/1.76
数据源服务器上的磁盘 sysbench --threads=4 --file-test-mode=rndrw --time=60 --file-block-size=4K --file-total-size=1G fileio run sysbench 1.0.17 (using system LuaJIT 2.0.4) Running the test with following options: Number of threads: 4 Initializing random number generator from current time Extra file open flags: (none) 128 files, 8MiB each 1GiB total file size Block size 4KiB Number of IO requests: 0 Read/Write ratio for combined random IO test: 1.50 Periodic FSYNC enabled, calling fsync() each 100 requests. Calling fsync() at the end of test, Enabled. Using synchronous I/O mode Doing random r/w test Initializing worker threads... Threads started! File operations: reads/s: 4587.95 writes/s: 3058.66 fsyncs/s: 9795.73 Throughput: read, MiB/s: 17.92 written, MiB/s: 11.95 General statistics: total time: 60.0241s total number of events: 1046492 Latency (ms): min: 0.00 avg: 0.23 max: 14.45 95th percentile: 0.94 sum: 238629.34 Threads fairness: events (avg/stddev): 261623.0000/1849.14 execution time (avg/stddev): 59.6573/0.00
备份存储服务器上的磁盘 sysbench --threads=4 --file-test-mode=rndrw --time=60 --file-block-size=4K --file-total-size=1G fileio run sysbench 1.0.17 (using system LuaJIT 2.0.4) Running the test with following options: Number of threads: 4 Initializing random number generator from current time Extra file open flags: (none) 128 files, 8MiB each 1GiB total file size Block size 4KiB Number of IO requests: 0 Read/Write ratio for combined random IO test: 1.50 Periodic FSYNC enabled, calling fsync() each 100 requests. Calling fsync() at the end of test, Enabled. Using synchronous I/O mode Doing random r/w test Initializing worker threads... Threads started! File operations: reads/s: 11.37 writes/s: 7.58 fsyncs/s: 29.99 Throughput: read, MiB/s: 0.04 written, MiB/s: 0.03 General statistics: total time: 73.8868s total number of events: 3104 Latency (ms): min: 0.00 avg: 78.57 max: 3840.90 95th percentile: 297.92 sum: 243886.02 Threads fairness: events (avg/stddev): 776.0000/133.26 execution time (avg/stddev): 60.9715/1.59
服务器之间的网络速度 iperf3 -c backup Connecting to host backup, port 5201 [ 4] local xxxx port 59402 connected to yyyy port 5201 [ ID] Interval Transfer Bandwidth Retr Cwnd [ 4] 0.00-1.00 sec 419 MBytes 3.52 Gbits/sec 810 182 KBytes [ 4] 1.00-2.00 sec 393 MBytes 3.30 Gbits/sec 810 228 KBytes [ 4] 2.00-3.00 sec 378 