你好
许多人想开始为Android编写应用程序,但他们不希望不使用Android Studio和/或Java。 怎么了 因为这太过分了。 “我只想创建Snake,仅此而已!”
让我们在没有Java的情况下走蛇! (最后有奖金)
为什么还要创建另一个蛇教程?如果您是python程序员,并且想学习android的gamedev,则必须已经在Google上搜索了“ snake on android”,并找到
了(Eng)或其
翻译(Rus) 。 我也是。不幸的是,我发现这篇文章极其无用,因为:
他们的代码不好
次要问题:
- 对我来说,用“ tile”和“ head”代替“ tiles”或“ cells”是没有意义的。 磁头与磁贴的区别不够大,无法成为不同的变量。
- 用于self.update的Clock.schedule从... self.update调用。
- 第二层类Playground是在开始时实现的,而第一类SnakeApp是在末尾实现的。
- 使用方向名称(“上”,“下”,...)代替矢量((0,1),(1,0)...)。
主要问题:
- 大多数动态对象(例如水果)都附加到了kv文件中,因此您制作的苹果不能超过1个,因为这时您应该重写此部分
- 蛇的动作而不是“一个接一个的接一个”的动作的怪异逻辑。
- 该代码很长,超过350行。
对于新手来说,这篇文章不清楚
这是我个人的看法。 而且,我不保证我的教程会更加有趣和清晰。 但是,我会竭尽所能,并在我的文章中保证:
- 代码很短
- 蛇很好
- 该说明将具有清晰的分步实施方式,并通过过渡步骤使从“ hello,world”顺利过渡到现成的蛇。
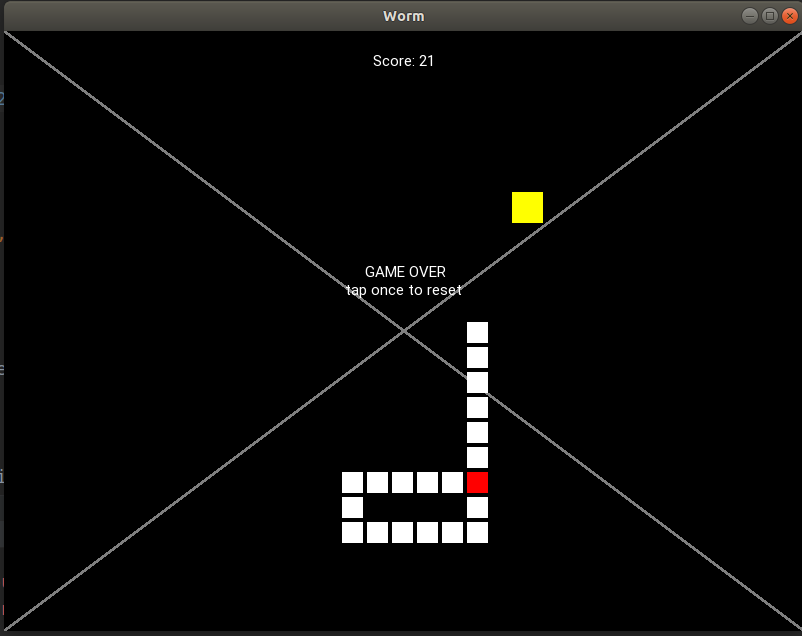
不良结果

单元格之间没有空格,三角形令人尴尬,图形出现故障。
熟悉
第一个应用
请确认您已安装Kivy(如果没有,请按照
说明进行操作 )并运行
在项目目录中的
buildozer init 。
让我们运行第一个应用程序:
main.py
from kivy.app import App from kivy.uix.widget import Widget class WormApp(App): def build(self): return Widget() if __name__ == '__main__': WormApp().run()

我们创建了一个小部件。 类似地,我们可以创建一个按钮或任何其他UI元素:
from kivy.app import App from kivy.uix.widget import Widget from kivy.uix.button import Button class WormApp(App): def build(self): self.but = Button() self.but.pos = (100, 100) self.but.size = (200, 200) self.but.text = "Hello, cruel world" self.form = Widget() self.form.add_widget(self.but) return self.form if __name__ == '__main__': WormApp().run()

哇! 恭喜你! 您已经创建了一个按钮!