MBytes 3.17 Gbits/sec 810 197 KBytes [ 4] 3.00-4.00 sec 380 MBytes 3.19 Gbits/sec 855 198 KBytes [ 4] 4.00-5.00 sec 375 MBytes 3.15 Gbits/sec 810 182 KBytes [ 4] 5.00-6.00 sec 379 MBytes 3.17 Gbits/sec 765 228 KBytes [ 4] 6.00-7.00 sec 376 MBytes 3.15 Gbits/sec 810 180 KBytes [ 4] 7.00-8.00 sec 379 MBytes 3.18 Gbits/sec 765 253 KBytes [ 4] 8.00-9.00 sec 380 MBytes 3.19 Gbits/sec 810 239 KBytes [ 4] 9.00-10.00 sec 411 MBytes 3.44 Gbits/sec 855 184 KBytes - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - [ ID] Interval Transfer Bandwidth Retr [ 4] 0.00-10.00 sec 3.78 GBytes 3.25 Gbits/sec 8100 sender [ 4] 0.00-10.00 sec 3.78 GBytes 3.25 Gbits/sec receiver
测试方法
- 在测试服务器上准备了具有第一个测试集的文件系统,并在必要时在备份存储服务器上初始化了存储库。
备份过程开始,并测量其时间。 - 文件被迁移到测试服务器上的第二个测试套件。 备份过程开始,并测量其时间。
- 测试服务器将迁移到第三个测试套件。 备份过程开始,并测量其时间。
- 产生的第三个测试集将被新的第一个测试集接受; 点1-3再重复2次。
- 将数据输入到数据透视表中,并添加带有netdata的图形。
- 使用单独的备份方法准备报告。
预期结果
由于所有3个候选者都基于相同的技术(rsync),因此预期结果将接近通常的rsync,包括其所有优点,即:
- 存储库中的文件将“按原样”存储。
- 存储库的大小只会增加,包括备份之间的差异。
- 传输数据时,网络上的负载将相对较大,而处理器上的负载将较小。
常规rsync的测试运行将用作参考,其结果
这些是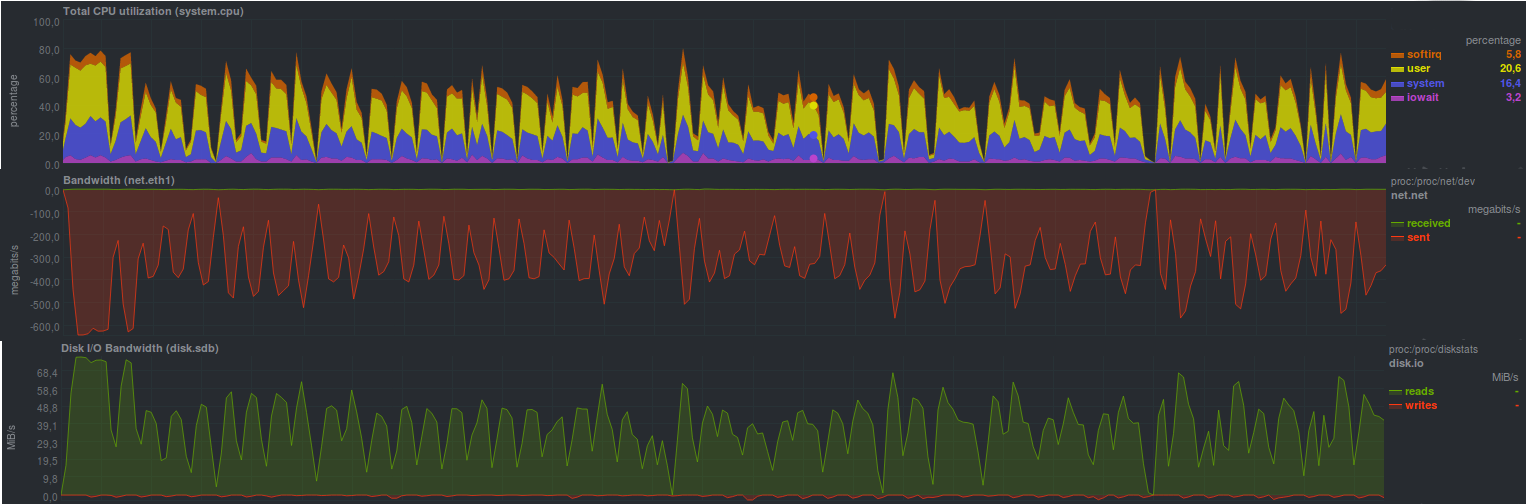
瓶颈是以基于HDD的磁盘的形式出现在备份存储服务器上的,它在图表中以锯子的形式很明显地可见。
数据在4分15秒内被复制。
测试rdiff备份