.kv文件
但是,还有另一种创建UI元素的方法。 首先,我们实现以下形式:
from kivy.app import App from kivy.uix.widget import Widget from kivy.uix.button import Button class Form(Widget): def __init__(self): super().__init__() self.but1 = Button() self.but1.pos = (100, 100) self.add_widget(self.but1) class WormApp(App): def build(self): self.form = Form() return self.form if __name__ == '__main__': WormApp().run()
然后,我们创建“ worm.kv”文件。
蠕虫病毒
<Form>: but2: but_id Button: id: but_id pos: (200, 200)
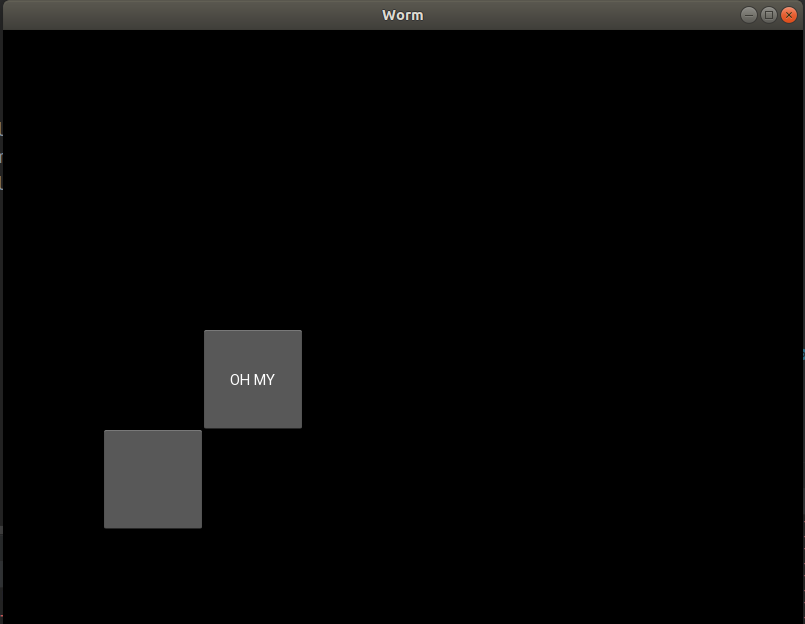
刚刚发生了什么? 我们创建了另一个Button并分配ID but_id。 然后,将but_id与该格式的but2匹配。 这意味着现在我们可以通过but2来引用此按钮
class Form(Widget): def __init__(self): super().__init__() self.but1 = Button() self.but1.pos = (100, 100) self.add_widget(self.but1) # self.but2.text = "OH MY"
图形
接下来,我们将创建一个图形元素。 首先,我们在worm.kv中实现它:
<Form>: <Cell>: canvas: Rectangle: size: self.size pos: self.pos
我们将矩形的位置链接到self.pos并将其大小链接到self.size。 因此,现在可以从Cell中获得这些属性,例如,一旦创建了一个单元,就可以
class Cell(Widget): def __init__(self, x, y, size): super().__init__() self.size = (size, size)
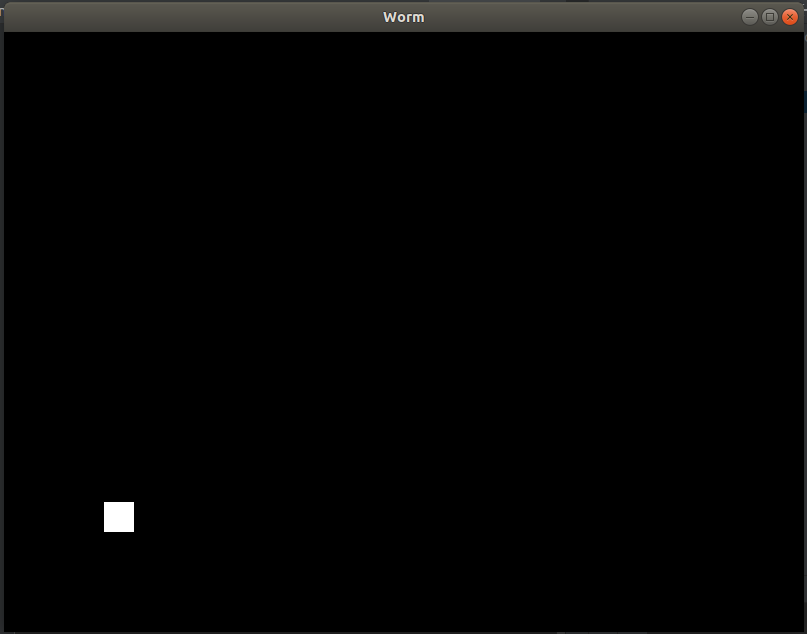
好的,我们已经创建了一个单元。
不必要的方法
让我们尝试移动它。 为此,我们应该添加Form.update函数并安排它。
from kivy.app import App from kivy.uix.widget import Widget from kivy.clock import Clock class Cell(Widget): def __init__(self, x, y, size): super().__init__() self.size = (size, size) self.pos = (x, y) class Form(Widget): def __init__(self): super().__init__() self.cell = Cell(100, 100, 30) self.add_widget(self.cell) def start(self): Clock.schedule_interval(self.update, 0.01) def update(self, _): self.cell.pos = (self.cell.pos[0] + 2, self.cell.pos[1] + 3) class WormApp(App): def build(self): self.form = Form() self.form.start() return self.form if __name__ == '__main__': WormApp().run()
单元格将跨表格移动。 如您所见,我们可以使用Clock安排任何功能。
接下来,让我们进行触摸事件。 重写表格:
class Form(Widget): def __init__(self): super().__init__() self.cells = [] def start(self): Clock.schedule_interval(self.update, 0.01) def update(self, _): for cell in self.cells: cell.pos = (cell.pos[0] + 2, cell.pos[1] + 3) def on_touch_down(self, touch): cell = Cell(touch.x, touch.y, 30) self.add_widget(cell) self.cells.append(cell)
每个touch_down都会创建一个坐标=(touch.x,touch.y)且大小为30的单元格。然后,将其作为AND形式的小部件添加到我们自己的数组中(以便于访问它们)。
现在,您可以点击表格并生成单元格。
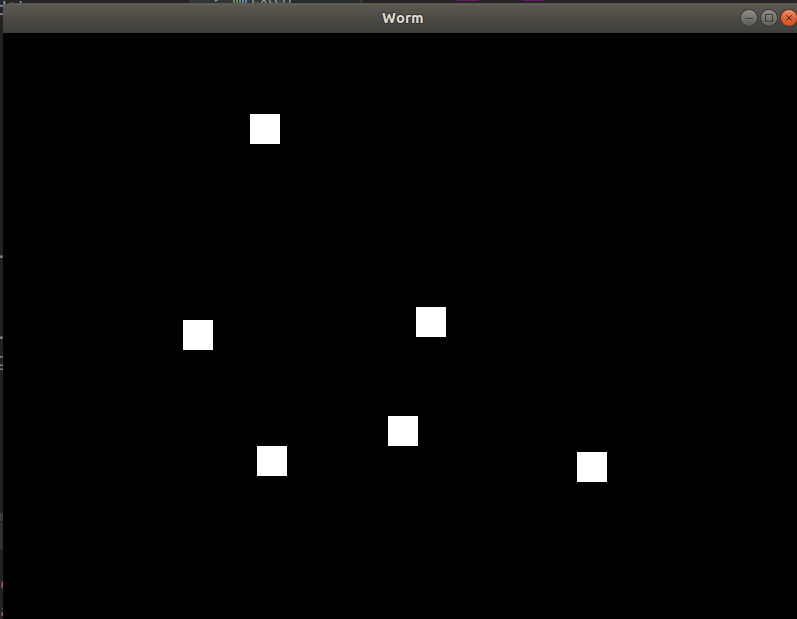
整洁的设置
因为我们想得到一条漂亮的蛇,所以我们应该区分图形位置和单元格的实际位置。
怎么了这样做的原因很多。 所有逻辑都应与所谓的实际数据联系起来,而图形数据是实际数据的结果。 例如,如果要进行边距处理,则单元格的实际位置将为(100,100),而矩形的图形位置为-(102,102)。
PS:如果我们处理经典的on_draw,我们不会这样做。 但是在这里我们不必编程on_draw。
让我们修复worm.kv文件:
<Form>: <Cell>: canvas: Rectangle: size: self.graphical_size pos: self.graphical_pos
和main.py:
... from kivy.properties import * ... class Cell(Widget): graphical_size = ListProperty([1, 1]) graphical_pos = ListProperty([1, 1]) def __init__(self, x, y, size, margin=4): super().__init__() self.actual_size = (size, size) self.graphical_size = (size - margin, size - margin) self.margin = margin self.actual_pos = (x, y) self.graphical_pos_attach() def graphical_pos_attach(self): self.graphical_pos = (self.actual_pos[0] - self.graphical_size[0] / 2, self.actual_pos[1] - self.graphical_size[1] / 2) ... class Form(Widget): def __init__(self): super().__init__() self.cell1 = Cell(100, 100, 30) self.cell2 = Cell(130, 100, 30) self.add_widget(self.cell1) self.add_widget(self.cell2) ...
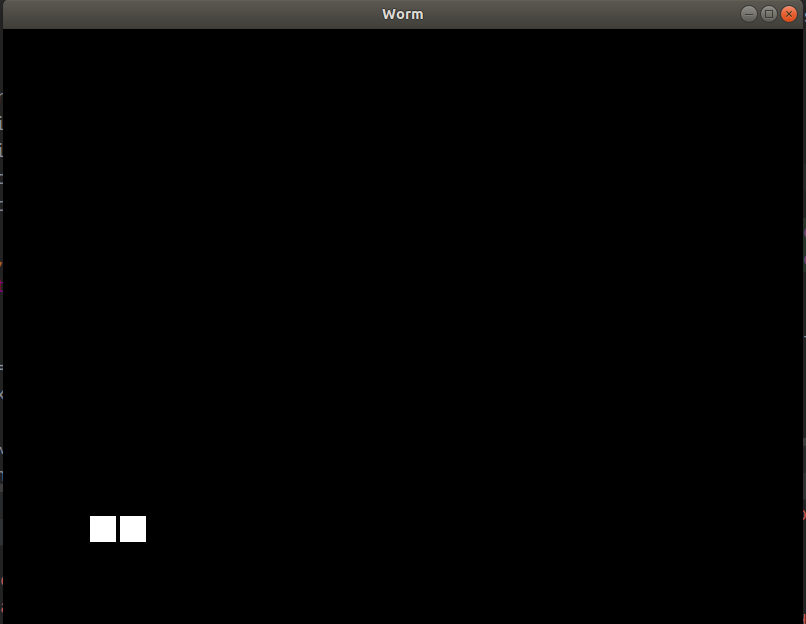
尽管我们用X = 130而不是132创建了第二个像元,但出现了边距,因此看起来很漂亮。稍后,我们将基于Actual_pos与graphics_pos之间的距离进行平滑运动。
编码蠕虫
实作
main.py中的初始化配置
class Config: DEFAULT_LENGTH = 20 CELL_SIZE = 25 APPLE_SIZE = 35 MARGIN = 4 INTERVAL = 0.2 DEAD_CELL = (1, 0, 0, 1) APPLE_COLOR = (1, 1, 0, 1)
(相信我,您会爱上它!)
然后,为应用分配配置:
class WormApp(App): def __init__(self): super().__init__() self.config = Config() self.form = Form(self.config) def build(self): self.form.start() return self.form
重写init并开始:
class Form(Widget): def __init__(self, config): super().__init__() self.config = config self.worm = None def start(self): self.worm = Worm(self.config) self.add_widget(self.worm) Clock.schedule_interval(self.update, self.config.INTERVAL)
然后,该单元格:
class Cell(Widget): graphical_size = ListProperty([1, 1]) graphical_pos = ListProperty([1, 1]) def __init__(self, x, y, size, margin=4): super().__init__() self.actual_size = (size, size) self.graphical_size = (size - margin, size - margin) self.margin = margin self.actual_pos = (x, y) self.graphical_pos_attach() def graphical_pos_attach(self): self.graphical_pos = (self.actual_pos[0] - self.graphical_size[0] / 2, self.actual_pos[1] - self.graphical_size[1] / 2) def move_to(self, x, y): self.actual_pos = (x, y) self.graphical_pos_attach() def move_by(self, x, y, **kwargs): self.move_to(self.actual_pos[0] + x, self.actual_pos[1] + y, **kwargs) def get_pos(self): return self.actual_pos def step_by(self, direction, **kwargs): self.move_by(self.actual_size[0] * direction[0], self.actual_size[1] * direction[1], **kwargs)
希望它或多或少清楚。
最后是蠕虫:
class Worm(Widget): def __init__(self, config): super().__init__() self.cells = [] self.config = config self.cell_size = config.CELL_SIZE self.head_init((100, 100)) for i in range(config.DEFAULT_LENGTH): self.lengthen() def destroy(self): for i in range(len(self.cells)): self.remove_widget(self.cells[i]) self.cells = [] def lengthen(self, pos=None, direction=(0, 1)):
让我们为蠕虫赋予生命。

动作
现在,我们将其移动。
很简单:
class Worm(Widget): ... def move(self, direction): for i in range(len(self.cells) - 1, 0, -1): self.cells[i].move_to(*self.cells[i - 1].get_pos()) self.cells[0].step_by(direction)
class Form(Widget): def __init__(self, config): super().__init__() self.config = config self.worm = None self.cur_dir = (0, 0) def start(self): self.worm = Worm(self.config) self.add_widget(self.worm) self.cur_dir = (1, 0) Clock.schedule_interval(self.update, self.config.INTERVAL) def update(self, _): self.worm.move(self.cur_dir)

还活着! 还活着!