第一个候选对象是rdiff-backup,这是一个将一个目录备份到另一个目录的python脚本。 同时,当前备份副本按“原样”存储,而较早进行的备份将增量存储在特殊的子目录中,从而节省了空间。
我们将检查典型的操作模式,即 备份过程的开始由客户端自行启动,在服务器端,启动接收数据的过程以进行备份。
让我们来看看
在我们的条件下他有什么能力。
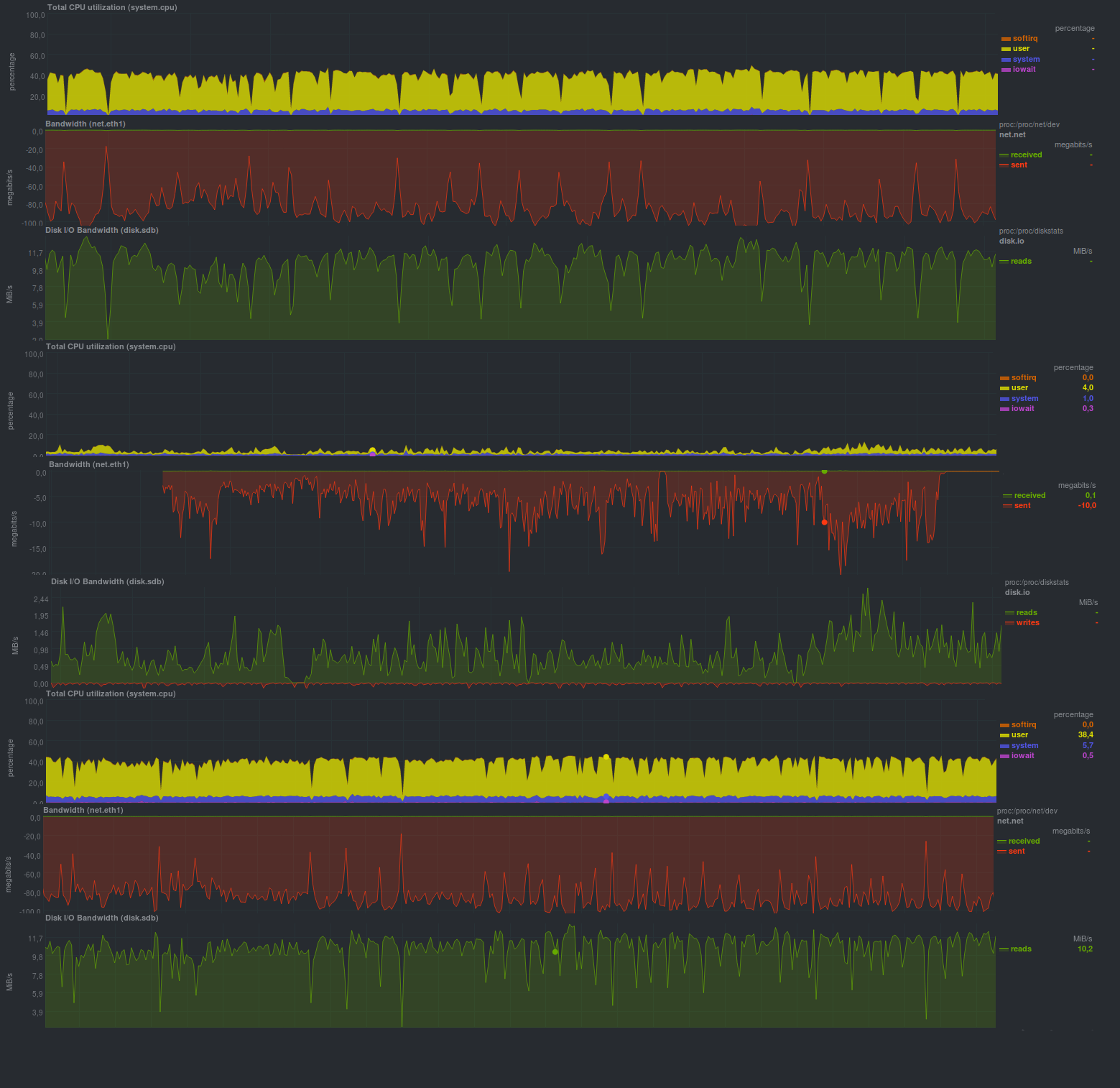
每次测试运行的时间:
Rdiff备份对任何大数据更改都会非常痛苦地做出反应,并且也没有完全利用网络。
测试rsnapshot
第二个候选者rsnapshot是一个perl脚本,其有效工作的主要要求是对硬链接的支持。 这样可以节省磁盘空间。 同时,自上次备份以来未更改的文件将使用硬链接引用到原始文件。
备份过程的逻辑也被颠倒了:服务器主动在客户端上“行走”并获取数据。
测试结果
它的工作非常非常快,比rdiff-backup快得多,并且非常接近纯rsync。
打p测试
另一个选择是在librsync之上的C实现-burp,它具有包括客户端授权在内的客户端-服务器体系结构以及一个Web界面(不包含在基本软件包中)。 另一个有趣的功能是没有从客户端恢复的权利的备份。
让我们来看看
表现。
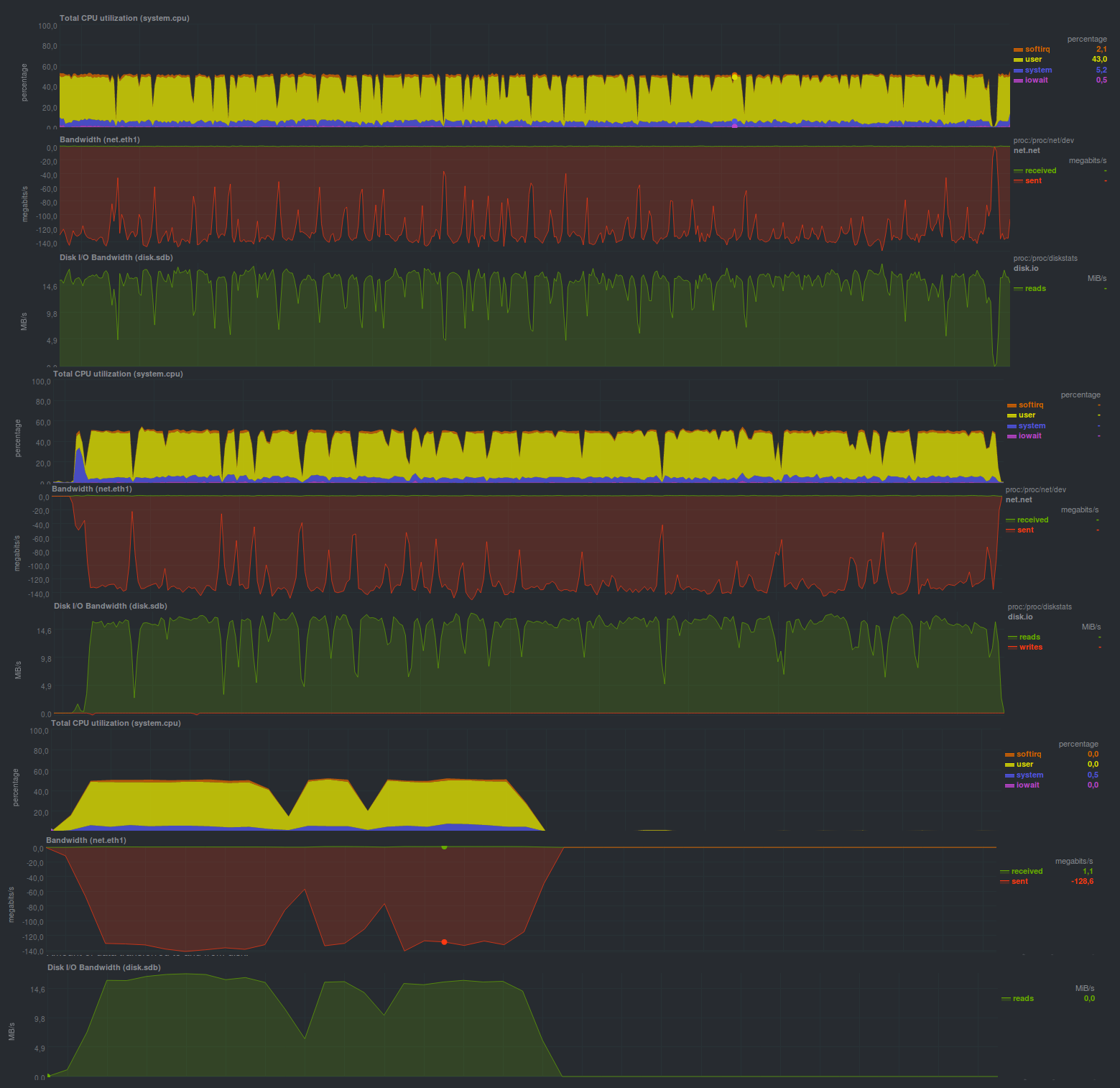
它的工作速度比rsnapshot慢2倍,但速度也相当快,当然rdiff-backup也更快。 这些图有点锯齿-性能仍然取决于备份存储服务器的磁盘子系统,尽管这并不像rsnapshot那样明显。
结果
由于rsync的特殊性,所有候选存储库的大小大致相同,即,首先增长到10 GB,然后增长到15 GB,然后增长到18 GB,等等。 还值得注意的是,所有候选对象都是单线程的(双核计算机的CPU利用率约为50%)。 所有这三个候选程序都提供了“按原样”还原最后一个备份的机会,也就是说,可以在不使用任何第三方程序(包括用于创建存储库的程序)的情况下还原文件。 这也是rsync的“通用遗产”。
结论
备份系统越复杂,其功能越不同,其运行速度就越慢,但是对于要求不是很高的项目,除了rdiff-backup之外,其他任何一个都可以。
公告公告
本说明继续备份周期。
备份,第1部分:为什么需要备份,方法,技术概述备份,第2部分:概述和测试基于rsync的备份工具备份,第3部分:概述和测试重复性,重复备份,第4部分:概述和测试zbackup,restic,borgbackup备份,第5部分:测试Linux的Bacula和Veeam备份备份:读者要求的部分:AMANDA审查,UrBackup,BackupPC备份,第6部分:比较备份工具备份第7部分:结论由 Finnix 发布