控制性
通过预览图像可以判断,蛇的控件如下:
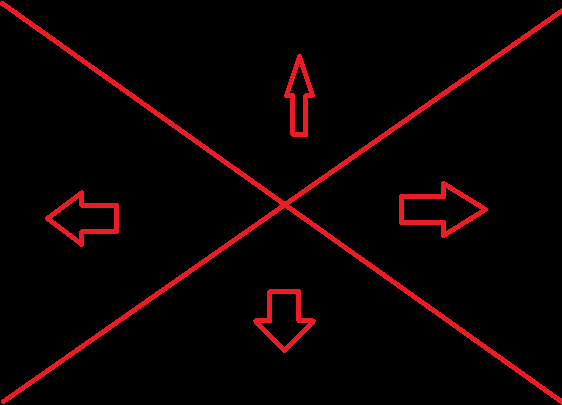
class Form(Widget): ... def on_touch_down(self, touch): ws = touch.x / self.size[0] hs = touch.y / self.size[1] aws = 1 - ws if ws > hs and aws > hs: cur_dir = (0, -1)

好酷
创造水果
首先,我们对其进行初始化。
class Form(Widget): ... def __init__(self, config): super().__init__() self.config = config self.worm = None self.cur_dir = (0, 0) self.fruit = None ... def random_cell_location(self, offset): x_row = self.size[0] // self.config.CELL_SIZE x_col = self.size[1] // self.config.CELL_SIZE return random.randint(offset, x_row - offset), random.randint(offset, x_col - offset) def random_location(self, offset): x_row, x_col = self.random_cell_location(offset) return self.config.CELL_SIZE * x_row, self.config.CELL_SIZE * x_col def fruit_dislocate(self): x, y = self.random_location(2) self.fruit.move_to(x, y) ... def start(self): self.fruit = Cell(0, 0, self.config.APPLE_SIZE, self.config.MARGIN) self.worm = Worm(self.config) self.fruit_dislocate() self.add_widget(self.worm) self.add_widget(self.fruit) self.cur_dir = (1, 0) Clock.schedule_interval(self.update, self.config.INTERVAL)
当前结果:

现在我们应该实现一些蠕虫方法:
class Worm(Widget): ...
集合位置的其他好处顺便说一句,在实现collect_positions之后,我们可以更改fruit_dislocate:
class Form(Widget): def fruit_dislocate(self): x, y = self.random_location(2) while (x, y) in self.worm.gather_positions(): x, y = self.random_location(2) self.fruit.move_to(x, y)
此时,水果不会位于蠕虫的瓷砖中。
...并添加此检查以更新()
class Form(Widget): ... def update(self, _): self.worm.move(self.cur_dir) if self.worm.head_intersect(self.fruit): directions = [(0, 1), (0, -1), (1, 0), (-1, 0)] self.worm.lengthen(direction=random.choice(directions)) self.fruit_dislocate()
检测自身瓷砖撞击
我们想知道头部与蠕虫细胞之一的位置是否相同。
class Form(Widget): ... def __init__(self, config): super().__init__() self.config = config self.worm = None self.cur_dir = (0, 0) self.fruit = None self.game_on = True def update(self, _): if not self.game_on: return self.worm.move(self.cur_dir) if self.worm.head_intersect(self.fruit): directions = [(0, 1), (0, -1), (1, 0), (-1, 0)] self.worm.lengthen(direction=random.choice(directions)) self.fruit_dislocate() if self.worm_bite_self(): self.game_on = False def worm_bite_self(self): for cell in self.worm.cells[1:]: if self.worm.head_intersect(cell): return cell return False
着色,修饰和代码重构
让我们从代码重构开始。
重写并添加
class Form(Widget): ... def start(self): self.worm = Worm(self.config) self.add_widget(self.worm) if self.fruit is not None: self.remove_widget(self.fruit) self.fruit = Cell(0, 0, self.config.APPLE_SIZE) self.fruit_dislocate() self.add_widget(self.fruit) Clock.schedule_interval(self.update, self.config.INTERVAL) self.game_on = True self.cur_dir = (0, -1) def stop(self): self.game_on = False Clock.unschedule(self.update) def game_over(self): self.stop() ... def on_touch_down(self, touch): if not self.game_on: self.worm.destroy() self.start() return ...
现在,如果蠕虫死了(冻结),再次单击该蠕虫,将重置游戏。
现在让我们去装饰和着色。
蠕虫病毒
<Form>: popup_label: popup_label score_label: score_label canvas: Color: rgba: (.5, .5, .5, 1.0) Line: width: 1.5 points: (0, 0), self.size Line: width: 1.5 points: (self.size[0], 0), (0, self.size[1]) Label: id: score_label text: "Score: " + str(self.parent.worm_len) width: self.width Label: id: popup_label width: self.width <Worm>: <Cell>: canvas: Color: rgba: self.color Rectangle: size: self.graphical_size pos: self.graphical_pos
重写WormApp:
class WormApp(App): def build(self): self.config = Config() self.form = Form(self.config) return self.form def on_start(self): self.form.start()

让我们上色吧。 重写.kv中的单元格:
<Cell>: canvas: Color: rgba: self.color Rectangle: size: self.graphical_size pos: self.graphical_pos
将此添加到Cell .__ init__
self.color = (0.2, 1.0, 0.2, 1.0)
然后到Form.start
self.fruit.color = (1.0, 0.2, 0.2, 1.0)
太好了,享受你的蛇

最后,我们将制作一个“游戏结束”标签
class Form(Widget): ... def __init__(self, config): ... self.popup_label.text = "" ... def stop(self, text=""): self.game_on = False self.popup_label.text = text Clock.unschedule(self.update) def game_over(self): self.stop("GAME OVER" + " " * 5 + "\ntap to reset")
并将命中单元格设为红色:
代替
def update(self, _): ... if self.worm_bite_self(): self.game_over() ...
写
def update(self, _): cell = self.worm_bite_self() if cell: cell.color = (1.0, 0.2, 0.2, 1.0) self.game_over()
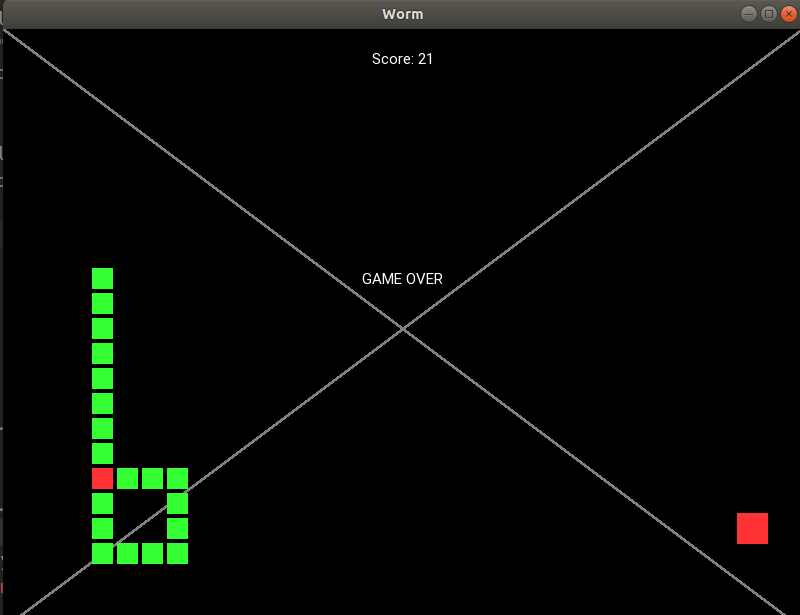
您还在注意吗? 接下来是最有趣的部分。
奖励部分-平稳运动
因为蠕虫的步长等于cell_size,所以它并不那么平滑。 但是我们希望使其步伐尽可能频繁,而不必重写游戏的全部逻辑。 因此,我们需要创建一种机制来移动图形姿势,而不是实际姿势。 所以,我写了一个简单的文件:
光滑的
from kivy.clock import Clock import time class Timing: @staticmethod def linear(x): return x class Smooth: def __init__(self, interval=1.0/60.0): self.objs = [] self.running = False self.interval = interval def run(self): if self.running: return self.running = True Clock.schedule_interval(self.update, self.interval) def stop(self): if not self.running: return self.running = False Clock.unschedule(self.update) def setattr(self, obj, attr, value): exec("obj." + attr + " = " + str(value)) def getattr(self, obj, attr): return float(eval("obj." + attr)) def update(self, _): cur_time = time.time() for line in self.objs: obj, prop_name_x, prop_name_y, from_x, from_y, to_x, to_y, start_time, period, timing = line time_gone = cur_time - start_time if time_gone >= period: self.setattr(obj, prop_name_x, to_x) self.setattr(obj, prop_name_y, to_y) self.objs.remove(line) else: share = time_gone / period acs = timing(share) self.setattr(obj, prop_name_x, from_x * (1 - acs) + to_x * acs) self.setattr(obj, prop_name_y, from_y * (1 - acs) + to_y * acs) if len(self.objs) == 0: self.stop() def move_to(self, obj, prop_name_x, prop_name_y, to_x, to_y, t, timing=Timing.linear): self.objs.append((obj, prop_name_x, prop_name_y, self.getattr(obj, prop_name_x), self.getattr(obj, prop_name_y), to_x, to_y, time.time(), t, timing)) self.run() class XSmooth(Smooth): def __init__(self, props, timing=Timing.linear, *args, **kwargs): super().__init__(*args, **kwargs) self.props = props self.timing = timing def move_to(self, obj, to_x, to_y, t): super().move_to(obj, *self.props, to_x, to_y, t, timing=self.timing)
对于那些不喜欢我的代码的人此模块不是最优雅的解决方案©。 这是一个糟糕的解决方案,我承认。 这是一个唯一的世界解决方案。
因此,您只需创建smooth.py并将此代码复制粘贴到文件中即可。
最后,让它工作:
class Form(Widget): ... def __init__(self, config): ... self.smooth = smooth.XSmooth(["graphical_pos[0]", "graphical_pos[1]"])
然后我们将self.worm.move()替换为
class Form(Widget): ... def update(self, _): ... self.worm.move(self.cur_dir, smooth_motion=(self.smooth, self.config.INTERVAL))
这就是Cell方法的外观
class Cell(Widget): ... def graphical_pos_attach(self, smooth_motion=None): to_x, to_y = self.actual_pos[0] - self.graphical_size[0] / 2, self.actual_pos[1] - self.graphical_size[1] / 2 if smooth_motion is None: self.graphical_pos = to_x, to_y else: smoother, t = smooth_motion smoother.move_to(self, to_x, to_y, t) def move_to(self, x, y, **kwargs): self.actual_pos = (x, y) self.graphical_pos_attach(**kwargs) def move_by(self, x, y, **kwargs): self.move_to(self.actual_pos[0] + x, self.actual_pos[1] + y, **kwargs)
就是这样,谢谢您的关注!
最终结果如何工作:
最终代码main.py from kivy.app import App from kivy.uix.widget import Widget from kivy.clock import Clock from kivy.properties import * import random import smooth class Cell(Widget): graphical_size = ListProperty([1, 1]) graphical_pos = ListProperty([1, 1]) color = ListProperty([1, 1, 1, 1]) def __init__(self, x, y, size, margin=4): super().__init__() self.actual_size = (size, size) self.graphical_size = (size - margin, size - margin) self.margin = margin self.actual_pos = (x, y) self.graphical_pos_attach() self.color = (0.2, 1.0, 0.2, 1.0) def graphical_pos_attach(self, smooth_motion=None): to_x, to_y = self.actual_pos[0] - self.graphical_size[0] / 2, self.actual_pos[1] - self.graphical_size[1] / 2 if smooth_motion is None: self.graphical_pos = to_x, to_y else: smoother, t = smooth_motion smoother.move_to(self, to_x, to_y, t) def move_to(self, x, y, **kwargs): self.actual_pos = (x, y) self.graphical_pos_attach(**kwargs) def move_by(self, x, y, **kwargs): self.move_to(self.actual_pos[0] + x, self.actual_pos[1] + y, **kwargs) def get_pos(self): return self.actual_pos def step_by(self, direction, **kwargs): self.move_by(self.actual_size[0] * direction[0], self.actual_size[1] * direction[1], **kwargs) class Worm(Widget): def __init__(self, config): super().__init__() self.cells = [] self.config = config self.cell_size = config.CELL_SIZE self.head_init((100, 100)) for i in range(config.DEFAULT_LENGTH): self.lengthen() def destroy(self): for i in range(len(self.cells)): self.remove_widget(self.cells[i]) self.cells = [] def lengthen(self, pos=None, direction=(0, 1)): if pos is None: px = self.cells[-1].get_pos()[0] + direction[0] * self.cell_size py = self.cells[-1].get_pos()[1] + direction[1] * self.cell_size pos = (px, py) self.cells.append(Cell(*pos, self.cell_size, margin=self.config.MARGIN)) self.add_widget(self.cells[-1]) def head_init(self, pos): self.lengthen(pos=pos) def move(self, direction, **kwargs): for i in range(len(self.cells) - 1, 0, -1): self.cells[i].move_to(*self.cells[i - 1].get_pos(), **kwargs) self.cells[0].step_by(direction, **kwargs) def gather_positions(self): return [cell.get_pos() for cell in self.cells] def head_intersect(self, cell): return self.cells[0].get_pos() == cell.get_pos() class Form(Widget): worm_len = NumericProperty(0) def __init__(self, config): super().__init__() self.config = config self.worm = None self.cur_dir = (0, 0) self.fruit = None self.game_on = True self.smooth = smooth.XSmooth(["graphical_pos[0]", "graphical_pos[1]"]) def random_cell_location(self, offset): x_row = self.size[0] // self.config.CELL_SIZE x_col = self.size[1] // self.config.CELL_SIZE return random.randint(offset, x_row - offset), random.randint(offset, x_col - offset) def random_location(self, offset): x_row, x_col = self.random_cell_location(offset) return self.config.CELL_SIZE * x_row, self.config.CELL_SIZE * x_col def fruit_dislocate(self): x, y = self.random_location(2) while (x, y) in self.worm.gather_positions(): x, y = self.random_location(2) self.fruit.move_to(x, y) def start(self): self.worm = Worm(self.config) self.add_widget(self.worm) if self.fruit is not None: self.remove_widget(self.fruit) self.fruit = Cell(0, 0, self.config.APPLE_SIZE) self.fruit.color = (1.0, 0.2, 0.2, 1.0) self.fruit_dislocate() self.add_widget(self.fruit) self.game_on = True self.cur_dir = (0, -1) Clock.schedule_interval(self.update, self.config.INTERVAL) self.popup_label.text = "" def stop(self, text=""): self.game_on = False self.popup_label.text = text Clock.unschedule(self.update) def game_over(self): self.stop("GAME OVER" + " " * 5 + "\ntap to reset") def align_labels(self): try: self.popup_label.pos = ((self.size[0] - self.popup_label.width) / 2, self.size[1] / 2) self.score_label.pos = ((self.size[0] - self.score_label.width) / 2, self.size[1] - 80) except: print(self.__dict__) assert False def update(self, _): if not self.game_on: return self.worm.move(self.cur_dir, smooth_motion=(self.smooth, self.config.INTERVAL)) if self.worm.head_intersect(self.fruit): directions = [(0, 1), (0, -1), (1, 0), (-1, 0)] self.worm.lengthen(direction=random.choice(directions)) self.fruit_dislocate() cell = self.worm_bite_self() if cell: cell.color = (1.0, 0.2, 0.2, 1.0) self.game_over() self.worm_len = len(self.worm.cells) self.align_labels() def on_touch_down(self, touch): if not self.game_on: self.worm.destroy() self.start() return ws = touch.x / self.size[0] hs = touch.y / self.size[1] aws = 1 - ws if ws > hs and aws > hs: cur_dir = (0, -1) elif ws > hs >= aws: cur_dir = (1, 0) elif ws <= hs < aws: cur_dir = (-1, 0) else: cur_dir = (0, 1) self.cur_dir = cur_dir def worm_bite_self(self): for cell in self.worm.cells[1:]: if self.worm.head_intersect(cell): return cell return False class Config: DEFAULT_LENGTH = 20 CELL_SIZE = 25 APPLE_SIZE = 35 MARGIN = 4 INTERVAL = 0.3 DEAD_CELL = (1, 0, 0, 1) APPLE_COLOR = (1, 1, 0, 1) class WormApp(App): def build(self): self.config = Config() self.form = Form(self.config) return self.form def on_start(self): self.form.start() if __name__ == '__main__': WormApp().run()
光滑的 from kivy.clock import Clock import time class Timing: @staticmethod def linear(x): return x class Smooth: def __init__(self, interval=1.0/60.0): self.objs = [] self.running = False self.interval = interval def run(self): if self.running: return self.running = True Clock.schedule_interval(self.update, self.interval) def stop(self): if not self.running: return self.running = False Clock.unschedule(self.update) def setattr(self, obj, attr, value): exec("obj." + attr + " = " + str(value)) def getattr(self, obj, attr): return float(eval("obj." + attr)) def update(self, _): cur_time = time.time() for line in self.objs: obj, prop_name_x, prop_name_y, from_x, from_y, to_x, to_y, start_time, period, timing = line time_gone = cur_time - start_time if time_gone >= period: self.setattr(obj, prop_name_x, to_x) self.setattr(obj, prop_name_y, to_y) self.objs.remove(line) else: share = time_gone / period acs = timing(share) self.setattr(obj, prop_name_x, from_x * (1 - acs) + to_x * acs) self.setattr(obj, prop_name_y, from_y * (1 - acs) + to_y * acs) if len(self.objs) == 0: self.stop() def move_to(self, obj, prop_name_x, prop_name_y, to_x, to_y, t, timing=Timing.linear): self.objs.append((obj, prop_name_x, prop_name_y, self.getattr(obj, prop_name_x), self.getattr(obj, prop_name_y), to_x, to_y, time.time(), t, timing)) self.run() class XSmooth(Smooth): def __init__(self, props, timing=Timing.linear, *args, **kwargs): super().__init__(*args, **kwargs) self.props = props self.timing = timing def move_to(self, obj, to_x, to_y, t): super().move_to(obj, *self.props, to_x, to_y, t, timing=self.timing)
蠕虫病毒 <Form>: popup_label: popup_label score_label: score_label canvas: Color: rgba: (.5, .5, .5, 1.0) Line: width: 1.5 points: (0, 0), self.size Line: width: 1.5 points: (self.size[0], 0), (0, self.size[1]) Label: id: score_label text: "Score: " + str(self.parent.worm_len) width: self.width Label: id: popup_label width: self.width <Worm>: <Cell>: canvas: Color: rgba: self.color Rectangle: size: self.graphical_size pos: self.graphical_pos
代码,由@tshirtman调整我的代码出现了一些问题,例如,Kivy项目的贡献者之一tshirtman建议我不要将Cells作为Widgets,而应该编写Point指令。 但是,尽管在UI和游戏开发方面确实比我的代码更好,但我发现它比我的代码更容易理解。 无论如何,代码:
main.py from kivy.app import App from kivy.uix.widget import Widget from kivy.clock import Clock from kivy.properties import * import random import smooth class Cell: def __init__(self, x, y): self.actual_pos = (x, y) def move_to(self, x, y): self.actual_pos = (x, y) def move_by(self, x, y): self.move_to(self.actual_pos[0] + x, self.actual_pos[1] + y) def get_pos(self): return self.actual_pos class Fruit(Cell): def __init__(self, x, y): super().__init__(x, y) class Worm(Widget): margin = NumericProperty(4) graphical_poses = ListProperty() inj_pos = ListProperty([-1000, -1000]) graphical_size = NumericProperty(0) def __init__(self, config, **kwargs): super().__init__(**kwargs) self.cells = [] self.config = config self.cell_size = config.CELL_SIZE self.head_init((self.config.CELL_SIZE * random.randint(3, 5), self.config.CELL_SIZE * random.randint(3, 5))) self.margin = config.MARGIN self.graphical_size = self.cell_size - self.margin for i in range(config.DEFAULT_LENGTH): self.lengthen() def destroy(self): self.cells = [] self.graphical_poses = [] self.inj_pos = [-1000, -1000] def cell_append(self, pos): self.cells.append(Cell(*pos)) self.graphical_poses.extend([0, 0]) self.cell_move_to(len(self.cells) - 1, pos) def lengthen(self, pos=None, direction=(0, 1)): if pos is None: px = self.cells[-1].get_pos()[0] + direction[0] * self.cell_size py = self.cells[-1].get_pos()[1] + direction[1] * self.cell_size pos = (px, py) self.cell_append(pos) def head_init(self, pos): self.lengthen(pos=pos) def cell_move_to(self, i, pos, smooth_motion=None): self.cells[i].move_to(*pos) to_x, to_y = pos[0], pos[1] if smooth_motion is None: self.graphical_poses[i * 2], self.graphical_poses[i * 2 + 1] = to_x, to_y else: smoother, t = smooth_motion smoother.move_to(self, "graphical_poses[" + str(i * 2) + "]", "graphical_poses[" + str(i * 2 + 1) + "]", to_x, to_y, t) def move(self, direction, **kwargs): for i in range(len(self.cells) - 1, 0, -1): self.cell_move_to(i, self.cells[i - 1].get_pos(), **kwargs) self.cell_move_to(0, (self.cells[0].get_pos()[0] + self.cell_size * direction[0], self.cells[0].get_pos()[1] + self.cell_size * direction[1]), **kwargs) def gather_positions(self): return [cell.get_pos() for cell in self.cells] def head_intersect(self, cell): return self.cells[0].get_pos() == cell.get_pos() class Form(Widget): worm_len = NumericProperty(0) fruit_pos = ListProperty([0, 0]) fruit_size = NumericProperty(0) def __init__(self, config, **kwargs): super().__init__(**kwargs) self.config = config self.worm = None self.cur_dir = (0, 0) self.fruit = None self.game_on = True self.smooth = smooth.Smooth() def random_cell_location(self, offset): x_row = self.size[0] // self.config.CELL_SIZE x_col = self.size[1] // self.config.CELL_SIZE return random.randint(offset, x_row - offset), random.randint(offset, x_col - offset) def random_location(self, offset): x_row, x_col = self.random_cell_location(offset) return self.config.CELL_SIZE * x_row, self.config.CELL_SIZE * x_col def fruit_dislocate(self, xy=None): if xy is not None: x, y = xy else: x, y = self.random_location(2) while (x, y) in self.worm.gather_positions(): x, y = self.random_location(2) self.fruit.move_to(x, y) self.fruit_pos = (x, y) def start(self): self.worm = Worm(self.config) self.add_widget(self.worm) self.fruit = Fruit(0, 0) self.fruit_size = self.config.APPLE_SIZE self.fruit_dislocate() self.game_on = True self.cur_dir = (0, -1) Clock.schedule_interval(self.update, self.config.INTERVAL) self.popup_label.text = "" def stop(self, text=""): self.game_on = False self.popup_label.text = text Clock.unschedule(self.update) def game_over(self): self.stop("GAME OVER" + " " * 5 + "\ntap to reset") def align_labels(self): self.popup_label.pos = ((self.size[0] - self.popup_label.width) / 2, self.size[1] / 2) self.score_label.pos = ((self.size[0] - self.score_label.width) / 2, self.size[1] - 80) def update(self, _): if not self.game_on: return self.worm.move(self.cur_dir, smooth_motion=(self.smooth, self.config.INTERVAL)) if self.worm.head_intersect(self.fruit): directions = [(0, 1), (0, -1), (1, 0), (-1, 0)] self.worm.lengthen(direction=random.choice(directions)) self.fruit_dislocate() cell = self.worm_bite_self() if cell is not None: self.worm.inj_pos = cell.get_pos() self.game_over() self.worm_len = len(self.worm.cells) self.align_labels() def on_touch_down(self, touch): if not self.game_on: self.worm.destroy() self.start() return ws = touch.x / self.size[0] hs = touch.y / self.size[1] aws = 1 - ws if ws > hs and aws > hs: cur_dir = (0, -1) elif ws > hs >= aws: cur_dir = (1, 0) elif ws <= hs < aws: cur_dir = (-1, 0) else: cur_dir = (0, 1) self.cur_dir = cur_dir def worm_bite_self(self): for cell in self.worm.cells[1:]: if self.worm.head_intersect(cell): return cell return None class Config: DEFAULT_LENGTH = 20 CELL_SIZE = 26
光滑的 from kivy.clock import Clock import time class Timing: @staticmethod def linear(x): return x class Smooth: def __init__(self, interval=1.0/60.0): self.objs = [] self.running = False self.interval = interval def run(self): if self.running: return self.running = True Clock.schedule_interval(self.update, self.interval) def stop(self): if not self.running: return self.running = False Clock.unschedule(self.update) def set_attr(self, obj, attr, value): exec("obj." + attr + " = " + str(value)) def get_attr(self, obj, attr): return float(eval("obj." + attr)) def update(self, _): cur_time = time.time() for line in self.objs: obj, prop_name_x, prop_name_y, from_x, from_y, to_x, to_y, start_time, period, timing = line time_gone = cur_time - start_time if time_gone >= period: self.set_attr(obj, prop_name_x, to_x) self.set_attr(obj, prop_name_y, to_y) self.objs.remove(line) else: share = time_gone / period acs = timing(share) self.set_attr(obj, prop_name_x, from_x * (1 - acs) + to_x * acs) self.set_attr(obj, prop_name_y, from_y * (1 - acs) + to_y * acs) if len(self.objs) == 0: self.stop() def move_to(self, obj, prop_name_x, prop_name_y, to_x, to_y, t, timing=Timing.linear): self.objs.append((obj, prop_name_x, prop_name_y, self.get_attr(obj, prop_name_x), self.get_attr(obj, prop_name_y), to_x, to_y, time.time(), t, timing)) self.run() class XSmooth(Smooth): def __init__(self, props, timing=Timing.linear, *args, **kwargs): super().__init__(*args, **kwargs) self.props = props self.timing = timing def move_to(self, obj, to_x, to_y, t): super().move_to(obj, *self.props, to_x, to_y, t, timing=self.timing)
蠕虫病毒 <Form>: popup_label: popup_label score_label: score_label canvas: Color: rgba: (.5, .5, .5, 1.0) Line: width: 1.5 points: (0, 0), self.size Line: width: 1.5 points: (self.size[0], 0), (0, self.size[1]) Color: rgba: (1.0, 0.2, 0.2, 1.0) Point: points: self.fruit_pos pointsize: self.fruit_size / 2 Label: id: score_label text: "Score: " + str(self.parent.worm_len) width: self.width Label: id: popup_label width: self.width <Worm>: canvas: Color: rgba: (0.2, 1.0, 0.2, 1.0) Point: points: self.graphical_poses pointsize: self.graphical_size / 2 Color: rgba: (1.0, 0.2, 0.2, 1.0) Point: points: self.inj_pos pointsize: self.graphical_size / 2
随时问任何问题。